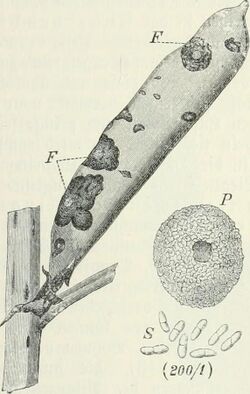
Biology:Ascochyta pisi
| Ascochyta pisi | |
|---|---|
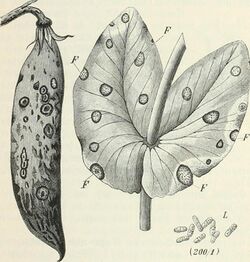
| |
| Ascochyta pisi on leaf and pod of pea | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Dothideomycetes |
| Order: | Pleosporales |
| Family: | Didymellaceae |
| Genus: | Ascochyta |
| Species: | A. pisi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ascochyta pisi Lib. (1830)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Ascochyta pisi is a fungal plant pathogen that causes ascochyta blight on pea, causing lesions of stems, leaves, and pods. These same symptoms can also be caused by Ascochyta pinodes, and the two fungi are not easily distinguishable.[1]
Hosts and symptoms
The host of Ascochyta pisi is the field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Ascochyta pisi also infects 20 genera of plants and more than 50 plant species including soybean, sweet pea, lentil, alfalfa, common bean, clover, black-eyed-pea, and broad bean.[2]
Field pea is an annual, cool season legume that is native to northwest and southwest Asia. Ascochyta blight of peas is one of the most important diseases of pea in terms of acreage affected. Yield losses of 5 to 15% are common during wet conditions.[2]
Symptoms include:
- spots on stems, leaves, tendrils, and pods (can be purplish, black, or brown in color)
- lesions on stems, leaves, tendrils, and pods (can be purplish, black, or brown in color)
- pod lesions become sunken
- black spore-producing structures form in the lesions[2]
- with high humidity spots can enlarge and coalesce, resulting in the lower leaves being completely blighted
- stem girdling
- pod lesions can happen in moist conditions or if pea has lodged[3]
- infected seeds can appear discolored and purplish-brown
- lightly infected seeds often appear healthy[4]
Disease cycle
Ascochyta blight of peas is caused by a fungus. More than one fungal species can cause this disease.[2] Other pathogens that cause Ascochyta blight, besides Ascochyta pisi, include: Mycosphaerella pinodes, Phoma medicaginis var. pinodella, and Phoma koolunga.[4] Mycosphaerella pinodes is the only species that develops a sexual spore stage on infected residue. This stage results in the production of wind-blown ascospores.[3] Ascospores can be dispersed several kilometers. Ascospore release begins in the spring and can continue into the summer if there is enough moisture.[3] Didymella pisi is the teliomorph stage of Ascochyta pisi [2]
All above ground parts of the pea plant and all growth stages are susceptible to Ascochyta pisi.[2] The fungus overwinters in seed, soil, or infected crop residues. Infected crop residue is the primary source of infection in the main pea producing areas.[3] The fungus survives on seeds and in the soil as resting spores, called chlamydospores.[5] The seed to seedling transmission rate is low.[2] Infected seeds turn purplish-brown and are often shriveled and smaller in size [6] The pathogen survives as hyphae in the seed coat and embryo.[6] New disease is established when spores of the fungus are carried to a new, healthy crop by wind or rain splash. These fungal spores then penetrate the leaf.[4] In the spring, it produces conidia in pycnidia.[3] The release of these spores begins in spring and can continue into the summer if moist conditions persist. The conidia are spread short distances by wind and rain.[5] Disease can also be established by planting infected seed.[4] Symptoms appear within 2–4 days after initial infection.[3]
The Ascochyta pisi spores are viable on crop debris, although they do not survive for more than a year. Other Ascochyta blight pathogens have thick walled chlamydospores, which can survive for up to a few years in the soil.[5]
Management
- Crop rotation: In order to reduce the risk of infection of pea crops from infected residue and soil-borne survival structures in a field, pea crops should be grown only every three to four years in the same field. It is important to plant pea crops as far from the previous years’ field as possible in order to limit the spread of infection.[3] The spores have a short distance dispersal during the growing season.[3] Crop rotation alone is not a recommended management tactic due to spores traveling several kilometers.[2]
- Stubble management: Practices include straw-chopping and harrowing to spread out the crop residue on the soil surface. This can be important in helping to speed up crop residue decomposition.[3]
- Variety selection: It is important to know the disease and lodging ratings of certain pea varieties in order to choose a variety that is most likely to resist disease.[3]
