Biology:Boronia coriacea
| Boronia coriacea | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Rutaceae |
| Genus: | Boronia |
| Species: | B. coriacea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Boronia coriacea Paul G.Wilson[1]
| |
Boronia coriacea is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the south-west of Western Australia. It is a small shrub with pinnate leaves and hairless pink, four-petalled flowers in small clusters on the ends of the branches.
Description
Boronia coriacea is a small ericoid shrub that grows to a height of 50 cm (20 in) with more or less glabrous stems, leaves and flowers. Its leaves are pinnate with three or five leathery leaflets and about 10–50 mm (0.4–2 in) long on a petiole 2–4 mm (0.08–0.2 in) long. The leaflets are wedge-shaped with narrower end towards the base, about 12 mm (0.5 in) long and 1–5 mm (0.04–0.2 in) wide. The flowers are pink and are borne in clusters on the end of the stems, each on a pedicel about 3 mm (0.1 in) long. The four sepals are egg-shaped to almost round, about 1 mm (0.04 in) long with their bases overlapping. The four petals are egg-shaped, about 5 mm (0.2 in) long with their bases overlapping. The eight stamens are club-shaped and erect, those nearest the sepals slightly longer than the stigma. Flowering occurs in April or from October to November.[2][3]
Taxonomy and naming
Boronia coriacea was first formally described in 1971 by Paul G. Wilson and the description was published in Nuytsia from a specimen collected on the road to Israelite Bay.[4][2] The specific epithet (coriacea) is a Latin word meaning "leathery".[5]
Distribution and habitat
This boronia grows is only known from the type locality where it grows in heath and in mallee vegetation.[2][3]
Conservation
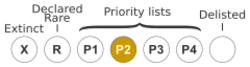
Boronia coriacea is classified as "Priority Two" by the Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife[3] meaning that it is poorly known and known from only a few locations but is not under imminent threat.[6]
References
- ↑ "Boronia coriacea". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/59671. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Wilson, Paul G. (1971). "Taxonomic notes on the family Rutaceae, principally of Western Australia". Nuytsia 1 (2): 203–204. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/223158#page/49/mode/1up. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Boronia coriacea". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/4410.
- ↑ "Boronia coriacea". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/464181. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ↑ Brown, Roland Wilbur (1956). The Composition of Scientific Words. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. p. 231.
- ↑ "Conservation codes for Western Australian Flora and Fauna". Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://www.dpaw.wa.gov.au/images/documents/plants-animals/threatened-species/Listings/Conservation%20code%20definitions.pdf. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
Wikidata ☰ Q15388563 entry
 |