Biology:Gintonin
| Major latex-like protein | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
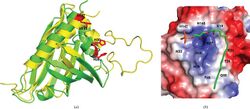 Gintonin bound to lysophosphatidic acid C18:2. (a) Superposition of ginseng major latex-like protein 151 (GLP;green) and the lowest energy major latex protein 28 conformer (yellow). The mutated residues in GLP are represented by red sticks. (b) The electrostatic molecular surface of GLP modelled with LPA C18:2 in close conformation. The positions of the residues that recognize LPA C18:2 are labelled.[1] | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Organism | |||||||
| Symbol | mlp151 | ||||||
| UniProt | B5THI3 | ||||||
| |||||||
Gintonin is a glycolipoprotein fraction isolated from Panax ginseng. The non-saponin ingredient was designated as gintonin, where gin was derived from ginseng, ton from the tonic effects of ginseng, and in from protein. The main component of gintonin is a complex of lysophosphatidic acids (LPA) and ginseng proteins such as ginseng major latex-like protein151 (GLP151) and ginseng ribonuclease-like storage protein.[2][3]
GLP151 is a first plant-derived LPA binding protein as one of Bet v 1 superfamily. GLP151 has a LPA binding domain on H147 and H148 at C-terminal. These two histidine residues bind to phosphate group of LPA.[4]
Biological action
Gintonin is believed to act by delivering LPA to lysophospholipid receptors, which are high affinity and selective target receptors. In animal cell cultures, gintonin induces [Ca2+] transients via activation of the said receptor.[4]
One Korean study claims that gintonin is orally active in rodents and shows anti-Alzheimer's disease effects through LPA receptor-mediated non-amyloidogenic pathways.[5][6] Oral gintonin is well-tolerated by human AD patients in a small study, but the benefits are unclear.[7]
A number of other effects are attributed to oral administration of gintonin-enriched extract in rodents.[8][9][10][11]
See also
References
- ↑ Choi, SH; Hong, MK; Kim, HJ; Ryoo, N; Rhim, H; Nah, SY; Kang, LW (2015). "Structure of ginseng major latex-like protein 151 and its proposed lysophosphatidic acid-binding mechanism". Acta Crystallographica Section D 71 (pt5): 1039–50. doi:10.1107/S139900471500259X. PMID 25945569.
- ↑ Pyo, M. K.; Choi, S. H.; Hwang, S. H.; Shin, T. J.; Lee, B. H.; Lee, S. M.; Lim, Y. H.; Kim, D. H. et al. (2011). "Novel Glycolipoproteins from Ginseng". Journal of Ginseng Research 35: 92–103. doi:10.5142/jgr.2011.35.1.092.
- ↑ Hwang, S. H.; Shin, T. J.; Choi, S. H.; Cho, H. J.; Lee, B. H.; Pyo, M. K.; Lee, J. H.; Kang, J. et al. (2012). "Gintonin, newly identified compounds from ginseng, is novel lysophosphatidic acids-protein complexes and activates G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors with high affinity". Molecules and Cells 33 (2): 151–162. doi:10.1007/s10059-012-2216-z. PMID 22286231.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Choi, SH; Hong, MK; Kim, HJ; Ryoo, N; Rhim, H; Nah, SY; Kang, LW (2015). "Structure of ginseng major latex-like protein 151 and its proposed lysophosphatidic acid-binding mechanism". Acta Crystallographica Section D 71 (pt5): 1039–50. doi:10.1107/S139900471500259X. PMID 25945569.
- ↑ Hwang SH, Shin EJ, Shin TJ, Lee BH, Choi SH, Kang J, Kim HJ, Kwon SH, Jang CG, Lee JH, Kim HC, Nah SY (2012). "Gintonin, a ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, attenuates Alzheimer's disease-related neuropathies: involvement of non-amyloidogenic processing". Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 31 (1): 207–223. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120439. PMID 22543851.
- ↑ Kim, HJ; Shin, EJ; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Jung, SW; Cho, IH; Hwang, SH; Kim, JY et al. (2015). "Oral Administration of Gintonin Attenuates Cholinergic Impairments by Scopolamine, Amyloid-β Protein, and Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease". Molecules and Cells 38 (9): 796–805. doi:10.14348/molcells.2015.0116. PMID 26255830.
- ↑ Moon J, Choi SH, Shim JY, Park HJ, Oh MJ, Kim M, Nah SY. (2017). "Gintonin Administration is Safe and Potentially Beneficial in Cognitively Impaired Elderly". Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 32 (1): 85–87. doi:10.1097/WAD.0000000000000213. PMID 29028648.
