Biology:Interpeduncular fossa
| Interpeduncular fossa | |
|---|---|
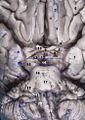
 Base of brain | |
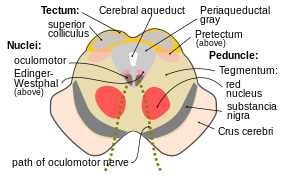 Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve (interpeduncular fossa not labeled, but visible at bottom center) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa interpeduncularis |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression[1] of the ventral surface of the midbrain[2]: 456 between the two crura cerebri.[2]: 456 [3]
It has been found in humans and macaques, but not in rats or mice, showing that this is a relatively new evolutionary region.[4]
Anatomy
The interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain.[5]
Features
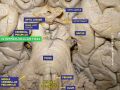
The lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa bears a groove - the oculomotor sulcus - from which[6] rootlets of the oculomotor nerve emerge from the substance of the brainstem[6][2]: 456 and aggregate into a single fascicle.[2]: 456
Anatomical relations
The ventral tegmental area lies at the depth of the interpeduncular fossa.[2]: 459
Boundaries
The interpeduncular fossa is in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles.[5]
The floor of interpeduncular fossa, from behind forward,[citation needed] are the posterior perforated substance,[1] corpora mamillaria, tuber cinereum, infundibulum, and pituitary gland.[citation needed]
Contents
Contents of interpeduncular fossa include oculomotor nerve, and circle of Willis.[citation needed]
The basal veins pass alongside the interpeduncular fossa before joining the great cerebral vein.[2]: 422
Clinical significance
The most common locations for neurocutaneous melanosis have occurred along the interpeduncular fossa, ventral brainstem, upper cervical cord, and ventral lumbosacral cord.[7]
See also
- Interpeduncular cistern
- Cerebral peduncles
Additional images
-
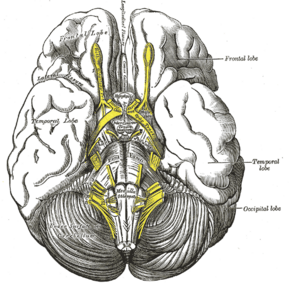
Human brainstem anterior view
-
Interpeduncular fossa. Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "fossa interpeduncularis". https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/fossa+interpeduncularis.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Susan Standring (42nd ed.). [New York]. 2021. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1201341621.
- ↑ Basinger, Hayden; Hogg, Jeffery P. (2022), "Neuroanatomy, Brainstem", StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing), PMID 31335017, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544297/, retrieved 2022-08-08
- ↑ "BrainInfo". http://braininfo.rprc.washington.edu/centraldirectory.aspx?ID=489.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Interpeduncular fossa" (in en). https://www.imaios.com/en/e-Anatomy/Anatomical-Parts/Interpeduncular-fossa.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "sulcus of the oculomotor nerve". https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/sulcus+of+the+oculomotor+nerve.
- ↑ Islam, Monica P. (2015). "Neurocutaneous melanosis". Neurocutaneous Syndromes. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 132. pp. 111–7. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62702-5.00007-X. ISBN 978-0-444-62702-5.
External links
 |