Biology:Rhadinorhynchidae
| Rhadinorhynchidae | |
|---|---|
| |
| Rhadinorhynchus oligospinosus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Acanthocephala |
| Class: | Palaeacanthocephala |
| Order: | Echinorhynchida |
| Family: | Rhadinorhynchidae Travassos, 1923 |
Rhadinorhynchidae[1] is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.
Species
Rhadinorhynchidae has 4 subfamilies (Golvanacanthinae, Gorgorhynchinae, Rhadinorhynchinae, and Serrasentoidinae) and the following species:[2][lower-alpha 1]
Golvanacanthinae Paggi and Orecchia, 1972
Golvanacanthus Paggi and Orecchia, 1972
- Golvanacanthus blennii Paggi and Orecchia, 1972
Gorgorhynchinae Van Cleave & Lincicome, 1940
Australorhynchus Lebedev, 1967
- Australorhynchus tetramorphacanthus Lebedev, 1967
Cleaveius Subrahmanian, 1927
- Cleaveius circumspinifer Subrahmanian, 1927
- Cleaveius clupei (Gupta & Sinha, 1992)
- Cleaveius durdanae Kumar, 1992
- Cleaveius fotedari (Gupta & Naqvi, 1980)
- Cleaveius inglisi (Gupta & Fatma, 1987)
- Cleaveius leiognathi Jain & Gupta, 1979
- Cleaveius longirostris Moravec and Sey, 1989
- Cleaveius mysti (Sahay and Sinha, 1971)
- Cleaveius portblairensis Jain & Gupta, 1979
- Cleaveius prashadi (Datta, 1940)
- Cleaveius puriensis (Gupta & Sinha, 1992)
- Cleaveius secundus (Tripathi, 1959)
- Cleaveius singhai (Gupta & Fatma, 1987)
- Cleaveius thapari (Gupta & Naqvi, 1980)
Edmondsacanthus Smales, 2009
- Edmondsacanthus blairi Smales, 2009
Gorgorhynchus Chandler, 1934
- Gorgorhynchus celebesensis (Yamaguti, 1954)
- Gorgorhynchus clavatus Van Cleave, 1940
- Gorgorhynchus lepidus Van Cleave, 1940
- Gorgorhynchus medius (Linton, 1908) Chandler, 1934
- Gorgorhynchus nemipteri Parukhin, 1973
- Gorgorhynchus occultus Smales, Barton, and Chisholm[3]
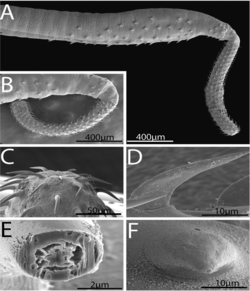
G. occultus has been found parasitising the Cobbler wobbegong (Sutorectus tentaculatus) in Bunbury, Western Australia. The proboscis of this worm has 18 to 20 rows of 8 or 9 hooks followed by a well-developed neck. The body contains irregular circles of small spines in a single anterior portion. The male reproductive system limited to the posterior quarter of the trunk. There are three cement glands.[3]
- Gorgorhynchus ophiocephali Furtado & Lau, 1971
- Gorgorhynchus polymixiae Kovalenko, 1981
- Gorgorhynchus robertdollfusi Golvan, 1956
- Gorgorhynchus satoi Morisita, 1937
- Gorgorhynchus tonkinensis Amin & Ha, 2011
- Gorgorhynchus trachinotus Noronha, Vicente, Pinto & Fábio, 1986
Leptorhynchoides Kostylev, 1924
- Leptorhynchoides acanthidion Steinauer & Nickol, 2015
- Leptorhynchoides aphredoderi Buckner & Buckner, 1976
- Leptorhynchoides apoglyphicus Steinauer & Nickol, 2015
- Leptorhynchoides atlanteus Steinauer & Nickol, 2015
- Leptorhynchoides macrorchis Steinauer & Nickol, 2015
- Leptorhynchoides nebularosis Steinauer & Nickol, 2015
- Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus (Westrum, 1821)
- Leptorhynchoides polycristatus Amin, Heckmann, Halajian, El-Naggar & Tavakol, 2013
- Leptorhynchoides seminolus Steinauer & Nickol, 2015
- Leptorhynchoides thecatus (Linton, 1891) Kostylev, 1924
Metacanthocephaloides Yamaguti, 1959
- Metacanthocephaloides zebrini Yamaguti, 1959
Metacanthocephalus Yamaguti, 1959
- Metacanthocephalus campbelli (Leiper & Atkinson, 1914)
- Metacanthocephalus dalmori Zdzitowiecki, 1983