- ↑ Kim, HJ; Kim, DJ; Shin, EJ; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Hwang, SH; Rhim, H; Cho, IH et al. (2016). "Effects of gintonin-enriched fraction on hippocampal cell proliferation in wild-type mice and an APPswe/PSEN-1 double Tg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease". Neurochemistry International 101: 56–65. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2016.10.006. PMID 27765516.
- ↑ Kim, HJ; Park, SD; Lee, RM; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Hwang, SH; Rhim, H; Kim, HC et al. (2017). "Gintonin attenuates depressive-like behaviors associated with alcohol withdrawal in mice". J Affect Disord 215: 23–29. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2017.03.026. PMID 28314177.
- ↑ Lee, BH; Kim, HK; Jang, M; Kim, HJ; Choi, SH; Hwang, SH; Kim, HC; Rhim, H et al. (2017). "Effects of Gintonin-Enriched Fraction in an Atopic Dermatitis Animal Model: Involvement of Autotaxin Regulation". Biol Pharm Bull 40 (7): 1063–1070. doi:10.1248/bpb.b17-00124. PMID 28674249.
- ↑ Hwang SH, Lee BH, Kim HJ, Cho HJ, Shin HC, Im KS, Choi SH, Shin TJ, Lee SM, Nam SW, Kim HC, Rhim H, Nah SY. (2012). "Suppression of metastasis of intravenously-inoculated B16/F10 melanoma cells by the novel ginseng-derived ingredient, gintonin: Involvement of autotaxin inhibition". International Journal of Oncology 42 (1): 317–326. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1709. PMID 23174888.
Further reading
- Pyo, M. K.; Choi, S. H.; Hwang, S. H.; Shin, T. J.; Lee, B. H.; Lee, S. M.; Lim, Y. H.; Kim, D. H. et al. (2011). "Novel Glycolipoproteins from Ginseng". Journal of Ginseng Research 35: 92–103. doi:10.5142/jgr.2011.35.1.092.
- Pyo, M. K.; Choi, S. H.; Shin, T. J.; Hwang, S. H.; Lee, B. H.; Kang, J. Y.; Kim, H. J.; Lee, S. H. et al. (2011). "A Simple Method for the Preparation of Crude Gintonin from Ginseng Root, Stem, and Leaf". Journal of Ginseng Research 35 (2): 209–218. doi:10.5142/jgr.2011.35.2.209. PMID 23717063.
- Choi, S. H.; Shin, T. J.; Lee, B. H.; Hwang, S. H.; Kang, J. Y.; Kim, H. J.; Park, C. W.; Nah, S. Y. (2011). "An Edible Gintonin Preparation from Ginseng". Journal of Ginseng Research 35 (4): 471–478. doi:10.5142/jgr.2011.35.4.471. PMID 23717094.
- Hwang, S. H.; Shin, T. J.; Choi, S. H.; Cho, H. J.; Lee, B. H.; Pyo, M. K.; Lee, J. H.; Kang, J. et al. (2012). "Gintonin, newly identified compounds from ginseng, is novel lysophosphatidic acids-protein complexes and activates G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors with high affinity". Molecules and Cells 33 (2): 151–162. doi:10.1007/s10059-012-2216-z. PMID 22286231.
- Hwang SH, Shin EJ, Shin TJ, Lee BH, Choi SH, Kang J, Kim HJ, Kwon SH, Jang CG, Lee JH, Kim HC, Nah SY (2012). "Gintonin, a ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, attenuates Alzheimer's disease-related neuropathies: involvement of non-amyloidogenic processing". Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 31 (1): 207–223. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120439. PMID 22543851.
- Nah, S. Y. (2012). "Gintonin: A novel ginseng-derived ligand that targets G protein- coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors". Current Drug Targets 13 (13): 1659–64. doi:10.2174/138945012803529947. PMID 23017203.
- Shin, T. J.; Kim, H. J.; Kwon, B. J.; Choi, S. H.; Kim, H. B.; Hwang, S. H.; Lee, B. H.; Lee, S. M. et al. (2012). "Gintonin, a ginseng-derived novel ingredient, evokes long-term potentiation through N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activation: Involvement of LPA receptors". Molecules and Cells 34 (6): 563–72. doi:10.1007/s10059-012-0254-4. PMID 23161173.
