Biology:Bacilladnaviridae
| Bacilladnaviridae | |
|---|---|
| |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Monodnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Shotokuvirae |
| Phylum: | Cressdnaviricota |
| Class: | Arfiviricetes |
| Order: | Baphyvirales |
| Family: | Bacilladnaviridae |
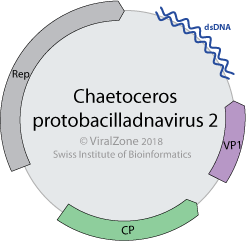
Bacilladnaviridae is a family of single-stranded DNA viruses that primarily infect diatoms.[1][2]
Characteristics
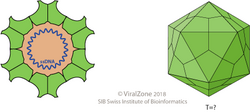
The genome of these viruses appears to be unique. It consists of a single molecule of covalently closed circular single stranded DNA of 4.5–6 kilobases as well as a segment of linear ssDNA of ~1 kilobase. The linear segment is complementary to a portion of the closed circle creating a partially double stranded region. There are at least three major open reading frames in the genome.
Similar to other eukaryotic ssDNA viruses, bacilladnaviruses are likely to replicate their genomes by the rolling-circle mechanism, initiated by the virus-encoded endonuclease (Rep). However, the latter protein of bacilladnaviruses displays unique conserved motifs and in phylogenetic trees forms a monophyletic clade separated from other groups of ssDNA viruses. The capsid protein of bacilladnaviruses has the jelly-roll fold and is most closely related to the corresponding proteins from members of the family Nodaviridae, which have ssRNA genomes.[3] [4]
The virions are about 34 nanometers (nm) in diameter and accumulate in the nucleus. Mature virions are released by lysis of the host cell.
Taxonomy
The following genera are recognized:[5]
- Diatodnavirus
- Kieseladnavirus
- Protobacilladnavirus
References
- ↑ "Virus Taxonomy: 2019 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. https://ictv.global/taxonomy.
- ↑ Tomaru, Y; Takao, Y; Suzuki, H; Nagumo, T; Koike, K; Nagasaki, K (2011). "Isolation and Characterization of a Single-Stranded DNA Virus Infecting Chaetoceros lorenzianus Grunow". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 77 (15): 5285–5293. doi:10.1128/AEM.00202-11. PMID 21666026. Bibcode: 2011ApEnM..77.5285T.
- ↑ Kazlauskas, D; Dayaram, A; Kraberger, S; Goldstein, S; Varsani, A; Krupovic, M (2017). "Evolutionary history of ssDNA bacilladnaviruses features horizontal acquisition of the capsid gene from ssRNA nodaviruses.". Virology 504: 114–121. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2017.02.001. PMID 28189969.
- ↑ Munke, A; Kimura, K; Tomaru, Y; Wang, H; Yoshida, K; Mito, S; Hongo, Y; Okamoto, K (20 July 2022). "Primordial Capsid and Spooled ssDNA Genome Structures Unravel Ancestral Events of Eukaryotic Viruses.". mBio 13 (4): e0015622. doi:10.1128/mbio.00156-22. PMID 35856561.
- ↑ "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. https://ictv.global/taxonomy.
External links
- Yuji Tomaru, Kensuke Toyoda, Hidekazu Suzuki, Tamotsu Nagumo, Kei Kimura & Yoshitake Takao: New single-stranded DNA virus with a unique genomic structure that infects marine diatom Chaetoceros setoensis. In: Nature Sci Rep 3, 3337. 26 November 2013. doi:10.1038/srep03337. Proposal of new species "Chaetoceros setoensis DNA virus" (CsetDNAV), ssDNA circular.
Wikidata ☰ Q52600201 entry
 |