Biology:Brachionus plicatilis
| Brachionus plicatilis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Rotifera |
| Class: | Monogononta |
| Order: | Ploima |
| Family: | Brachionidae |
| Genus: | Brachionus |
| Species: | B. plicatilis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Brachionus plicatilis (Müller, 1786)
| |
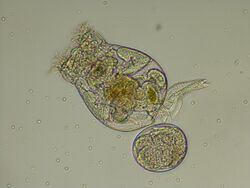
Brachionus plicatilis is a euryhaline (tolerate a wide range of salinity) rotifer in the family Brachionidae, and is possibly the only commercially important rotifer, being raised in the aquaculture industry as food for fish larvae. It has a broad distribution in salt lakes around the world and has become a model system for studies in ecology and evolution.
Reproduction
Brachionus species can normally reproduce asexually and sexually (cyclical parthenogenesis). Sexual reproduction (termed Mixis) is usually induced when population density increases. Mixis in Brachionus plicatilis has been shown to be induced by a density-dependent chemical cue.[1]
Genome size
Haploid '1C' genome sizes in the Brachionus plicatilis species complex range at least from 0.056 to 0.416 pg.[2]
The complete mitochondrial genome of B. plicatilis sensu stricto NH1L has been sequenced.[3]
Cryptic species complex
Brachionus plicatilis strains have long been divided into ‘L-’ and ‘S-type’ forms. However, studies on morphology, karyotype, genetics and reproductive behaviour revealed that these types seem to be different species (B. plicatilis and B. rotundiformis).
DNA sequencing studies in 2002 revealed Brachionus plicatilis to be a cryptic species complex comprising approximately 10 separate species, each of which has been diverging for several million years.[4] A recent study identified 22 potential different species within the Plicatilis species complex.[5]
The species, rather than the complex, is now usually referred to as Brachionus plicatilis s. s. (sensu stricto).
The species complex can be divided into 3 major clades (clade L = larger body and genome sizes e.g. B. plicatilis s.s., clade SM = medium body and genome sizes e.g. B. 'Almenara', clade SS = small body and genome size e.g. B. rotundiformis).
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2148/11/90/figure/F1
- List of the 22 suspected species of the B. plicatilis cryptic species complex
Species names and clade in () [6][7]
- * B01: B. 'Tiscar', S.? (B)
- * B02: unnamed, S. 6 (B)
- * B03: B. 'Persia', S. ? (B)
- * B04: B. 'Harvey', S. 14 (B)
- * B05: B. ibericus, S. 10 (B)
- * B06: B. Almenara (or MEG-2012), S. 9 (B)
- * B07: B. 'Towerinniensis, S. 7 (B)
- * B08: B. 'Coyrecupiensis', S. 8 (B)
- * B09: B. 'Cayman' (or B. koreanus), S. 5 (B)
- * B10: B. 'Cayman' (or B. koreanus), S. 5 (B)
- * B11: B. 'Austria', S. 4 (A)
- * B12: B. Nevada, S. 3 (A)
- * B13: B. Nevada, S. 3 (A)
- * B14: B. Nevada, S. 3 (A)
- * B15: B. plicatilis s.s., S. 1 (A)
- * B16: B. manjavacas, S. 2 (A)
- * B17: unnamed, S. 12 (C)
- * B18: unnamed, S. 12 (C)
- * B19: unnamed, S. 12 (C)
- * B20: B. rotundiformis, S. 11 (C)
- * B21: unnamed, S. ? (C)
- * B22: B. 'Lost', S. 13 (C)
References
- ↑ Induction of sexual reproduction in Brachionus plicatilis (Monogononta, Rotifera) by a density-dependent chemical cue CP Stelzer, TW Snell - Limnology and Oceanography, 2003
- ↑ Stelzer CP, Riss S and Stadler P. (2011): Genome size evolution at the speciation level: the cryptic species complex Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera). BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Apr 7;11:90. [1]
- ↑ Koushirou Suga, David B. Mark Welch, Yukari Tanaka, Yoshitaka Sakakura, and Atsushi Hagiwara (2008). Two Circular Chromosomes of Unequal Copy Number Make Up the Mitochondrial Genome of the Rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Mol Biol Evol (2008) 25(6): 1129-1137
- ↑ Gómez, Africa; Manuel Serra; Gary R Carvalho; David H Lunt (2002). "Speciation in ancient cryptic species complexes: evidence from the molecular phylogeny of Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera)". Evolution; International Journal of Organic Evolution 56 (7): 1431–44. doi:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb01455.x. ISSN 0014-3820. PMID 12206243.
- ↑ Extreme levels of hidden diversity in microscopic animals (Rotifera) revealed by DNA taxonomy D Fontaneto, M Kaya, EA Herniou… - Molecular Phylogenetics …, 2009 - Elsevier
- ↑ Extreme levels of hidden diversity in microscopic animals (Rotifera) revealed by DNA taxonomy D Fontaneto, M Kaya, EA Herniou… - Molecular Phylogenetics …, 2009 - Elsevier
- ↑ Diversity of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis species complex (Rotifera: Monogononta) in Iran through integrative taxonomy Reza Malekzadeh-Viayeh1,*, Razieh Pak-Tarmani1, Nasim Rostamkhani2 and Diego Fontaneto3 Article first published online: 7 JAN 2014 DOI: 10.1111/zoj.12106
Wikidata ☰ Q2488359 entry

