Biology:Boronia safrolifera
| Safrole boronia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Boronia safrolifera in Maranoa Gardens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Rutaceae |
| Genus: | Boronia |
| Species: | B. safrolifera
|
| Binomial name | |
| Boronia safrolifera Cheel[1]
| |
| |
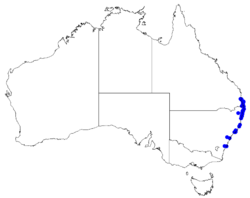
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium | |
Boronia safrolifera, commonly known as safrole boronia, is a species of flowering plant that is endemic to eastern Australia. It is an erect, woody shrub with pinnate leaves that have up to nineteen leaflets, and white to pink, four-petalled flowers.
Description
Boronia safrolifera is an erect, woody shrub that typically grows to a height of 0.5–2.5 m (1 ft 8 in–8 ft 2 in) with mostly hairless branches. The leaves are pinnate with mostly between seven and nineteen leaflets and 12–47 mm (0.47–1.85 in) long and 14–35 mm (0.55–1.38 in) wide in outline on a petiole 3–11 mm (0.12–0.43 in) long. The end leaflet is elliptic to narrow egg-shaped, mostly 2.5–7 mm (0.098–0.276 in) long and 1–2 mm (0.039–0.079 in) wide and the side leaflets are similar but longer. The lower side of the leaflet is a paler shade of green. The flowers are arranged in leaf axils and on the ends of branchlets in groups of between three and twelve on a peduncle 1–20 mm (0.039–0.787 in) long, the individual flowers on a pedicel 2–4 mm (0.079–0.157 in) long. The four sepals are triangular, 1–1.5 mm (0.039–0.059 in) long and hairless. The four petals are white to pale pink, 4.5–7 mm (0.18–0.28 in) long with a few soft hairs. The eight stamens are usually hairy and the stigma is about the same width as the style. Flowering mainly occurs from August to October and the fruit is a mostly hairless capsule 3–4.5 mm (0.12–0.18 in) long and 2–2.5 mm (0.079–0.098 in) wide.[2][3][4][5]
Taxonomy and naming
Boronia safrolifera was first formally described in 1924 by Edwin Cheel and the description was published in Journal and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New South Wales.[6][7] The specific epithet (safrolifera) refers to the odour of the volatile oil safrole apparently released from the crushed leaves of this plant. The ending -fera is a Latin suffix meaning "to carry" or "to bear".[4][8][9]
Distribution and habitat
Safrole boronia grows around the margins of swamps in near-coastal areas of New South Wales north from Port Stephens to Bribie Island in south-eastern Queensland.[2][4]
References
- ↑ "Boronia safrolifera". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/61135. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weston, Peter H.; Duretto, Marco f.. "Boronia safrolifera". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=sp&name=Boronia~safrolifera. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ Duretto, Marco F.; Wilson, Paul G.; Ladiges, Pauline Y.. "Boronia safrolifera". Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of the Environment and Energy, Canberra. https://profiles.ala.org.au/opus/foa/profile/Boronia%20safrolifera. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Duretto, Marco F. (2003). "Notes on Boronia (Rutaceae) in eastern and northern Australia". Muelleria 17: 71–73. https://www.rbg.vic.gov.au/documents/Muelleria_17,_p19-135,_Duretto,_Notes_on_Boronia.pdf. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ Holland, Alisa; Mayhew, Mellisa. "Safrole boronia - Boronia safrolifera". Queensland Government Department of Environment and Science. https://wetlandinfo.des.qld.gov.au/wetlands/ecology/components/species/?boronia-safrolifera. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ "Boronia safrolifera". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/466488. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ↑ Cheel, Edwin (1924). "Notes on Boronia in the Pinnatae section, with a description of a new species.". Journal and Procceding of the Royal Society of New South Wales 58: 146–147. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/174132#page/178/mode/1up. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ "Boronia safrolifera". Australian Native Plants Society (Australia). http://anpsa.org.au/b-saf.html. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ↑ Brown, Roland Wilbur (1956). The Composition of Scientific Words. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. p. 187.
External links
- "Boronia safrolifera Cheel". Atlas of Living Australia. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/http://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2902870.
Wikidata ☰ Q4946284 entry
 |

