Biology:Genetic viability
Genetic viability is the ability of the genes present to allow a cell, organism or population to survive and reproduce.[1][2] The term is generally used to mean the chance or ability of a population to avoid the problems of inbreeding.[1] Less commonly genetic viability can also be used in respect to a single cell or on an individual level.[1]
Inbreeding depletes heterozygosity of the genome, meaning there is a greater chance of identical alleles at a locus.[1] When these alleles are non-beneficial, homozygosity could cause problems for genetic viability.[1] These problems could include effects on the individual fitness (higher mortality, slower growth, more frequent developmental defects, reduced mating ability, lower fecundity, greater susceptibility to disease, lowered ability to withstand stress, reduced intra- and inter-specific competitive ability) or effects on the entire population fitness (depressed population growth rate, reduced regrowth ability, reduced ability to adapt to environmental change).[3] See Inbreeding depression. When a population of plants or animals loses their genetic viability, their chance of going extinct increases.[4]
Necessary conditions
To be genetically viable, a population of plants or animals requires a certain amount of genetic diversity and a certain population size.[5] For long-term genetic viability, the population size should consist of enough breeding pairs to maintain genetic diversity.[6] The precise effective population size can be calculated using a minimum viable population analysis.[7] Higher genetic diversity and a larger population size will decrease the negative effects of genetic drift and inbreeding in a population.[3] When adequate measures have been met, the genetic viability of a population will increase.[8]
Causes for decrease
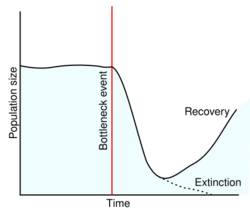
The main cause of a decrease in genetic viability is loss of habitat.[4][9][10] This loss can occur because of, for example urbanization or deforestation causing habitat fragmentation.[4] Natural events like earthquakes, floods or fires can also cause loss of habitat.[4] Eventually, loss of habitat could lead to a population bottleneck.[3] In a small population, the risk of inbreeding will increase drastically which could lead to a decrease in genetic viability.[3][4][11] If they are specific in their diets, this can also lead to habitat isolation and reproductive constraints, leading to greater population bottleneck, and decrease in genetic viability.[12] Traditional artificial propagation can also lead to decreases in genetic viability in some species.[13][14]
Genetic viability of particular wolf populations
A small highly inbred population of gray wolves (Canis lupus) residing in Isle Royale National Park, Michigan, USA has been undergoing population decline and is nearing extinction.[15] These gray wolves have been experiencing severe inbreeding depression primarily determined by the homozygous expression of strongly deleterious recessive mutations leading to decreased genetic viability.[15][16] Reduced genetic viability due to severe inbreeding was expressed as reduced reproduction and survival as well as specific defects such as malformed vertebrae, probable cataracts, syndactyly, an unusual “rope tail,” and anomalous fur phenotypes. A separate inbred Scandinavian population of gray wolves (Canis lupus), also suffering from loss of genetic viability, is experiencing inbreeding depression likely due to the homozygous expression of deleterious recessive mutations.[17]
Population conservation
Habitat protection is associated with more allelic richness and heterozygosity than in unprotected habitats.[18] Reduced habitat fragmentation and increased landscape permeability can promote allelic richness by facilitating gene flow between populations that are isolated or smaller.[18]
The minimum viable population needed to maintain genetic viability is where the loss of genetic variation because of small population size (genetic drift) is equal to genetic variation gained through mutation.[19] When the numbers of one sex is too low, there may be a need for crossbreeding to maintain viability.[20]
Analyzing
When genetic viability seems to be decreasing within a population, a population viability analysis (PVA) can be done to assess the risk of extinction of this species.[21][22][23] The result of a PVA could determine whether further action is needed regarding the preservation of a species.[21]
Applications
Genetic viability is applied by wildlife management staff in zoos, aquariums or other such ex situ habitats.[24] They use the knowledge of the animals' genetics, usually through their pedigrees, to calculate the PVA and manage the population viability.[24]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 A Primer of Population Genetics and Genomics (4th ed.). Oxford University Press. 2020-06-25. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198862291.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-19-886229-1. https://oxford.universitypressscholarship.com/view/10.1093/oso/9780198862291.001.0001/oso-9780198862291.
- ↑ "A quantitative genetics model for viability selection". Heredity 94 (3): 347–55. March 2005. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6800615. PMID 15536483.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "Importance of Genetic Variation to the Viability of Mammalian Populations". Journal of Mammalogy 78 (2): 320–335. 1997-05-21. doi:10.2307/1382885.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Find the weakest link. A comparison between demographic, genetic and demo-genetic metapopulation extinction times". BMC Evolutionary Biology 11 (1): 260. September 2011. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-260. PMID 21929788.
