Biology:Aphananthe philippinensis
| Native elm | |
|---|---|
| |
| Drawing by Margaret Flockton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Cannabaceae |
| Genus: | Aphananthe |
| Species: | A. philippinensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aphananthe philippinensis Planch.
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Aphananthe philippinensis is a common rainforest tree in the family Cannabaceae. In Australia it occurs from the Manning River in New South Wales to near Herberton in tropical Queensland. It was first described from the island of Luzon in the Philippines , hence the species name. The generic name of Aphananthe refers to insignificant flowers. This plant also occurs on the Solomon Islands and in Papua New Guinea
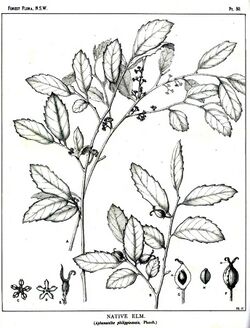
The Australian habitat includes dry rainforest sites. However, it is mostly seen by streams on moist alluvial soils. Common names in Australia include native elm, grey handlewood, axe handle wood, rough-leaved hickory and asbestos tree.
Description
Growing to 35 metres tall and 85 cm in width, though usually seen as a smaller sized tree. The trunk is fluted and irregular in shape, buttressed at the base. The brown bark sheds irregularly; pustules and bumps give a patchy appearance. Branchlets are grey in colour with longitudinal cracks.

Leaves
Leaves are alternate on the stem, hard, dry to touch and sandpapery, though easily snapped off and brittle. They are prominently toothed with a sharp prickly point, lanceolate in shape, 4 to 6 cm long, 1.5 to 3 cm wide. The leaves are green and veiny on both sides, paler below. The leaves have a midrib, with lateral and net veins visible. The midrib is depressed on the upper surface and raised underneath. The midrib is pale in colour under the leaf.
Flowers and fruit
Male flowers form on small cymes. Female flowers on the same plant, being in singles or rarely two together, forming on a 5 mm long stalk. Male and female flowers around 5 mm long, in the months of September to November.
The fruit is an egg-shaped black drupe, 6 mm long containing a single seed. The seed is 5 mm long, somewhat three angled. Fruit matures from February to June.
Ecology
Native elm is a food tree for the common aeroplane and rounded six-line blue butterflies. Fruit eaten by a variety of birds, including Australian king parrot, brown cuckoo-dove, black-faced cuckoo-shrike, figbird, green catbird, Lewin's honeyeater, olive-backed oriole, pied currawong, rainbow lorikeet, satin bowerbird, scaly-breasted lorikeet and yellow-eyed cuckoo-shrike.
References
- Floyd, A.G. (1989). Rainforest Trees of Mainland South-eastern Australia. Inkata Press. p. 399. ISBN 0-909605-57-2.
- Aphananthe philippinensis at NSW Flora Online Retrieved on 2009-08-28
External links
- "Aphananthe philippinensis Planch.". Atlas of Living Australia. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/http://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2904538.
Wikidata ☰ Q4779477 entry
 |

