Biology:Cheloctonus jonesii
| Cheloctonus jonesii | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Scorpiones |
| Family: | Hormuridae |
| Genus: | Cheloctonus |
| Species: | C. jonesii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cheloctonus jonesii Pocock, 1892
| |
Cheloctonus jonesii is a species of scorpion in the family Hormuridae native to southern Africa.[1]
Description
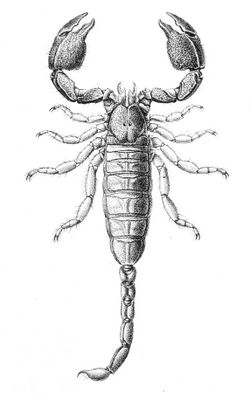
This scorpion grows to be to 9 cm (3.5 in) long. It is variable in appearance, from all black in northern KwaZulu-Natal to brown with yellow legs in Mpumalanga.[2] The legs are otherwise rust-coloured.[3] It has a heavy-set body with stocky legs and stout arms (pedipalps) with short pincers (chelae).[4] Its cephalothorax is around 11 mm long and broader (11.5 mm) across. The tail is around 3.5 cm (1.4 in) long. British naturalist R. I. Pocock described the scorpion in 1892, naming it after the person who collected the specimen in the Murchison Range in what was then Transvaal, C.R. Jones.[3]
Habitat
Cheloctonus jonesii is native to Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Eswatini and eastern South Africa, where it is especially common in KwaZulu-Natal, there reaching densities of two burrows per three square metres.[4] In Jozini, densities of four per square metre have been reported.[2] It lives in areas of clay-based soil with annual rainfall of 800–1250 mm (30–50 in),[4] shunning waterlogged locales.[2] It excavates a vertical burrow around 18 cm (7 in) long, generally located at the base of a tuft of grass or among multiple tufts. The scorpion takes 2–3 nights to complete this, using its pincers to loosen the ground and then pedipalps and pincers as spades to carry the soil away.[4]
It eats dung beetles, which fall into its burrow.[4] C. jonesii has also been reported killing the red-billed quelea.[5]
Among creatures that prey on C. jonesii are large centipedes of the genus Scolopendra, the ground foraging red-billed hornbill (Tockus erythrorhynchus) and eastern yellow-billed hornbill (T. flavirostris), bushveld gerbil (Gerbilliscus leucogaster), Cape porcupine (Hystrix africaeaustralis) and lesser red musk shrew (Crocidura hirta).[4]
References
- ↑ Rein, Jan Ove (2021). "Hormuridae". https://www.ntnu.no/ub/scorpion-files/hormuridae.php.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Leeming, Jonathan (2003). Scorpions of Southern Africa. Struik. p. 60. ISBN 9781868728046. https://books.google.com/books?id=vQFEeohchVQC&pg=PA60.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Reginald Innes Pocock (1892). "Descriptions of two new genera of scorpions, with notes upon some Species of Palamnæus". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 6 9 (49): 38–49 [44]. doi:10.1080/00222939208677269. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/15617687.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Harington, Alexis (1977). "Burrowing Biology of the Scorpion Cheloctonus jonesii Pocock (Arachnida: Scorpionida: Scorpionidae)". The Journal of Arachnology 5 (3): 243–49. http://www.americanarachnology.org/JoA_free/JoA_v5_n3/JoA_v5_p243.pdf.
- ↑ Vincent, Leonard S.; Breitman, Ty (2010). "The scorpion Cheloctonus jonesii Pocock, 1892 (Scorpiones, Liochelidae) as a possible predator of the red-billed quelea, Quelea quelea (Linnaeus, 1758)". Bulletin of the British Arachnological Society 15 (2): 59–60. doi:10.13156/arac.2010.15.2.59. http://britishspiders.org.uk/bulletin/150205.pdf.
Wikidata ☰ Q2962207 entry
 |

