Biology:Hakea microcarpa
| Small fruit hakea | |
|---|---|

| |
| Hakea microcarpa leaves and flowers | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Hakea |
| Species: | H. microcarpa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hakea microcarpa R.Br.[1]
| |
| |
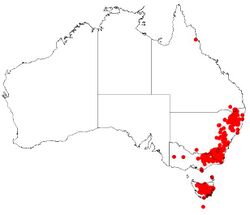
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Hakea microcarpa , commonly known as small-fruit hakea[2] is a flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia . It is a spreading shrub, often growing in woodlands, heathlands and near swamps in montane areas of eastern Australia .
Description
Hakea microcarpa is a shrub growing to 2 m (7 ft) tall but often wider than tall. Its leaves and branches are glabrous except for a few hairs on new growth and which are lost by the time of flowering. The leaves are usually needle-shaped, 3–11 cm (1–4 in) long and about 1.5 mm (0.06 in) wide but sometimes there are a few flat leaves up to 5 mm (0.2 in) wide. The flowers are off-white in colour and are arranged in groups of ten to forty in the leaf axils. The stalk of each flower is 2–5 mm (0.08–0.2 in) long and the perianth is 2.5–3.5 mm (0.098–0.14 in) long. Flowering occurs from September to February and is followed by the fruit which is a woody follicle containing two winged seeds. The follicle is oblong in shape, about 16 mm (0.6 in) long and 7 mm (0.3 in) wide with a small point 2–3 mm (0.08–0.1 in) long on each of the two sides.[2][3][4]
Taxonomy and naming
Hakea microcarpa was first formally described in 1810 by Robert Brown and the description was published in Transactions of the Linnean Society of London.[5][6] The specific epithet (microcarpa) is a derived from the ancient Greek words mikros (μικρός) meaning "small" and karpos (καρπός) meaning "fruit",[7] referring to the small fruit.[4][8]
Distribution and habitat
Small-fruited hakea grows on the east coast and ranges of Australia from Stanthorpe to Tasmania where it grows in subalpine bogs, or in forest or woodland in damp sites.[2][3][4]
Polblue Swamp, Barrington Tops State Conservation Area, Australia
References
- ↑ "Hakea microcarpa". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/96993.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Hakea microcarpa". Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria: VicFlora. https://vicflora.rbg.vic.gov.au/flora/taxon/d37dff54-0906-4c29-a6d8-2cc90ba6b3fb.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Hakea microcarpa". Plant Net NSW Flora Online. NSW Government. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=sp&name=Hakea~microcarpa.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Hakea microcarpa". State herbarium of South Australia. http://www.flora.sa.gov.au/efsa/lucid/Hakea/key/Australian%20Hakea%20species/Media/Html/Hakea_microcarpa.htm.
- ↑ "Hakea microcarpa". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/521892.
- ↑ "Transactions of the Linnean Society of London". https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/757212#page/190/mode/1up.
- ↑ Backer, C.A. (1936). Verklarend woordenboek der wetenschappelijke namen van de in Nederland en Nederlandsch-Indië in het wild groeiende en in tuinen en parken gekweekte varens en hoogere planten (Edition Nicoline van der Sijs).
- ↑ Holliday, Ivan (2005). Hakeas a Field and Garden Guide. Reed New Holland. ISBN 1-877069-14-0.
Wikidata ☰ Q5640395 entry
 |