- Choi, S. H.; Kim, H. J.; Kim, B. R.; Shin, T. J.; Hwang, S. H.; Lee, B. H.; Lee, S. M.; Rhim, H. et al. (2013). "Gintonin, a ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, potentiates ATP-gated P2X1 receptor channel currents". Molecules and Cells 35 (2): 142–50. doi:10.1007/s10059-013-2293-x. PMID 23456336.
- Choi, S. H.; Lee, B. H.; Hwang, S. H.; Kim, H. J.; Lee, S. M.; Kim, H. C.; Rhim, H. W.; Nah, S. Y. (2013). "Molecular Mechanisms of Large-Conductance Ca2+-Activated Potassium Channel Activation by Ginseng Gintonin". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013: 1–14. doi:10.1155/2013/323709. PMID 23662129.
- Lee, J. H.; Choi, S. H.; Lee, B. H.; Hwang, S. H.; Kim, H. J.; Rhee, J.; Chung, C.; Nah, S. Y. (2013). "Activation of lysophosphatidic acid receptor by gintonin inhibits Kv1.2 channel activity: Involvement of tyrosine kinase and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase α". Neuroscience Letters 548: 143–8. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2013.05.048. PMID 23769686.
- Im, D. S.; Nah, S. Y. (2013). "Yin and Yang of ginseng pharmacology: Ginsenosides vs gintonin". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 34 (11): 1367–73. doi:10.1038/aps.2013.100. PMID 24122014.
- Kim, B. J.; Nam, J. H.; Kim, K. H.; Joo, M.; Ha, T. S.; Weon, K. Y.; Choi, S.; Jun, J. Y. et al. (2014). "Characteristics of Gintonin-Mediated Membrane Depolarization of Pacemaker Activity in Cultured Interstitial Cells of Cajal". Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 34 (3): 873–90. doi:10.1159/000366306. PMID 25199952.
- Sun-Hye Choi, B. H. Lee. Kim HJ, Jung SW, Kim HS, Shin HC, Lee JH, Kim HC, Rhim H, Hwang SH, Ha TS, Kim HJ, Cho H, Nah SY (2014). "Ginseng Gintonin Activates the Human Cardiac Delayed Rectifier K+ Channel: Involvement of Ca2+/Calmodulin Binding Sites". Molecules and Cells 37 (9): 656–63. doi:10.14348/molcells.2014.0087. PMID 25234465.
- Hwang, SH; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Jung, SW; Kim, HS; Shin, HC; Park, HJ; Park, KH et al. (2015). "Gintonin, a novel ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, stimulates neurotransmitter release". Neuroscience Letters 584: 356–61. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2014.11.007. PMID 25445364.
- Park, H; Kim, s; Rhee, J; Kim, HJ; Han, JS; Nah, SY; Chung, C (2015). "Synaptic enhancement induced by gintonin via lysophosphatidic acid receptor activation in central synapses". Journal of Neurophysiology 113 (5): 1493–500. doi:10.1152/jn.00667.2014. PMID 25505112.
- Choi, SH; Hong, MK; Kim, HJ; Ryoo, N; Rhim, H; Nah, SY; Kang, LW (2015). "Structure of ginseng major latex-like protein 151 and its proposed lysophosphatidic acid-binding mechanism". Acta Crystallographica Section D 71 (pt5): 1039–50. doi:10.1107/S139900471500259X. PMID 25945569.
- Kim, H; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Kim, HJ; Jung, SW; Hwang, SH; Rhim, H; Kim, HC et al. (2015). "Gintonin stimulates gliotransmitter release in cortical primary astrocytes". Neuroscience Letters 603: 19–24. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.07.012. PMID 26191656.
- Kim, HJ; Shin, EJ; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Jung, SW; Cho, IH; Hwang, SH; Kim, JY et al. (2015). "Oral Administration of Gintonin Attenuates Cholinergic Impairments by Scopolamine, Amyloid-β Protein, and Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease". Molecules and Cells 38 (9): 796–805. doi:10.14348/molcells.2015.0116. PMID 26255830.
- Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Kim, HJ; Jung, SW; Kim, H; Shin, HC; Lee, JH; Hwang, SH et al. (2015). "Preparation of a Monoclonal Antibody against Gintonin and Its Use in an Enzyme Immunoassay". Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 38 (10): 1631–37. doi:10.1248/bpb.b15-00171. PMID 26424022.
