Biology:Castanea ozarkensis
| Ozark chinkapin | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Castanea |
| Species: | C. ozarkensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Castanea ozarkensis Ashe
| |
| |
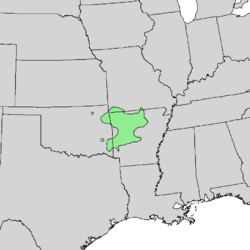
| Natural range of Castanea ozarkensis | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Castanea pumila var. ozarkensis | |
Castanea ozarkensis, also known as the Ozark chinkapin (also spelled chinquapin), is a species of tree that is native to the United States.[3] It is in the Castanea genus that includes chestnuts and types of chestnut known as chinkapins.
Taxonomy
Castanea ozarkensis was described by William Willard Ashe and published in the Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 50 (11): 360-361. 1923.[4]
Some authorities consider it a variant of the Allegheny chinkapin (C. pumila) as C. pumila ozarkensis.
Distribution
It grows in the Ozark Mountains and Ouachita Mountains of Missouri, Arkansas, Texas , Louisiana and Oklahoma.[3] It is possibly extirpated from Alabama.
Ecology
The nuts it produces provided food for indigenous people, early settlers, and various animals including eastern gray squirrel, chipmunk, white-tailed deer, turkey, and bobwhite quail.[3]
Conservation
Castanea ozarkensis is susceptible to chestnut blight and has been devastated by the disease, and largely now grows only as a small tree or shrub.[3] However, several mature individuals have survived the blight, with over 45 such individuals located so far since the 2000s. The discovery of these specimens has spurred an ongoing project to restore the species by using the offspring of these trees, headed by the Ozark Chinkapin Foundation.[5] An analysis has also found that Ozark chinkapin populations contain far more genetic diversity than those of the American chestnut, which was also devastated by the chestnut blight. The study also found that the Ozark chinkapin may actually be ancestral to the American chestnut and Allegheny chinkapin, rather than the other way around.[6][5] Another study has found that the surviving Ozark chinkapins are even more resistant to the chestnut blight than the Chinese chestnut, which is not affected by the blight.[5]
A large individual, designated a Champion Tree, grows in Barry County, Missouri.[7]
See also
- American chinquapin
References
- ↑ Carrero, C.; Lobdell, M. (2021). "Castanea ozarkensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T159384517A183955054. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T159384517A183955054.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/159384517/183955054. Retrieved 15 November 2022.
- ↑ "NatureServe Explorer 2.0". https://explorer.natureserve.org/Taxon/ELEMENT_GLOBAL.2.158033/Castanea_pumila_var_ozarkensis.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Castanea ozarkensis – Plant Finder". http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=280749&isprofile=0&.
- ↑ "Castanea ozarkensis". Tropicos.org.. http://www.tropicos.org/Name/13100251. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 "A legendary Ozark chestnut tree, thought extinct, is rediscovered". 2019-06-24. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2019/06/saving-chestnut-trees-ozarks/.
- ↑ Huang, Hongwen; Hawkins, Leigh K.; Dane, Fenny (1999-11-01). "Genetic Variation and Population Structure of Castanea pumila var. ozarkensis" (in en-US). Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science 124 (6): 666–670. doi:10.21273/JASHS.124.6.666. ISSN 2327-9788. https://journals.ashs.org/view/journals/jashs/124/6/article-p666.xml.
- ↑ "Ozark Chinkapin (Castanea ozarkensis)". American Forests. 15 September 2016. https://www.americanforests.org/big-trees/ozark-chinkapin-castanea-ozarkensis-2/.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
Wikidata ☰ Q5756707 entry
 |