Biology:Leucopogon malayanus
| Leucopogon malayanus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Leucopogon |
| Species: | L. malayanus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Leucopogon malayanus | |
| |
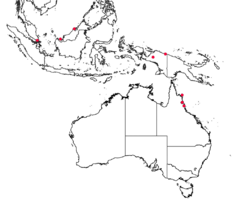
| Occurrence data from GBIF | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Leucopogon malayanum Jack orth. var. | |
Leucopogon malayanus is a plant in the family Ericaceae native to Cambodia, Malaya, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.[4] However occurrence data from GBIF,[5] shows it occurring in Queensland (Australia), Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei and India. It was first described by William Jack in 1820, who "found (it) abundantly at Singapore".[1][2]
There are two subspecies:
- Leucopogon malayanus subsp. novoguineensis (Sleumer) Pedley[6][7]
- Leucopogon malayanus subsp. malayanus
Description
Leucopogon malayanus subsp. novoguineensis
This plant is usually found as a small multistemmed windswept tree but also occurs as a shrub. The leaves may be stalked or without stalks and vary considerably in size (40-120 mm by 8-20 mm). There are about 8-12 parallel leaf veins but no obvious midrib. The flowers occur in spikes and the calyx lobes are about 2 by 1.9 mm and have hairy margins. The stamen filaments are about 1.5 mm long with anthers about 0.6 by 0.2 mm. The ovary has 8-10 locules. The fruits are squashed globules (about 5-6 by 7-9 mm diameter), and the calyx persists at the base. This subspecies is found only in north-east Queensland and New Guinea.[6]
Leucopogon malayanus subsp. malayanus
This subspecies is called Styphelia malayana var. malayana by Hermann Sleumer.[8]
It differs from L. malayanus subsp. novoguineensis in that it does not have the long hairs at the top of the ovary and at the base of the style of L. malayanus subsp. novoguineensis. Additionally, the ranges of the two subspecies do not overlap.[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Leucopogon malayans Jack". Australian Plant Name Index (APNI), IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/rest/name/apni/117488.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Jack, W. (1820). "Descriptions of Malayan Plants No 2". Malayan Miscellanies 1 (5): 20. http://www.sabrizain.org/malaya/library/miscellanies1.pdf.
- ↑ "Leucopogon malayanus Jack". Australian Plant Census (APC). https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/search?product=APC&tree.id=51209179. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ↑ "Leucopogon malayanus Jack | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science". http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:325372-1.
- ↑ Occdownload Gbif.Org (2020), Occurrence Download: Leucopogon malayanus, The Global Biodiversity Information Facility, doi:10.15468/dl.3qcyhz, https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/download/0054831-200221144449610, retrieved 2020-05-05
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Leucopogon malayanus subsp. novoguineensis". Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research (CANBR), Australian Government. 2020. https://apps.lucidcentral.org/rainforest/text/entities/Leucopogon_malayanus_subsp._novoguineensis.htm.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Pedley, L. (1990). "Notes on Leucopogon R.Br. (Epacridaceae) in Queensland". Austrobaileya 3 (2): 265–271.
- ↑ Sleumer, H. (1963). "Florae Malesianae Precursores XXXVII. Materials towards the knowledge of the Epacridaceae mainly in Asia, Malaysia, and the Pacific". Blumea 12 (1): 148–149. https://www.repository.naturalis.nl/document/564934.
Wikidata ☰ Q17241156 entry
 |

