Biology:BZIP intron candida
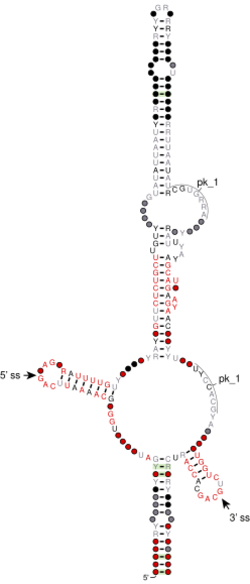
The bZIP intron candida is an unconventional bZIP intron located in the HAC1 mRNA in a subgroup of fungi from Saccharomycetales order. So far all species with this type of structure belong to Metschnikowiaceae or Debaryomycetaceae families. However, some of the best known representatives of Debaryomycetaceae - Candida albicans and its closest relatives - contain the shorter RNA structure instead (bZIP intron ascomycota-like).[1] The consensus structure consists of two well conserved hairpins with loop regions defining the unconventional splice sites. The hairpins are separated by a long insertion with conserved motifs and a predicted secondary structure. Splicing performed by Ire1 results in excision of a very long intron that was first described in Candida parapsilosis.[2]
References
- ↑ "Conserved RNA structures in the non-canonical Hac1/Xbp1 intron". RNA Biol 8 (4): 552–556. 2011. doi:10.4161/rna.8.4.15396. PMID 21593604.
- ↑ Iracane, Elise; Donovan, Paul D.; Ola, Mihaela; Butler, Geraldine; Holland, Linda M. (2018). Mitchell, Aaron P.. ed. "Identification of an Exceptionally Long Intron in the HAC1 Gene of Candida parapsilosis" (in en). mSphere 3 (6). doi:10.1128/mSphere.00532-18. ISSN 2379-5042. PMID 30404939.
 |

