Biology:Flustra foliacea
| Flustra foliacea | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Bryozoa |
| Class: | Gymnolaemata |
| Order: | Cheilostomatida |
| Family: | Flustridae |
| Genus: | Flustra |
| Species: | F. foliacea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Flustra foliacea | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Eschara foliacea Linnaeus, 1758 | |
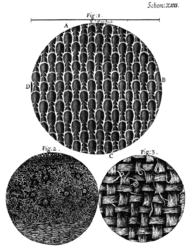
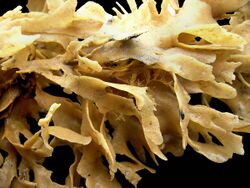
Flustra foliacea is a species of bryozoans found in the northern Atlantic Ocean. It is a colonial animal that is frequently mistaken for a seaweed. Colonies begin as encrusting mats, and only produce loose fronds after their first year of growth. They may reach 20 cm (8 in) long, and smell like lemons. Its microscopic structure was examined by Robert Hooke and illustrated in his 1665 work Micrographia.
Taxonomic history
Flustra foliacea was studied as early as 1665, when Robert Hooke published observations of various organisms and materials made with an early microscope.[1] It was first given a binomial name in 1758, when Carl Linnaeus included it in the 10th edition of his Systema Naturae as Eschara foliacea.[2] In later publications, Linnaeus divided bryozoans into more than one genus, and so the species came to be called Flustra foliacea. It is the type species of the genus Flustra.[3]
Description
Flustra foliacea is often mistaken for a seaweed, but is actually a colony of animals.[4] The fronds can reach a height of 20 centimetres (7.9 in) and have rounded ends.[4] They have a strong aroma of lemons.[4] It differs from the superficially similar Securiflustra securifrons by the tendency of the frond branches to become markedly wider towards the tip.[5] Each zooid is roughly rectangular, with 4–5 short spines at the distal end and 13–14 tentacles around the lophophore.[4]
Distribution and ecology
Flustra foliacea has a wide distribution in the north Atlantic Ocean, on both the European and American sides.[5] It is restricted to colder sublittoral waters, and reaches its southern limit in northern Spain .[6]
The fronds of Flustra foliacea are often used by other animals as a substrate to live on. Such epibionts include other bryozoa such as Crista eburnea, hydroids, sessile polychaete worms and the porcelain crab Pisidia longicornis.[4][7] Other animals feed on F. foliacea, including the sea urchins Echinus esculentus and Psammechinus miliaris and the nudibranch Crimora papillata; the pycnogonid Achelia echinata feeds preferentially on F. foliacea.[7]
Life cycle
Flustra foliacea colonies only grow in spring and summer, which can result in visible annual growth rings.[4] Breeding occurs between separate male and female zooids within the colony in autumn and winter.[4] The cells produce outgrowths known as ovicells, which contain embryos and are visible from October to February.[4] The larvae are released in spring and, after a short period, settle to the substrate. For the first year, colonies grow only along the surface (encrusting), with loose fronds only being formed in subsequent years.[4] These are produced when two encrusting colonies meet, and the two edges that make contact begin to grow upwards, back to back.[7] The total lifespan of a colony may reach 12 years.[4] It is frequently found washed up on beaches after storms.[8]
References
- ↑ "Flustra foliacea (broad-leaved hornwrack): biology". Natural History Museum. Archived from the original on 8 November 2011. https://web.archive.org/web/20111108014548/http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/species-of-the-day/collections/collecting/flustra-foliacea/biology/index.html.
- ↑ Hans G. Hansson (1999). "South Scandinavian marine "Lophophorata" check-list" (PDF). North East Atlantic Taxa. Tjärnö Marine Biological Laboratory. http://www.tmbl.gu.se/libdb/taxon/neat_pdf/NEAT*Lophophorata.pdf. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ↑ J. S. Ryland (1969). "A nomenclatural index to 'A history of the British Marine Polyzoa' by T. Hincks (1880)". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) 17: 207–260. http://biostor.org/reference/59528.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 John Fish & Susan Fish (2011). "Bryozoa (Ectoprocta)". A Student's Guide to the Seashore (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 382–393. ISBN 978-0-521-72059-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=1wD21-DC81YC&pg=PA391.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Käre Telnes. "Greater Horn Wrack – Flustra foliacea". The Marine Flora & Fauna of Norway. http://www.seawater.no/fauna/bryozoa/foliacea.html. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ↑ "Flustra foliacea (broad-leaved hornwrack): distribution". Natural History Museum. http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/species-of-the-day/collections/collecting/flustra-foliacea/distribution-ecology/index.html. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Hornwrack – Flustra foliacea – Importance". Marine Life Information Network (MarLIN). Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. http://www.marlin.ac.uk/speciesimportance.php?speciesID=3342. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ↑ "Flustra foliacea (broad-leaved hornwrack)". Natural History Museum. http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/species-of-the-day/collections/collecting/flustra-foliacea/index.html. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
External links
- Sally Rouse (June 9, 2011). "Flustra foliacea (Linnaeus, 1758)". Bryozoa of the British Isles. http://britishbryozoans.myspecies.info/category/bryozoa/bryozoa/gymnolaemata/cheilostomata/scrupariina/flustridae/flustra/flustra-foliacea-.
- B. E. Picton & C. C. Morrow (2010). "Flustra foliacea (Linnaeus, 1758)". Encyclopedia of Marine Life of Britain and Ireland. National Museums of Northern Ireland. http://www.habitas.org.uk/marinelife/species.asp?item=Y6940.
- Robert Hooke (1665). Micrographia: or Some Physiological Descriptions of Minute Bodies made by Magnifying Glasses with Observations and Inquiries thereupon. London: John Martyn & James Allestry. http://archive.nlm.nih.gov/proj/ttp/flash/hooke/hooke.html. Also available at Project Gutenberg
Wikidata ☰ Q2399981 entry
 |