Biology:Babingtonia maleyae
| Babingtonia maleyae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Babingtonia |
| Species: | B. maleyae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Babingtonia maleyae Rye & Trudgen[1]
| |
Babingtonia maleyae, commonly known as the Narrogin babingtonia,[2] is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It is a compact shrub with narrowly egg-shaped to elliptic leaves and white flowers usually arranged singly in leaf axils, each flower with 17 to 20 stamens.
Description
Babingtonia maleyae is a compact shrub that typically grows to a height of 0.8–1.3 m (2 ft 7 in–4 ft 3 in) and has erect, slender stems. The leaves are mostly narrowly egg-shaped with the narrower end towards the base, 1.7–4 mm (0.067–0.157 in) long and 0.6–1.1 mm (0.024–0.043 in) wide on a petiole 0.2–0.3 mm (0.0079–0.0118 in) long. The flowers are usually arranged in singly in leaf axils on a peduncle 1.5–5 mm (0.059–0.197 in) long with a bracteole 0.8–1.3 mm (0.031–0.051 in) long at the base. The sepals are 0.5–0.8 mm (0.020–0.031 in) long and 1.3–1.8 mm (0.051–0.071 in) wide and the petals are white, 3.0–3.5 mm (0.12–0.14 in) long with 17 to 20 stamens in each flower. The ovary has three locules and the style is 1.7–2.2 mm (0.067–0.087 in) long. Flowering has been observed in January and February, and the fruit is a capsule 1.5–2 mm (0.059–0.079 in) long and 2.5–3 mm (0.098–0.118 in) in diameter.[2][3]
Taxonomy
Babingtonia maleyae was first formally described in 2015 by Barbara Rye and Malcolm Trudgen in the journal Nuytsia from specimens collected east of Narrogin in 2001.[4] The specific epithet (maleyae) honours Sandra Maley, who prepared draft descriptions of many new species of Chamelaucieae.[3]
Distribution and habitat
This species is only known from a few locations near Narrogin, where it grows in sandy loam with lateritic gravel, in the Avon Wheatbelt biogeographic region of south-western Western Australia.[2][3]
Conservation status
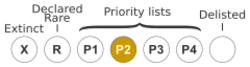
Babingtonia maleyae is listed as "Priority Two" by the Western Australian Government Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions,[2] meaning that it is poorly known and from only one or a few locations.[5]
References
- ↑ "Babingtonia maleyae". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/4555583.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Babingtonia maleyae". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/45400.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Rye, Barbara L. (2015). "A revision of the south-western Australian genus Babingtonia (Myrtaceae: Chamelaucieae).". Nuytsia 25: 242–243. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/282457#page/248/mode/1up. Retrieved 2 November 2023.
- ↑ "Babingtonia maleyae". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/4556069.
- ↑ "Conservation codes for Western Australian Flora and Fauna". Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://www.dpaw.wa.gov.au/images/documents/plants-animals/threatened-species/Listings/Conservation%20code%20definitions.pdf. Retrieved 3 November 2023.
Wikidata ☰ Q30688849 entry
 |