Biology:Hakea falcata
| Sickle hakea | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Hakea |
| Species: | H. falcata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hakea falcata | |
| |
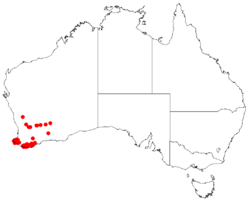
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Hakea falcata, commonly known as sickle hakea,[2] is a shrub in the family Proteacea and is endemic to southern Western Australia. It has narrow egg-shaped leaves, cream flowers and blooms in spring.
Description
The erect loose non-lignotuberous shrub typically grows to a height of 2 to 4 metres (6.6 to 13.1 ft).[3] The branchlets have a patchy covering of pale rusty-brown coloured hairs. The flat curved evergreen leaves have a linear to narrowly obovate shape with a length of 5 to 14 centimetres (2.0 to 5.5 in) and a width of 3 to 14 millimetres (0.118 to 0.551 in) and have three or rarely four longitudinal veins.[4] It blooms from September to November and produces white-yellow or white-pink flowers.[3] Each solitary inflorescence contains 25 to 40 flowers with a creamy coloured perianth and a cream pistil with a length of 4.5 to 6.5 mm (0.177 to 0.256 in). After flowering an obliquely narrowly ovate, curved and prominently beaked fruit is produced which is 2 to 2.5 cm (0.8 to 1.0 in) in length and 7 to 10 mm (0.276 to 0.394 in) wide. The fruit contain narrowly ovate shaped blackish brown seeds with a wing down one side.[4]
Taxonomy and naming
The species was first formally described by the botanist Robert Brown in 1830 as part of the work Supplementum primum prodromi florae Novae Hollandiae.[5][6] The only synonym is Hakea falcata var. falcata as described by Carl Meissner.[7] The specific epithet is taken from the Latin word falcatus meaning curved like a sickle, referring to the shape of the leaves.[4]
Distribution
It is endemic to an area along the coast in the South West and Great Southern regions of Western Australia between around Busselton and Albany and with a small population isolated in the Stirling Range around Cranbrook. It is found in winter wet depressions and other damp areas growing in peaty-sandy or sandy-clay soils.[3] The shrub is often part of the understorey in jarrah forest or open Eucalypt woodland communities.[4]
References
- ↑ "Hakea falcata". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/69996.
- ↑ "Hakea falcata Sickle hakea". Nindethana Australian Seeds. https://www.nindethana.net.au/Product-Detail.aspx?p=3295.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Hakea falcata". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/2159.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Hakea falcata". Electronic flora of South Australia. Government of South Australia. http://www.flora.sa.gov.au/efsa/lucid/Hakea/key/Australian%20Hakea%20species/Media/Html/Hakea_falcata.htm.
- ↑ "Hakea falcata". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/rest/instance/apni/480271.
- ↑ "Proteaceas Novas. Supplementum primum prodromi florae Novae Hollandiae". https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/77294#page/543/mode/1up.
- ↑ "Hakea falcata R.Br.". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/http://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2903588#names.
Wikidata ☰ Q18081281 entry
 |