- Agronomics: Seed rate and planting date can have a major effect on exposure of the crop to disease and on susceptibility. Agronomic practices promoting varieties and conditions that limit lodging and avoiding fields with excess nitrogen can reduce the spread and intensity of disease.[3]
- Seed quality: It is suggested that farmers have their seed tested for germination levels and seed-borne disease levels. Seed with infection levels of 10% or more should be treated with fungicide. It is advised to plant seed with less than 10% ascochyta infection if that quality of seed can be sourced.[3]
- Seed treatments: Treatments provide protection against seed and soil-borne diseases. Apron Maxx RTA® and Vitaflo 280® are products registered for seed-borne ascochyta.[3]
- Scouting: Disease scouting is critical to catch ascochyta blight early. It is recommended to begin scouting during the vegetative stage and to continue scouting into the early flowering stage. The reason for this is to observe whether disease symptoms are moving upwards and are present on tendrils and flowers. If symptoms of ascochyta blight are present in at least 50% of the bottom third of the crop canopy and are progressing into the middle third of the canopy, fungicide control may be recommended. A few other reasons to use fungicides are if the weather has been humid, if there is a forecast for rain, and if a high yield of peas would justify the cost of spraying fungicides.[3]
- Foliar Fungicides: The registered fungicides used for field peas to control ascochyta blight are Bravo 500®, Headline EC®, Lance®, and Quadris®. Early flowering is the ideal time to apply these fungicides. They work by protecting the healthy green plant material, but will not repair plants affected by foot rot. High water volumes are necessary for full coverage of leaves and penetration of the plant canopy.[3]
Before planting, some recommended management practices include destroying infected crop residues, crop rotation, and planting the current crop far from the previously infected crops’ field or residues. Disease can be managed in multiple ways during and after planting. One method to manage disease is to follow the recommended seeding dates and rates to avoid fostering an ideal environment for the pathogen. If the seed density is too high and planted too early, there is increased exposure to the plant pathogen. This seeding practice also creates an ideal environment for the pathogen because the plants often produce larger canopies and experience more lodging, which creates a close, high-humidity environment ideal for the pathogen.[5] Long term crop rotation with non-host crops is recommended. Chemical control with fungicidal seed dressings is another effective method of control.[4]
Environment
This pathogen needs cool, moist conditions, and development occurs more quickly as plant tissues age. An increase in severity of infection is often noted when the crop canopy closes due to the dense growth that prevents dry air from penetrating the canopy. This creates a cool, humid, moist environment under the canopy, and as a result, the disease symptoms are most prevalent at the base of the canopy and spread up the plant.[5] Plant lodging also creates a dense, humid environment favorable for the pathogen. The optimal temperature for disease establishment and development is around 20 °C. Spore dispersal and the development of the disease are slowed in the absence of high levels of moisture.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Pea Ascochyta Blight Symptoms
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "Ascochyta Blight of Peas". http://www.plantmanagementnetwork.org/pub/php/diagnosticguide/2011/pea/. Retrieved 2015-10-15.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 "Ascochyta Blights of Field Pea - Agriculture -". Archived from the original on 2012-09-16. https://web.archive.org/web/20120916072054/http://www.agriculture.gov.sk.ca/Ascochyta_blight_FAQ. Retrieved 2015-10-15.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Victoria, Department of Environment and Primary Industries. "Ascochyta Blight of Field Peas". http://agriculture.vic.gov.au/agriculture/pests-diseases-and-weeds/plant-diseases/grains-pulses-and-cereals/ascochyta-blight-of-field-peas. Retrieved 2015-10-15.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Gossen, B.. "Managing the ascochyta blight complex on field pea in western Canada". Prairie Soils & Crops Journal. http://www.prairiesoilsandcrops.ca/articles/volume-4-15-screen.pdf.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Identifying & Managing Ascochyta in Field Peas | Alberta Pulse Growers". http://pulse.ab.ca/producers/varieties-management/peas/disease-control-fungicide/ascochyta/. Retrieved 2015-12-23.
Wikidata ☰ Q4803966 entry
 |