- Choi, SH; Jung, SW; Kim, H; Kim, HJ; Lee, BH; Kim, JY; Kim, JH; Hwang, SH et al. (2015). "A Brief method for preparation of gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng". Journal of Ginseng Research 39 (4): 398–405. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2015.05.002. PMID 26869834.
- Kim, HJ; Kim, DJ; Shin, EJ; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Hwang, SH; Rhim, H; Cho, IH et al. (2016). "Effects of gintonin-enriched fraction on hippocampal cell proliferation in wild-type mice and an APPswe/PSEN-1 double Tg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease". Neurochemistry International 101: 56–65. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2016.10.006. PMID 27765516.
- Hwang, SH; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Kim, HJ; Won, KJ; Lee, HM; Rhim, H; Kim, HC et al. (2016). "Effects of gintonin on the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of human umbilical-vein endothelial cells: involvement of lysophosphatidic-acid receptors and vascular-endothelial-growth-factor signaling". Journal of Ginseng Research 40 (4): 325–333. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2015.10.002. PMID 27746684.
- Nah, SY; Kim, KH; Choi, MS; Ha, KS; Lim, DY (2016). "Gintonin facilitates catecholamine secretion from the perfused adrenal medulla". Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 20 (6): 629–639. doi:10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.6.629. PMID 27847440.
- Kim, HJ; Park, SD; Lee, RM; Lee, BH; Choi, SH; Hwang, SH; Rhim, H; Kim, HC et al. (2017). "Gintonin attenuates depressive-like behaviors associated with alcohol withdrawal in mice". J Affect Disord 215: 23–29. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2017.03.026. PMID 28314177.
- Lee, BH; Kim, HK; Jang, M; Kim, HJ; Choi, SH; Hwang, SH; Kim, HC; Rhim, H et al. (2017). "Effects of Gintonin-Enriched Fraction in an Atopic Dermatitis Animal Model: Involvement of Autotaxin Regulation". Biol Pharm Bull 40 (7): 1063–1070. doi:10.1248/bpb.b17-00124. PMID 28674249.
- Lee BH; Kim HK; Jang M; Kim HJ; Choi SH; Hwang SH; Kim HC; Rhim H et al. (2017). "Effects of Gintonin-Enriched Fraction in an Atopic Dermatitis Animal Model: Involvement of Autotaxin Regulation". Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 40 (7): 1063–70. doi:10.1248/bpb.b17-00124. PMID 28674249.
- Moon J; Choi SH; Shim JY; Park HJ; Oh MJ; Kim M; Nah SY (2018). "EGintonin Administration Is Safe and Potentially Beneficial in Cognitively Impaired Elderly". Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 32 (1): 85–87. doi:10.1097/WAD.0000000000000213. PMID 29028648.
- Lee BH; Choi SH; Kim HJ; Park SD; Rhim H; Kim HC; Hwang SH; Nah SY (2018). "Gintonin Absorption in Intestinal Model Systems". J Ginseng Res 42 (1): 35–41. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2016.12.007. PMID 29348720.
- Kim DG; Jang M; Choi SH; Kim HJ; Jhun H; Kim HC; Rhim H; Cho IH et al. (2018). "Gintonin, a Ginseng-Derived Exogenous Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Ligand, Enhances Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Brain Delivery". Int J Biol Macromol 114: 1325–1337. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.158. PMID 29604355.
- Choi JH; Jang M; Oh S; Nah SY; Cho IH (2018). "Multi-Target Protective Effects of Gintonin in 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-Mediated Model of Parkinson's Disease via Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors". Front Pharmacol 9: 515. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00515. PMID 29875659.
- Choi SH; Kim HJ; Cho HJ; Park SD; Lee NE; Hwang SH; Cho IH; Hwang H et al. (2019). "Gintonin, a Ginseng-Derived Exogenous Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Ligand, Protects Astrocytes From Hypoxic and Re-oxygenation Stresses Through Stimulation of Astrocytic Glycogenolysis". Mol Neurobiol 56 (5): 3280–3294. doi:10.1007/s12035-018-1308-1. PMID 30117105.
- Nam SM; Hwang H; Seo M; Chang BJ; Kim HJ; Choi SH; Rhim H; Kim HC et al. (2018). "Gintonin Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Hippocampal Senescence by Improving Long-Term Hippocampal Potentiation, Neurogenesis, and Cognitive Functionss". Gerontology 64 (6): 562–575. doi:10.1159/000491113. PMID 30138913.
