Biology:Cheloniellon
| Cheloniellon | |
|---|---|
| |
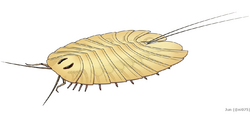
| Reconstruction of Cheloniellon calmani | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia
|
| Phylum: | |
| Superclass: | †Vicissicaudata
|
| Order: | |
| Family: | †Cheloniellidae
|
| Genus: | †Cheloniellon
Broili 1932 |
| Species | |
| |
Cheloniellon is a monotypic genus of cheloniellid arthropod, known only by one species, Cheloniellon calmani, discovered from the Lower Devonian Hunsrück Slate of Germany .[1]
Morphology
Cheloniellon range about 20 centimeters in body length (excluding appendages).[1] The flattened, ovoid body compose of 11 tergites (dorsal exoskeleton), all but the posteriormost are laterally expanded and covered the appendages underneath each of them. The boundaries between tergites have a radiated appearance. Dorsal surface of the first tergite have a pair of kidney-shaped eyes.[1] Based on the differentiation of corresponding appendages, the first 2 tergites and the remaining 9 tergites were interpreted as those of cephalon (head) and trunk, respectively.[1] Contray to the widely-referred reconstruction by Stürmer & Bergström (1978),[1] but as most of the Cheloniellids, There is no evidence of telson (a medial tail-like terminal structure) in any described fossil materials.[2]
Underneath the tergites were numerous pairs of appendages. The anteriormost appendage pair were antennae, followed by a pair of specialized second appendages that bore spines and esthetasc-like brushes, and 4 pairs of leg-like appendages that have overlapped gnathobases (jaw-like structure on leg base).[1] The mouth was covered by a labrum with spiny surface, situated between the second appendages and the first gnathobasic appendages.[1] The last gnathobasic appendage pair and the remaining 5 appendage pairs anterior to it were interpreted as corresponding to the second tergite and first tergite, respectively.[1] Appendages posterior to the cephalon were 8 pairs of biramous appendages (each compose of a leg-like endopod and a lobe-like exopod) and a pair of furcae, corresponding to the remaining 9 trunk tergites.[1]
Paleoecology
Cheloniellon may have been a benthic predator,[3] using its gnathobases to crush prey while the spiny labrum may have helped lead food items toward the mouth opening.[1] The specialized second appendages are too fragile to be raptorial, instead they may have played a tactile role, sensing the property and position of food items.[1] The endopod and exopod of the trunk appendages may have had a locomotory and respiratory function, respectively.[1][2]
Classification
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylogenetic position of Cheloniellon.[4][5] |
Cheloniellon is a genus of Cheloniellida, an extinct arthropod taxon that have a controversial phylogenetic position. It was previously thought to be chelicerate-related,[1][2] but later studies repeatedly suggests it as a member of Artiopoda, forming the clade Vicissicaudata with Aglaspidida and related genera.[4][5][6] Within Cheloniellida, Cheloniellon branched next to Neostrabops but basal to Triopus and Duslia.[4][5]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 Stürmer, Wilhelm; Bergström, Jan (1978-06-01). "The arthropod Cheloniellon from the devonian hunsrück shale" (in en). Paläontologische Zeitschrift 52 (1): 57–81. doi:10.1007/BF03006730.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Wendruff, Andrew James, et al. "New cheloniellid arthropod with large raptorial appendages from the Silurian of Wisconsin, USA." BioRxiv (2018): 407379. [1]
- ↑ Rust, Jes; Bergmann, Alexandra; Bartels, Christoph; Schoenemann, Brigitte; Sedlmeier, Stephanie; Kühl, Gabriele (2016-03-01). "The Hunsrück biota: A unique window into the ecology of Lower Devonian arthropods" (in en). Arthropod Structure & Development. Special Issue: Fossils as Living Beings 45 (2): 140–151. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2016.01.004. ISSN 1467-8039. PMID 26826500. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1467803916000050.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ortega‐Hernández, Javier; Legg, David A.; Braddy, Simon J. (2013). "The phylogeny of aglaspidid arthropods and the internal relationships within Artiopoda" (in en). Cladistics 29 (1): 15–45. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2012.00413.x. ISSN 1096-0031. PMID 34814371.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Zhu, Xuejian; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2017-09-11). "The Vicissicaudata revisited – insights from a new aglaspidid arthropod with caudal appendages from the Furongian of China" (in en). Scientific Reports 7 (1): 11117. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11610-5. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 28894246.
- ↑ Du, Kun‐sheng; Ortega‐Hernández, Javier; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xi‐guang (2019–2020). "A soft‐bodied euarthropod from the early Cambrian Xiaoshiba Lagerstätte of China supports a new clade of basal artiopodans with dorsal ecdysial sutures" (in en). Cladistics 35 (3): 269–281. doi:10.1111/cla.12344. ISSN 0748-3007. PMID 34622993.
Wikidata ☰ Q96386650 entry
 |



