Biology:Leucopogon fraseri
| Leucopogon fraseri | |
|---|---|

| |
| Near Adaminaby | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Leucopogon |
| Species: | L. fraseri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Leucopogon fraseri A.Cunn.[1]
| |
| |
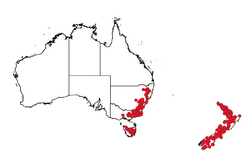
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Styphelia fraseri (A.Cunn.) F.Muell. nom. illeg. | |
Leucopogon fraseri is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is native to south-eastern continental Australia and New Zealand, where it is known as Styphelia nesophila, pātōtara, or dwarf mingimingi.[2] It is a prickly, prostrate to trailing or low-growing shrub with egg-shaped leaves, and erect, tube-shaped white flowers usually arranged singly in leaf axils.
Description
Leucopogon fraseri is a prickly, prostrate to trailing, low-growing shrub that typically grows to a height of up to 30 cm (12 in) and has bristly branchlets. Its leaves are egg-shaped to lance-shaped with the narrower end towards the base, 3–8 mm (0.12–0.31 in) long and 1–2.5 mm (0.039–0.098 in) wide. The leaves are glabrous, pale-edged, and have a thin, sharp point up to 1.5 mm (0.059 in) long on the tip. The flowers are usually arranged singly in leaf axils on a peduncle about 1 mm (0.039 in) long, with bracteoles 1.1–1.8 mm (0.043–0.071 in) long at the base. The sepals are 2.5–3.9 mm (0.098–0.154 in) long, the petals forming a tube 4–5 mm (0.16–0.20 in) long and hairy inside, the petal lobes 2.0–3.4 mm (0.079–0.134 in) long. Flowering occurs from August to October and the fruit is a glabrous, yellow, egg-shaped to elliptic drupe 4.7–5.3 mm (0.19–0.21 in) long.[2][3][4]
Taxonomy
Leucopogon fraseri was first formally described in 1838 by Allan Cunningham in the journal, Annals of Natural History from a specimen found in 1820, "among ferns on the hills near the Bay of Islands" by Charles Fraser.[5][6]
Distribution and habitat
This leucopogon grows in forest, shrubland and heath, often in poorly-drained or sandy soils or among rocks, and usually occurs at an altitude of above about 500 m (1,600 ft). It is found on the tablelands of northern and southern New South Wales, in eastern Victoria, on the Central Plateau of Tasmania, and in New Zealand.[2][3][4]
Conservation status
Leucopogon fraseri is listed as "not threatened" in New Zealand.[2]
Ecology
The fleshy fruits are dispersed by frugivory.[7]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Leucopogon fraseri. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Leucopogon fraseri". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/239860. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Leucopogon fraseri" (in en). https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/flora/species/leucopogon-fraseri/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Powell, Jocelyn M. (1992). "Leucopogon fraseri". Plantnet - Flora Online. NSW Government. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=in&name=Leucopogon~fraseri.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Powell, Jocelyn M.; Walsh, Neville G.; Brown, Elizabeth A.. "Styphelia nesophila". Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria. https://vicflora.rbg.vic.gov.au/flora/taxon/19c82d92-1dd3-4de4-ae9b-03107c8eace3.
- ↑ Cunningham, Allan (1838). "Florae insularum Novae Zelandiae precursor.". Annals of Natural History 2 (7): 47–48. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/42901110#page/59/mode/1up. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ↑ "Leucopogon fraseri". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/752247. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
- ↑ Thorsen, M.J.; Dickinson, K.J.M.; Seddon, P.J. (2009). "Seed dispersal systems in the New Zealand flora". Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics 11 (4): 285–309. doi:10.1016/j.ppees.2009.06.001. ISSN 1433-8319.
Wikidata ☰ Q17242160 entry
 |


