Biology:Paulschulzia
| Paulschulzia | |
|---|---|
| |
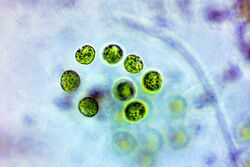
| Paulschulzia pseudovolvox | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Viridiplantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Chlorophyceae |
| Order: | Chlamydomonadales |
| Family: | Tetrasporaceae |
| Genus: | Paulschulzia Skuja[1] |
Paulschulzia is a genus of green algae, specifically of the family Tetrasporaceae.[1]
The genus was circumscribed by Heinrich Leonhards Skuja in Symb. Bot. Upsal. vol.9 (3) on page 118 in 1948.
The genus name of Paulschulzia is in honour of Paul Schulz(-Danzig) (x – 1935), who was a German naturalist (Phycology and Palaeontology), teacher in Danzig.[2]
Paulschulzia consists of spherical to ellipsoidal colonies with usually 4 to 64 cells (sometimes more) embedded in a mucilaginous matrix; within the matrix there are subgroups of 4, 8, or 16 cells each with their own mucilage layer. Cells are spherical to ovoid, and sometimes with two long pseudoflagella extending out of the outer mucilage layer. Cells contain one nucleus and one cup-shaped or stellate chloroplast with a single pyrenoid. Asexual reproduction occurs by the fragmentation of colonies, or by biflagellate zoospores.[3]
Paulschulzia is similar to and closely related to the genus Tetraspora, with both consisting of colonies of cells embedded in an amorphous, mucilaginous matrix. Paulschulzia having subgroups of cells surrounded by their own mucilage layer.[4] However, the two genera separately do not form monophyletic groups.[5]
Species
As accepted by WoRMS;[6]
- Paulschulzia indica M.O.P.Iyengar, 1960
- Paulschulzia pseudovolvox (P.Schultz) Skuja, 1948
- Paulschulzia tenera (Korshikov) J.W.G.Lund, 1961
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. (2008). "Paulschulzia". AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org/browse/taxonomy/?id=43484.
- ↑ Burkhardt, Lotte (2022) (in German) (pdf). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen. Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi:10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8. https://doi.org/10.3372/epolist2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ↑ Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. (2008). "Paulschulzia". AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org/browse/taxonomy/?id=43484.
- ↑ The freshwater algal flora of the British Isles: an identification guide to freshwater and terrestrial algae. Cambridge University Press. 2002. ISBN 978-0-521-77051-4.
- ↑ Sausen, Nicole; Malavasi, Veronica; Melkonian, Michael (2018). "Molecular phylogeny, systematics, and revision of the type species of Lobomonas, L. francei (Volvocales, Chlorophyta) and closely related taxa". Journal of Phycology 54 (2): 198–214. doi:10.1111/jpy.12615. Bibcode: 2018JPcgy..54..198S.
- ↑ "Paulschulzia Skuja, 1948". WoRMS – World Register of Marine Species. https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=578424.
External links
Scientific references
- PubMed references for Paulschulzia
- PubMed Central references for Paulschulzia
- Google Scholar references for Paulschulzia
Scientific databases
- NCBI taxonomy page for Paulschulzia
- Search Tree of Life taxonomy pages for Paulschulzia
- Search Species2000 page for Paulschulzia
- AlgaTerra database
- Index Nominum Genericorum
Wikidata ☰ Q7155353 entry
 |

