Biology:Asterolasia grandiflora
| Asterolasia grandiflora | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Rutaceae |
| Genus: | Asterolasia |
| Species: | A. grandiflora
|
| Binomial name | |
| Asterolasia grandiflora (Hook.) Benth.[1]
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Asterolasia grandiflora is a species of weak, open shrub or sub-shrub that is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It has oblong, elliptical or egg-shaped leaves and pink to mauve flowers arranged in umbels of about three flowers with a thick covering of star-shaped hairs on the back of the petals.
Description
Asterolasia grandiflora is a weak, open shrub or sub-shrub that typically grows to a height of 20–60 cm (7.9–23.6 in). The leaves are oblong, elliptical or egg-shaped, 4–20 mm (0.16–0.79 in) long and 1.5–6 mm (0.059–0.236 in) wide on a short petiole. The upper surface of the leaves has star-shaped hairs when young but the lower surface is densely covered with star-shaped hairs. The flowers are arranged in three or four in leaf axils and on the ends of branchlets, each flower on a pedicel 5–17 mm (0.20–0.67 in) long and covered with thick, star-shaped hairs. The petals are pink to mauve, broadly elliptical to egg-shaped, 6–15 mm (0.24–0.59 in) long and 3–9 mm (0.12–0.35 in) wide, with thick-centred, star-shaped hairs on the back that formed a shield over the flower bud. There are between twelve and twenty-four stamens.[2][3][4]
Taxonomy
This species was first formally described in 1863 by William Jackson Hooker who gave it the name Phebalium grandiflorum and published the description in Icones Plantarum.[5][6] In 1863, George Bentham changed the name to Asterolasia grandiflora, publishing the change in Flora Australiensis.[7][8]
Distribution and habitat
Asterolasia grandiflora grows on breakaways and hills mostly between Toodyay and York in Western Australia.[2][3]
Conservation status
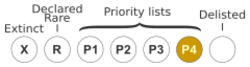
Asterolasia grandiflora is classified as "Priority Four" by the Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife,[2] meaning that is rare or near threatened.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Asterolasia grandiflora". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/108166. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Asterolasia grandiflora". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/4398.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wilson, Paul G.. "Asterolasia grandiflora". Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment, Canberra. https://profiles.ala.org.au/opus/foa/profile/Asterolasia%20grandiflora. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ Wege, Juliet A. (2017). "Taxonomic notes on Asterolasia (Rutaceae) in Western Australia to inform conservation". Nuytsia 28: 142–143. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/science/nuytsia/837.pdf. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ "Phebalium grandiflorum". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/499200. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ Hooker, William Jackson (1844). Icones Plantarum (Volume 8). London: Longman, Rees, Orme, Brwn Green & Longman. p. 724. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/54715#page/230/mode/1up. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ "Asterolasia grandiflora". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/538868. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ Bentham, George; von Mueller, Ferdinand (1863). Flora Australiensis. London: Lovell Reeve & Co.. pp. 352–353. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/3669#page/410/mode/1up. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ↑ "Conservation codes for Western Australian Flora and Fauna". Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://www.dpaw.wa.gov.au/images/documents/plants-animals/threatened-species/Listings/Conservation%20code%20definitions.pdf. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
Wikidata ☰ Q15388462 entry
 |