Biology:Eucalyptus laeliae
| Darling Range ghost gum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Eucalyptus laeliae in Kalamunda National Park | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Eucalyptus |
| Species: | E. laeliae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eucalyptus laeliae Podger & Chippendale[1]
| |
| |
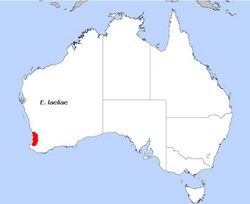
| Eucalyptus laeliae, field distribution | |
Eucalyptus laeliae, commonly known as the Darling Range ghost gum[2] or butter gum,[3] is a species of small to medium-sized tree occurring only on the western side of the Darling Range. It has smooth white, powdery bark, lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of between seven and eleven, creamy white flowers and cup-shaped to barrel-shaped fruit.
Description
Eucalyptus laeliae is a tree that typically grows to a height of 5 to 20 metres (16 to 66 ft) and forms a lignotuber. The bark is smooth, powdery, usually white but in autumn, butter yellow. Young plants and coppice regrowth have bluish green, egg-shaped to lance-shaped leaves that are 65–125 mm (2.6–4.9 in) long and 23–45 mm (0.91–1.77 in) wide. Adult leaves are arranged alternately, the same dull bluish green or yellowish on both sides, lance-shaped to curved, 85–135 mm (3.3–5.3 in) long and 10–25 mm (0.39–0.98 in) wide on a petiole 8–20 mm (0.31–0.79 in) long.[2][4][5][6]
The flower buds are arranged in leaf axils in groups of seven, nine or eleven on an unbranched peduncle 8–15 mm (0.31–0.59 in) long, the individual buds on pedicels 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in) long. Mature buds are oval or club-shaped, 6–7 mm (0.24–0.28 in) long and 3–5 mm (0.12–0.20 in) wide with a rounded operculum with a small point on the top. Flowering occurs between December and February and the flowers are creamy white or white, soft and bristly. The fruit is a woody, cup-shaped or barrel-shaped capsule 5–7 mm (0.20–0.28 in) long and 4–6 mm (0.16–0.24 in) wide with the disc descending and the valves near rim level.[2][5][6][7][8]
Taxonomy and naming
Eucalyptus laeliae was first formally described by the botanists Francis Podger and George Chippendale in 1969 in the Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia. The type specimen was collected by Leslie McGann near North Dandalup in 1966.[9][10][11] The species name laeliae is taken from the names of one of the vestal virgins, referring to the smooth, column-like trunk.[5][7]
Distribution and habitat
The Darling Range ghost gum is found on hills and amongst granite outcrops along the west coast in the Peel and South West regions of Western Australia between Kalamunda in the north, Wandering to the east and Capel to the south where it grows in sandy-clay-loam soils.[2]
Use in horticulture
The tree can be bought commercially as a seedling or as seeds. It grows well in full sun in a range of well-drained soil types. It can be susceptible to leaf blister, a form of insect attack.[7]
Conservation status
This eucalypt is classified as "not threatened" in Western Australia by the Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Eucalyptus laeliae". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/61475.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Eucalyptus laeliae". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/5688.
- ↑ "Butter gum (Eucalyptus laeliae)". Tree Pictures, South-Western Australia. Robert Powell. 2016. http://www.robertpowelltrees.org/butter-gum-eucalyptus-laeliae/.
- ↑ Brooker, M.I.H. & Kleinig, D.A. Field Guide to Eucalyptus, Bloomings, Melbourne 2001
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Eucalyptus laeliae". Euclid: Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research. https://apps.lucidcentral.org/euclid/text/entities/eucalyptus_laeliae.htm.
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 Chippendale, George M.. "Eucalyptus laeliae". Flora of Australia. Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of the Environment and Energy, Canberra. https://profiles.ala.org.au/opus/foa/profile/Eucalyptus%20laeliae.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Eucalyptus laeliae". Government of Western Australia. January 2016. https://www.bgpa.wa.gov.au/about-us/conservation/plant-of-the-month/2109-january-2016.
- ↑ "Eucalyptus laeliae". EucaLink A Web Guide to the Eucalypts. Royal Botanic Garden, Sydney. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/euctax.pl?/PlantNet/Euc=&name=Eucalyptus+laeliae.
- ↑ "Eucalyptus laeliae". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/454661.
- ↑ Podger, Francis D.; Chippendale, George M. (1969). "A new species of Eucalyptus from Western Australia". Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia 51 (3): 65–67. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/173671#page/3/mode/1up. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- ↑ "McGann, Leslie Roy (1935 - )". Council of Heads of Australasian Herbaria. http://www.anbg.gov.au/biography/mcgann-leslie-roy.html.
Wikidata ☰ Q2712404 entry
 |