- Metacanthocephalus johnstoni Zdzitowiecki, 1983
- Metacanthocephalus ovicephalus (Zhukov, 1963)
- Metacanthocephalus pleuronichthydis Yamaguti, 1959
- Metacanthocephalus rennicki (Leiper & Atkinson, 1914)
Micracanthorhynchina Strand, 1936
- Micracanthorhynchina atherinomori Smales, 2014
- Micracanthorhynchina chandrai Bhattacharya, 2007
- Micracanthorhynchina cynoglossi Wang, 1980
- Micracanthorhynchina dakusuiensis (Harada, 1938)
- Micracanthorhynchina golvani Gupta & Sinha, 1992
- Micracanthorhynchina hemiculturus Demshin, 1965
- Micracanthorhynchina hemirhamphi (Baylis, 1944)
- Micracanthorhynchina indica Farooqi, 1980
- Micracanthorhynchina kuwaitensis Amin & Sey, 1996
- Micracanthorhynchina lateolabracis Wang, 1980
- Micracanthorhynchina motomurai (Harada, 1935)
- Micracanthorhynchina segmentata (Yamaguti, 1959)
Paracanthorhynchus Edmonds, 1967
- Paracanthorhynchus galaxiasus Edmonds, 1967
Pseudauchen Yamaguti, 1963
- Pseudauchen epinepheli (Yamaguti, 1939)
Pseudoleptorhynchoides Salgado-Maldonado, 1976
- Pseudoleptorhynchoides lamothei Salgado-Maldonado, 1976
Rhadinorhynchinae Lühe, 1912
File:Parasite140083-fig5 Figs 31-36 Cathayacanthus spinitruncatus.tif Cathayacanthus Golvan, 1969
- Cathayacanthus bagarii Moravec and Sey, 1989
- Cathayacanthus exilis (Van Cleave, 1928)
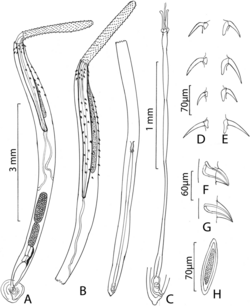
- Cathayacanthus spinitruncatus Amin, Heckmann & Ha, 2014[5][6]
Megistacantha Golvan, 1960
- Megistacantha horridum (Lühe, 1912)
- Megistacantha sanghaensis Kvach, Jirků & Scholz, 2016[7]
Paragorgorhynchus Golvan, 1957
- Paragorgorhynchus albertianus Golvan, 1957
- Paragorgorhynchus chariensis Troncy, 1970
Pseudogorgorhynchus Moravec, Wolter & Korting, 2000
- Pseudogorgorhynchus arii Moravec, Wolter & Korting, 2000
Raorhynchus Tripathi, 1959
- Raorhynchus cadenati Gupta & Sinha, 1992
- Raorhynchus guptai Gupta & Kumar, 1987
- Raorhynchus inexspectatus Golvan, 1969
- Raorhynchus megalaspisi Wang, Wang and Wu, 1993
- Raorhynchus mayeri (Heinz, 1934)
- Raorhynchus polynemi Tripathi, 1959
- Raorhynchus schmidti George & Nadakal, 1978
- Raorhynchus terebra Rudolphi, 1819
- Raorhynchus thapari Gupta & Fatma, 1981
Rhadinorhynchus Lühe, 1911
- Rhadinorhynchus africanus (Golvan, Houin and Deltour, 1963)
- Rhadinorhynchus atheri (Farooqui, 1981)
- Rhadinorhynchus bicircumspinis Hooper, 1983
- Rhadinorhynchus biformis Smales, 2014
- Rhadinorhynchus cadenati (Golvan & Houin, 1964)
- Rhadinorhynchus camerounensis Golvan, 1969
- Rhadinorhynchus capensis Bray, 1974
- Rhadinorhynchus carangis Yamaguti, 1939
- Rhadinorhynchus chongmingnensis Huang, Zheng, Deng, Fan and Ni, 1988
- Rhadinorhynchus cololabis Laurs & McCauley, 1964
- Rhadinorhynchus decapteri (Braicovich, Lanfranchi, Farber, Marvaldi, Luque and Timi, 2014)[8] [lower-alpha 2]
R. decapteri is a parasite of the marine fish Round scad (Decapterus punctatus) and is found coastal waters of Brazil . It has 10 longitudinal rows of 22–26 hooks. The species name decapteri was derived from the genus (Decapterus) of the type host.[8]
- Rhadinorhynchus ditrematus Yamaguti, 1939
- Rhadinorhynchus dollfusi Gupta & Fatma, 1987
- Rhadinorhynchus dorsoventrospinosus Amin, Heckmann & Há, 2011
- Rhadinorhynchus dujardini Golvan, 1969
- Rhadinorhynchus echeneisi Gupta and Gupta, 1980
- Rhadinorhynchus erumeii (Gupta & Fatma, 1981)
- Rhadinorhynchus ganapatii Chandra, Hanumantha-Rao & Shyamasundari, 1985
