Biology:In vitro recombination
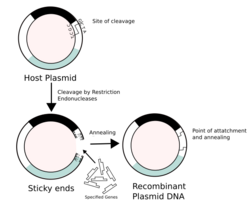
Recombinant DNA (rDNA), or molecular cloning, is the process by which a single gene, or segment of DNA, is isolated and amplified. Recombinant DNA is also known as in vitro recombination. A cloning vector is a DNA molecule that carries foreign DNA into a host cell, where it replicates, producing many copies of itself along with the foreign DNA. There are many types of cloning vectors such as plasmids and phages. In order to carry out recombination between vector and the foreign DNA, it is necessary the vector and DNA to be cloned by digestion, ligase the foreign DNA into the vector with the enzyme DNA ligase. And DNA is inserted by introducing the DNA into bacteria cells by transformation.
Steps
Preparation of foreign DNA
There are two major sources of foreign DNA for molecular cloning is genomic DNA (gDNA) and complementary (or copy) DNA (cDNA). cDNA molecules are DNA copies of mRNA molecules, produced in vitro by action of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. In order to obtain the cDNA for a specific gene, it is first necessary to construct a cDNA library.
Fragmenting gDNA
The DNA of interest needs to be fragmented to provide a relevant DNA segment of suitable size. Preparation of DNA fragments for cloning is achieved by means of PCR, but it may also be accomplished by restriction enzyme digestion and fractionation by gel electrophoresis.
Preparing cDNA libraries
To prepare a cDNA library, the first step is to isolate the total mRNA from the cell type of interest. Then, the enzyme reverse transcriptase is used to generate cDNAs. Reverse transcriptase is a RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. It depends on the presence of a primer, usually a poly-dT oligonucleotide, to prime DNA synthesis. DNA polymerase can use these single–stranded primers to initiate second strand DNA synthesis on the mRNA templates. After the single-stranded DNA molecules are converted into double-stranded DNA molecules by DNA polymerase, they are inserted into vectors and cloned. To do this, the cDNA are frequently methylated with a specific methyl transferase. These synthetic oligonucleotides can either be “linkers”, the overhangs are generated by digestion with the appropriate restriction enzyme.
Plasmid Vector
Recombinant DNA vectors function as carriers of the foreign DNA. Plasmids are small, closed-circular DNA molecules that exist from the chromosomes of their host. Their replication is to be under stringent control (low copy number) or relaxed (high copy number). The restriction sites, called the multiple cloning site or polylinker, give a wide choice of restriction site for use in the cloning step.
References
Mark F. Wiser,"Lecture Notes for Methods in Cell Biology
 |