- Kim HJ; Jung SW; Kim SY; Cho IH; Kim HC; Rhim H; Kim M; Nah SY (2018). "Panax Ginseng as an Adjuvant Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease". J Ginseng Res 42 (4): 401–411. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2017.12.008. PMID 30337800.
- Jo MG; Ikram M; Jo MH; Yoo L; Chung KC; Nah SY; Hwang H; Rhim H et al. (2019). "Gintonin Mitigates MPTP-Induced Loss of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons and Accumulation of α-Synuclein via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway". Mol Neurobiol 56 (1): 39–55. doi:10.1007/s12035-018-1020-1. PMID 29675576.
- Irfan M; Jeong D; Saba E; Kwon HW; Shin JH; Jeon BR; Kim S; Kim SD et al. (2019). "Gintonin Modulates Platelet Function and Inhibits Thrombus Formation via Impaired Glycoprotein VI Signaling". Platelets 30 (5): 589–598. doi:10.1080/09537104.2018.1479033. PMID 29870296.
- Jang M; Choi JH; Chang Y; Lee SJ; Nah SY; Cho IH (2019). "Gintonin, a Ginseng-Derived Ingredient, as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Huntington's Disease: Activation of the Nrf2 Pathway Through Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors". Brain Behav Immun 80: 146–162. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2019.03.001. PMID 30853569.
- Cho HJ; Choi SH; Kim HJ; Lee BH; Rhim H; Kim HC; Hwang SH; Nah SY (2019). "Bioactive Lipids in Gintonin-Enriched Fraction From Ginseng". J Ginseng Res 43 (2): 209–217. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2017.11.006. PMID 30962735.
- Choi SH; Kim HJ; Cho HJ; Park SD; Lee NE; Hwang SH; Rhim H; Kim HC et al. (2019). "Gintonin-mediated Release of Astrocytic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Protects Cortical Astrocytes From Hypoxia-Induced Cell Damages". J Ginseng Res 43 (2): 305–311. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2018.05.006. PMID 30976168.
- Mijan MA; Kim JY; Moon SY; Choi SH; Nah SY; Yang HJ (2019). "Gintonin Enhances Proliferation, Late Stage Differentiation, and Cell Survival From Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress of Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells". Front Pharmacol 10: 1211. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01211. PMID 31680979.
- Lee R; Lee NE; Hwang H; Rhim H; Cho IH; Nah SY (2019). "Ginseng Gintonin Enhances Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen Release From Human Dermal Fibroblasts Through Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Interaction". Molecules 24 (24): 4438. doi:10.3390/molecules24244438. PMID 31817172.
- Kim HJ; Choi SH; Lee NE; Cho HJ; Rhim H; Kim HC; Hwang SH; Nah SY (2020). "Effects of Gintonin-Enriched Fraction on Methylmercury-Induced Neurotoxicity and Organ Methylmercury Elimination". Int J Environ Res Public Health 17 (3): 838. doi:10.3390/ijerph17030838. PMID 32013120.
- Lee NE; Park SD; Hwang H; Choi SH; Lee RM; Nam SM; Choi JH; Rhim H et al. (2020). "Effects of a Gintonin-Enriched Fraction on Hair Growth: An in vitro and in vivo Study". J Ginseng Res 44 (1): 168–177. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.013. PMID 32095099.
- Chei S; Song JH; Oh HJ; Lee K; Jin H; Choi SH; Nah SY; Lee BY (2020). "Gintonin-Enriched Fraction Suppresses Heat Stress-Induced Inflammation Through LPA Recepto". Molecules 25 (5): 1019. doi:10.3390/molecules25051019. PMID 32106493.
- Cho YJ; Choi SH; Lee R; Hwang H; Rhim H; Cho IH; Kim HC; Lee JI et al. (2020). "Ginseng Gintonin Contains Ligands for GPR40 and GPR55". Molecules 25 (5): 1102. doi:10.3390/molecules25051102. PMID 32121640.
- Nam SM; Choi SH; Cho HJ; Seo JS; Choi M; Nahm SS; Chang BJ; Nah SY (2020). "Ginseng Gintonin Attenuates Lead-Induced Rat Cerebellar Impairments During Gestation and Lactation". Biomolecules 10 (3): 385. doi:10.3390/biom10030385. PMID 32131481.
- Rahman MA; Hwang H; Nah SY; Rhim H (2020). "Gintonin Stimulates Autophagic Flux in Primary Cortical Astrocytes". J Ginseng Res 44 (1): 67–78. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2018.08.004. PMID 32148391.
 |