- Rhadinorhynchus hiansi Soota & Bhattacharya, 1981
- Rhadinorhynchus japonicus Fujita, 1920
- Rhadinorhynchus johnstoni Golvan, 1969
- Rhadinorhynchus keralensis Gupta & Fatma, 1987
- Rhadinorhynchus laterospinosus Amin, Heckmann & Há, 2011[11]
- Rhadinorhynchus lintoni Cable & Linderoth, 1963
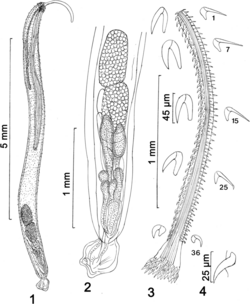
- Rhadinorhynchus oligospinosus Amin & Heckmann, 2017[12]
- Rhadinorhynchus mariserpentis (Steinauer, Garcia-Vedrenne, Weinstein & Kuris, 2019)[lower-alpha 3]
R. mariserpentis parasitizes the Oarfish, Regalecus russelii and has been collected near Wakamatsu-ku, Kitakyūshū, Japan .
- Rhadinorhynchus ornatus Van Cleave, 1918
- Rhadinorhynchus pelamysi Gupta & Gupta, 1980
- Rhadinorhynchus pichelinae Smales, 2014
- Rhadinorhynchus plagioscionis Thatcher, 1980
- Rhadinorhynchus plotosi Parukhin, 1985
- Rhadinorhynchus polydactyli Smales, 2014
- Rhadinorhynchus polynemi Gupta & Lata, 1967
- Rhadinorhynchus pomatomi Smales, 2014
- Rhadinorhynchus pristis (Rudolphi, 1802)
- Rhadinorhynchus saltatrix Troncy & Vassiliades, 1973
- Rhadinorhynchus selkirki Van Cleave, 1921
- Rhadinorhynchus seriolae (Yamaguti, 1963)
- Rhadinorhynchus stunkardii Gupta & Fatma, 1987
- Rhadinorhynchus trachuri Harada, 1935
R. trachuri is one of the most widespread acanthocephalans infesting fish from the Eastern Pacific, Western Pacific, and Indian Oceans. On the South pacific coast of Vietnam, it was found infesting the Frigate tuna (Auxis thazard), and the Torpedo scad (Megalaspis cordyla).[13]
- Rhadinorhynchus trivandricus George & Nadkal, 1978
- Rhadinorhynchus vancleavei Golvan, 1969
- Rhadinorhynchus zhukovi Golvan, 1969
Slendrorhynchus Amin & Sey, 1996
- Slendrorhynchus breviclaviproboscis Amin & Sey, 1996
Serrasentoidinae Parukhin, 1982
Serrasentoides Parukhin, 1971
- Serrasentoides fistulariae Parukhin, 1971
Hosts
Rhadinorhynchidae species parasitize fish hosts.
- Hosts for Rhadinorhynchidae species
The Round scad is a host of Rhadinorhynchus decapteri
The oarfish Regalecus russelii is a host of Rhadinorhynchus mariserpentis
Notes
- ↑ A binomial authority in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than the present genus.
- ↑ Gymnorhadinorhynchus decapteri was combined with Rhadinorhynchus decapteri based on genetic analysis.[10] The original family and genus names are a combination of the Greek word gymnos (naked) and Rhadinorhynchidae/Rhadinorhynchus, a family/genus of similar morphology, but lacking somatic spines.[8] A phylogenetic analysis had been conducted to confirm that Gymnorhadinorhynchus is a well supported clade within the monophyletic order Echinorhynchida[8] but the new analysis superseded this one. Previously, Gymnorhadinorhynchidae can be distinguished from other families of Echinorhynchida by the combination of the following morphological characteristics: a cylindrical proboscis with longitudinal row of hooks, basal circle of hooks larger than anterior hooks, an absence of trunk spines, asymmetry of hook shape, four cement glands, and a spineless trunk.[9]
- ↑ Genetic analysis resulted in the move of Gymnorhadinorhynchus mariserpentis to the genus Rhadinorhynchus[10]
References
- ↑ Van Cleave, Harley J.; Lincicome, David R. (1940). "A Reconsideration of the Acanthocephalan Family Rhadinorhynchidae". Journal of Parasitology 26 (1): 75. doi:10.2307/3272266. ISSN 0022-3395.
