Biology:Mixotoxodon
Mixotoxodon ("mixture Toxodon") is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene epoch, from 1,800,000–12,000 years ago.[1][2]
Description
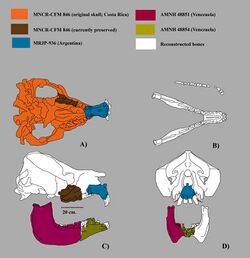

Mixotoxodon is known by fragmentary remains, usually mandible fragments and teeth. Although the general appearance probably was very similar to another toxodontid from the Pleistocene, the better known Toxodon, their fossils shown that the outer borders of the symphysis in the lower jaw don't diverge anteriorly, and the incisors form a semicircular structure that protrude less than the incisors of Toxodon; the snout was cylindrical, instead of the broad hippo-like muzzle of Toxodon. The straight snout and the narrow lower incisors closely packed, suggest that this animal had a different feeding strategy compared to their southern relative, although the teeth of both genera were adapted to deal with abrasive food.[3] It was a rhino-sized animal, a 2012 study estimated a weight of up to 3.8 tonnes (4.2 short tons), which makes it the largest member of Notoungulata,[4] though this may be an overestimate.[5]
Mixotoxodon is known from a single species, M. larensis. Mixotoxodon is the only notoungulate known to have migrated out of South America during the Great American Interchange. Its fossils have been found in northern South America, in Central America,[6][7] in Veracruz and Michoacán, Mexico (with a possible find in Tamaulipas),[8][9][10] and eastern Texas, US.[11] The genus was also one of the last surviving notoungulates, along with related genera such as the better-known Toxodon. The name refers to the fact that Mixotoxodon combines characteristics typical of different toxodontid subfamilies.[12]
Phylogeny
The cladogram below is based in the study published by Analía Forasiepi and colleagues (2014), showing the position of Mixotoxodon inside Toxodontidae:[13]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fossil distribution
This list indicates the countries and places where Mixotoxodon fossils have been found. The list follows Rincón, 2011,[14] unless otherwise indicated:
- North America
- United States
- Harris County, Texas[15]
- Mexico
- Hihuitlán, Michoacán
- La Estribera, Veracruz (Polaco et al., 2004)
- Guatemala
- Santa Amelia River, Petén Department (Woodburne, 1969)
- Honduras
- Yeroconte, Lempira department (Webb and Perrigo, 1984)
- Orillas del Humuya, Comayagua department
- El Salvador
- Tomayate, San Salvador department (Cisneros, 2005)
- Cuscatlán Formation, Barranca del Sisimico, San Vicente department
- Hormiguero, San Miguel department (Webb and Perrigo, 1984)
- Nicaragua
- El Bosque, Estelí department (Leidy, 1886)
- Costa Rica
- Bajo de los Barrantes, Alajuela province (Laurito, 1993; Valerio, 1939; Spencer et al., 1997)
- Panama
- Ocú, Herrera Province (Gazin, 1956)
- South America
- Colombia
- Rotinet Formation, Chívolo, Magdalena (De Porta 1959; Villarroel and Clavijo, 2005)
- Venezuela
- Mene de Inciarte, Zulia (Rincón, 2011)
- Quebrada Ocando, Falcón State (Bocquentin-Villanueva, 1984)
- Muaco, Falcón State (Royo y Gómez, 1960, Bocquentin-Villanueva, 1979)
- Cerro Misión, Falcón State (Rincón, 2004)
- Zumbador Cave, Falcón State
- Agua Viva del Totumo, Lara State (Karsten, 1886)
- San Miguel, Lara Sate (Van Frank, 1957)
- El Tocuyo, Lara State
- El Breal de Orocual, Monagas State (Rincón et al., 2009)
- Brazil
- Juruá River, Acre State (Paula Couto, 1982; Rancy, 1981)
- Araras/Periquitos, Rondônia
- Bolivia
- Cara Cara, Beni Department (Hoffstetter, 1968)
- Argentina
- Dique Los Quiroga, Santiago del Estero[16]
References
- ↑ Mixotoxodon at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ "NEW REMAINS OF Mixotoxodon larensis Van Frank 1957 (Mammalia: Notoungulata) FROM MENE DE INCIARTE TAR PIT, NORTH-WESTERN VENEZUELA Ascanio D. Rincó". http://www.redalyc.org/pdf/339/33921507005.pdf.
- ↑ Paula-Couto, 1979, p. 404.
- ↑ Elissamburu, 2012, p. 108.
- ↑ Nelson, Allison; Engelman, Russell K.; Croft, Darin A. (September 2023). "How to weigh a fossil mammal? South American notoungulates as a case study for estimating body mass in extinct clades" (in en). Journal of Mammalian Evolution 30 (3): 773–809. doi:10.1007/s10914-023-09669-1. ISSN 1064-7554. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10914-023-09669-1.
- ↑ McKenna & Bell, 1997, p. 461; Cisneros, 2005, p. 246.