- ↑ "African wild dogs: Genetic viability of translocated populations across South Africa" (in en). Biological Conservation 234: 131–139. 2019-06-01. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2019.03.033.
- ↑ "Genetic diversity and population structure of wolverine (Gulo gulo) populations at the southern edge of their current distribution in North Americawith implications for genetic viability" (in en). Conservation Genetics 7 (2): 197–211. 2006-04-01. doi:10.1007/s10592-006-9126-9.
- ↑ "Assessing minimum viable population size: Demography meets population genetics". Trends in Ecology & Evolution 8 (7): 234–9. July 1993. doi:10.1016/0169-5347(93)90197-W. PMID 21236157.
- ↑ "Genetic viability and population history of the giant panda, putting an end to the "evolutionary dead end"?". Molecular Biology and Evolution 24 (8): 1801–10. August 2007. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm099. PMID 17513881.
- ↑ "The genealogy and genetic viability of reintroduced Yellowstone grey wolves". Molecular Ecology 17 (1): 252–74. January 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03468.x. PMID 17877715.
- ↑ Agroforestry and biodiversity conservation in tropical landscapes. Schroth, G. (Goetz). Washington: Island Press. 2004. pp. 290–314. ISBN 1-4237-6551-6. OCLC 65287651.
- ↑ (in en) Genetics, Demography and Viability of Fragmented Populations. Cambridge University Press. 2000-10-12. ISBN 978-0-521-79421-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=hk452JHmPrcC&q=population+bottleneck+genetic+viability&pg=PP1.
- ↑ "Genetic viability and population history of the giant panda, putting an end to the "evolutionary dead end"?". Molecular Biology and Evolution 24 (8): 1801–10. August 2007. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm099. PMID 17513881.
- ↑ "Genetic changes from artificial propagation of Pacific salmon affect the productivity and viability of supplemented populations". ICES Journal of Marine Science 56 (4): 459–466. August 1, 1999. doi:10.1006/jmsc.1999.0455.
- ↑ "Evolutionary effects of alternative artificial propagation programs: implications for viability of endangered anadromous salmonids". Evolutionary Applications 1 (2): 356–75. May 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1752-4571.2008.00034.x. PMID 25567637.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Robinson JA, Räikkönen J, Vucetich LM, Vucetich JA, Peterson RO, Lohmueller KE, Wayne RK. Genomic signatures of extensive inbreeding in Isle Royale wolves, a population on the threshold of extinction. Sci Adv. 2019 May 29;5(5):eaau0757. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau0757. PMID: 31149628; PMCID: PMC6541468
- ↑ Kyriazis CC, Wayne RK, Lohmueller KE. Strongly deleterious mutations are a primary determinant of extinction risk due to inbreeding depression. Evol Lett. 2020 Dec 17;5(1):33-47. doi: 10.1002/evl3.209. PMID: 33552534; PMCID: PMC7857301
- ↑ Smeds L, Ellegren H. From high masked to high realized genetic load in inbred Scandinavian wolves. Mol Ecol. 2023 Apr;32(7):1567-1580. doi: 10.1111/mec.16802. Epub 2022 Dec 13. PMID: 36458895
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "Minimum habitat thresholds required for conserving mountain lion genetic diversity". Ecology and Evolution 10 (19): 10687–10696. October 2020. doi:10.1002/ece3.6723. PMID 33072289.
- ↑ "Pragmatic population viability targets in a rapidly changing world". Biological Conservation 143 (1): 28-34. January 2010. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2009.09.001.
- ↑ "Balancing genetic diversity, genetic merit and population viability in conservation programmes". Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics 120 (3): 137–149. 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0388.2003.00383.x.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Population Viability Analysis for an Endangered Plant" (in en). Conservation Biology 4 (1): 52–62. 1990. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.1990.tb00267.x. ISSN 0888-8892.
- ↑ Population viability analysis. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. 2002. ISBN 0-226-04177-8. OCLC 48100035.
- ↑ "Population Viability Analysis" (in en). Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 23 (1): 481–497. 1992-11-01. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.23.110192.002405. ISSN 0066-4162.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Lessons from 30 years of population viability analysis of wildlife populations". Zoo Biology 38 (1): 67–77. January 2019. doi:10.1002/zoo.21468. PMID 30585658.
 |
