Biology:Extrapolation based molecular systems biology
Please use PROD only on articles. It is proposed that this article be deleted because of the following concern:
If you can address this concern by improving, copyediting, sourcing, renaming, or merging the page, please edit this page and do so. You may remove this message if you improve the article or otherwise object to deletion for any reason. Although not required, you are encouraged to explain why you object to the deletion, either in your edit summary or on the talk page. If this template is removed, do not replace it. This message has remained in place for seven days, so the article may be deleted without further notice. Nominator: Please consider notifying the author/project: {{subst:proposed deletion notify|Biology:Extrapolation based molecular systems biology|concern=Unreferenced (list of authors but no titles), orphaned since 2009}} ~~~~Timestamp: 20210520120703 12:07, 20 May 2021 (UTC) Administrators: delete |
Extrapolation based Molecular Systems Biology is the utilization of molecular data from one or many sub-cellular levels to indirectly infer the remaining components of a sub-cellular system via statistical algorithms and priori biological knowledge. The motivation to rebuild remaining components of a system is driven primarily by adopting a systems biologist's view of a biological phenomenon where a pan-omic view is a consistent requirement (... Denis Noble "The Music of Life").
The term "extrapolation" is chosen to provide caution due to a high potential of false positives with high levels of extrapolation. On average, fewer levels (and smaller leaps) of inference and greater levels of observational data is recommended for a statistically significant extrapolated system.
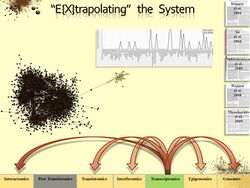
Sub-cellular levels may include one or more of the following (but not limited to) (see Systems Biology): Genomics, Epigenomics / Epigenetics, Transcriptomics, Interferomics, Translatomics / Proteomics, Metabolomics, Glycomics, Lipidomics, Interactomics, and Fluxomics.
Example (see image on right): Molecular level of quantitative data is illustrated in green, inferred levels are illustrated in yellow, and non-active/missing molecular levels are illustrated in grey. Data source(s) & Algorithm(s) are listed on the right. Acknowledgements:Irizarry et al. 2004, Su et al. 2004, Subramanium et al. 2005, Warren et al. 2008, Theocharidis et al. 2009.