- ↑ "NEW REMAINS OF Mixotoxodon larensis Van Frank 1957 (Mammalia: Notoungulata) FROM MENE DE INCIARTE TAR PIT, NORTH-WESTERN VENEZUELA Ascanio D. Rincó". http://www.redalyc.org/pdf/339/33921507005.pdf.
- ↑ Arroyo-Cabrales et al., 2010, pp. 193-194
- ↑ "A New Occurrence of Toxodonts in the Pleistocene of México". https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230820008.
- ↑ Lucas, Spencer G.; Morgan, Gary S.; Spielmann, Justin A.; Prothero, Donald R. (2008-01-01) (in en). Neogene Mammals: Bulletin 44. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. https://books.google.com/books?id=vW_aBwAAQBAJ.
- ↑ Lundelius et al., p. 229.
- ↑ van Frank, 1957, p. 6.
- ↑ Forasiepi, A. A. M.; Cerdeño, E.; Bond, M.; Schmidt, G. I.; Naipauer, M.; Straehl, F. R.; Martinelli, A. N. G.; Garrido, A. C. et al. (2014). "New toxodontid (Notoungulata) from the Early Miocene of Mendoza, Argentina". Paläontologische Zeitschrift 89 (3): 611–634. doi:10.1007/s12542-014-0233-5. http://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/handle/10915/127531.
- ↑ Rincón 2011, p. 896.
- ↑ Lundelius et al., 2013, p.229
- ↑ Chimento & Agnolin, 2011, p. 90
Bibliography and further reading
- Arroyo-Cabrales, Joaquín; Polaco, Oscar J.; Johnson, Eileen; Ferrusquía-Villafranca, Ismael (2010-02-01). "A perspective on mammal biodiversity and zoogeography in the Late Pleistocene of México". Quaternary International (Elsevier) 212 (2): 187–197. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2009.05.012. Bibcode: 2010QuInt.212..187A.
- Chimento, Nicolás R., and Federico L. Agnolin. Mamíferos del Pleistoceno Superior de Santiago del Estero (Argentina) y sus afinidades paleobiogeográficas. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia 51.6 (2011): 83-100.
- Cisneros, J.C. 2005. New Pleistocene vertebrate fauna from El Salvador. Revista Brasileira de Paleontologia, 8(3):239-255.
- De Porta, Jaime., 1959: Nueva subespecie de Toxodóntido del Cuaternario de Colombia.- Boletín de Geolología, Universidad Industrial de Santander, 3: 55-61.
- Elissamburu A., 2012. Estimación de la masa corporal en géneros del Orden Notoungulata. Estudios Geológicos, Vol 68, No 1, doi:10.3989/egeol.40336.133
- Laurito, César Alberto. Análisis topológico y sistemático del Toxodonte de Bajo de los Barrantes, provincia de Alajuela, Costa Rica. Revista Geológica de América Central 16 (1993).
- Lucas, Spencer G., Guillermo E. Alvarado, and Eduardo Vega. The pleistocene mammals of Costa Rica. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 17.2 (1997): 413-427.
- Lundelius, E. L.; Bryant, V. M.; Mandel, R.; Thies, K. J.; Thoms, A. (January 2013). "The first occurrence of a toxodont (Mammalia, Notoungulata) in the United States". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 33 (1): 229–232. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.711405. Bibcode: 2013JVPal..33..229L.
- MacFadden, Bruce J. (2005). Diet and habitat of toxodont megaherbivores (Mammalia, Notoungulata) from the late Quaternary of South and Central America. Quaternary Research 64 (2005) 113 – 124.
- McKenna, Malcolm C., and Bell, Susan K. 1997. Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level. Columbia University Press, New York, 631 pp. ISBN 0-231-11013-8
- Paula-Couto, C. (1979). Capítulo XXI, Ordem Notoungulata Roth, 1903. In Tratado de Paleomastozoologia. Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 590 p, Rio de Janeiro.
- Rincón, Ascanio D. Los mamíferos fósiles del Pleistoceno de la cueva del Zumbador (fa. 116), Estado Falcón, Venezuela. Boletín de la Sociedad Venezolana de Espeleología 37 (2003): 18-26.
- Rincón, Ascanio D. New remains of Mixotoxodon larensis Van Frank 1957 (Mammalia: Notoungulata) from Mene de Inciarte tar pit, north-western Venezuela. Interciencia 36.12 (2011): 894-899.
- Van Frank, R. 1957. A fossil collection from northern . 1, Toxodontidae (Mammalia, Notoungulata). American Museum Novitates, 1850:1-38.
- Villarroel A., C. & J. Clavijo ( 2005). Los mamíferos fósiles y las edades de las sedimentitas continentales del Neógeno de la Costa Caribe Colombiana. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias 29 (112): 345-356. ISSN 0370-3908.
Template:Meridiungulata Wikidata ☰ Q141979 entry
 |