- ↑ "ITIS - Report: Rhadinorhynchidae". https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=64319#null.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Smales, L.R., Barton, D.P. & Chisholm, L.A. Acanthocephalans from Australian elasmobranchs (Chondrichthyes) with a description of a new species in the genus Gorgorhynchus Chandler, 1934 (Rhadinorhynchidae). Syst Parasitol 96, 565–573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09871-x
- ↑ Amin, O. A, Heckmann, R. A & Ha, N. V. (2014) Acanthocephalans from fishes and amphibians in Vietnam, with descriptions of five new species. Parasite, 21, 53 doi:10.1051/parasite/2014052PMID 25331738

- ↑ Amin, Omar Mohamed; Heckmann, Richard Anderson; Ha, Nguyen Van (2014). "Acanthocephalans from fishes and amphibians in Vietnam, with descriptions of five new species". Parasite 21: 53. doi:10.1051/parasite/2014052. ISSN 1776-1042. PMID 25331738.

- ↑ Van Ha, Nguyen; Amin, Omar M.; Ngo, Ha Duy; Heckmann, Richard A. (2018). "Descriptions of acanthocephalans, Cathayacanthus spinitruncatus (Rhadinorhynchidae) male and Pararhadinorhynchus magnus n. sp. (Diplosentidae), from marine fish of Vietnam, with notes on Heterosentis holospinus (Arhythmacanthidae)". Parasite 25: 35. doi:10.1051/parasite/2018032. ISSN 1776-1042. PMID 30040609.

- ↑ Kvach Y.; Jirků M.; Scholz T. (2016). "Acanthocephalans of the genus Megistacantha Golvan, 1960 (Palaeacanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) in two African mormyrid fishes (Actinopterygii: Mormyridae)". Systematic Parasitology 93 (9): 927–933. doi:10.1007/s11230-016-9672-6. PMID 27743240.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Braicovich, P. E., Lanfranchi, A. L., Farber, M. D., Marvaldi, A. E., Luque, J. L. & Timi, J. T. (2014). Genetic and morphological evidence reveals the existence of a new family, genus and species of Echinorhynchida (Acanthocephala). Folia Parasitologica, 61(4), 377–384.url=https://ri.conicet.gov.ar/bitstream/handle/11336/32227/CONICET_Digital_Nro.b0fcac17-fd1e-44a2-b39d-2aa43e46a71c_A.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Steinauer, M. L., Garcia-Vedrenne, A. E., Weinstein, S. B., & Kuris, A. M. (2019). Acanthocephalan parasites of the oarfish, Regalecus russelii (Regalecidae), with a description of a new species of Gymnorhadinorhynchus (Acanthocephala: Gymnorhadinorhynchidae). Journal of Parasitology, 105(1), 124-132. url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331146734_Acanthocephalan_Parasites_of_the_Oarfish_Regalecus_russelii_Regalecidae_With_A_Description_of_A_New_Species_of_Gymnorhadinorhynchus_Acanthocephala_Gymnorhadinorhynchidae
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecular characterisation of acanthocephalans from Australian marine teleosts: proposal of a new family, synonymy of another and transfer of taxa between orders. Systematic Parasitology, 1-23.
- ↑ Amin, Omar Mohamed; Heckmann, Richard Anderson; Dallarés, Sara; Constenla, María; Ha, Nguyen Van (2019). "Morphological and molecular description of Rhadinorhynchus laterospinosus Amin, Heckmann & Ha, 2011 (Acanthocephala, Rhadinorhynchidae) from marine fish off the Pacific coast of Vietnam". Parasite 26: 14. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019015. ISSN 1776-1042. PMID 30838975.

- ↑ Amin, Omar M.; Heckmann, Richard A. (2017). "Rhadinorhynchus oligospinosus n. sp. (Acanthocephala, Rhadinorhynchidae) from mackerels in the Pacific Ocean off Peru and related rhadinorhynchids in the Pacific, with notes on metal analysis". Parasite 24: 19. doi:10.1051/parasite/2017022. ISSN 1776-1042. PMID 28593837.

- ↑ Amin, O.M. Redescription of Rhadinorhynchus trachuri Harada, 1935 (Acanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) from Marine Fish in Vietnam and California with a Discussion of its Zoogeography. Acta Parasit. (2019). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-019-00130-z
Wikidata ☰ Q2446824 entry
 |