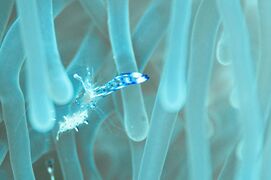
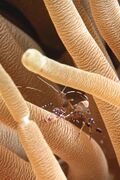
Biology:Periclimenes
| Periclimenes | |
|---|---|

| |
| Periclimenes imperator | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Order: | Decapoda |
| Suborder: | Pleocyemata |
| Infraorder: | Caridea |
| Family: | Palaemonidae |
| Genus: | Periclimenes Costa, 1844 [1] |
| Type species | |
| Periclimenes amethysteus (Risso, 1827) [2]
| |
Periclimenes, commonly known as glass shrimp or cleaner shrimp, is a commensal and often symbiotic genus of semi-transparent shrimp within the family Palaemonidae.[3][4] Species of this large genus feature a wide variety of coloration and patterns, widespread distribution throughout much of the world's tropical oceans, and are often sought out for aquarium trade.[5]
Taxonomy
This genus has undergone several changes in classification based on recent molecular studies comparing species within the genus. However, most recent molecular studies have only involved approximately 20% of the known species likely to belong to the genus. Additionally, most of the molecular studies performed involved Indo-Pacific species of Periclimenes and did not include presumed Periclimenes found in the Atlantic Ocean. Periclimenes has previously been suggested as being a polyphyletic taxa, and has already undergone splits into several new genera. It is likely the genus will undergo changes in classification in coming years with further research.[6]
The genus contains the following species:[7]
- Periclimenes acanthimerus Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes aegylios Grippa & d'Udekem d'Acoz, 1996
- Periclimenes affinis (Zehntner, 1894)
- Periclimenes albatrossae Chace & Bruce, 1993
- Periclimenes albolineatus Bruce & Coombes, 1997
- Periclimenes alcocki Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes aleator Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes alexanderi X. Li, 2008
- Periclimenes amethysteus (Risso, 1826)
- Periclimenes andresi Macpherson, 1988
- Periclimenes antipathophilus Spotte, Heard & Bubucis, 1994
- Periclimenes batei (Borradaile, 1917)
- Periclimenes boucheti X. Li, Mitsuhashi & Chan, 2008
- Periclimenes bowmani Chace, 1972
- Periclimenes brevicarpalis (Schenkel, 1902)
- Periclimenes brevinaris Nobili, 1906
- Periclimenes brevirostris Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes brucei Duriš, 1990
- Periclimenes burrup Bruce, 2007
- Periclimenes calcaratus Chace & Bruce, 1993
- Periclimenes calmani Tattersal, 1921
- Periclimenes canalinsulae Bruce & Coombes, 1997
- Periclimenes cannaphilus Komai, Nemoto & Tsuchida, 2010
- Periclimenes carinidactylus Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes chacei X. Li, Bruce & Manning, 2004
- Periclimenes colemani Bruce, 1975
- Periclimenes colesi De Grave & Anker, 2009
- Periclimenes commensalis Borradaile, 1915
- Periclimenes compressus Borradaile, 1915
- Periclimenes consobrinus (De Man, 1902)
- Periclimenes coriolis Bruce, 1985
- Periclimenes crinoidalis Chace, 1969
- Periclimenes cristimanus Bruce, 1965
- Periclimenes crosnieri X. Li & Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes curvirostris Kubo, 1940
- Periclimenes dardanicola Bruce & Okuno, 2006
- Periclimenes delagoae Barnard, 1958
- Periclimenes dentidactylus Bruce, 1984
- Periclimenes difficilis Bruce, 1976
- Periclimenes digitalis Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes diversipes Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes eleftherioui Koukouras & Türkay, 1996
- Periclimenes exederens Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes fenneri Bruce, 2005
- Periclimenes fimbriatus (Borradaile, 1915)
- Periclimenes finlayi Chace, 1972
- Periclimenes forcipulatus Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes foresti Bruce, 1981
- Periclimenes forgesi X. Li & Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes foveolatus Bruce, 1981
- Periclimenes fujinoi Bruce, 1990
- Periclimenes gonioporae Bruce, 1989
- Periclimenes granulatus Holthuis, 1950
- Periclimenes granulimanus Bruce, 1978
- Periclimenes granuloides Hayashi in Baba, Hayashi & Toriyama, 1986
- Periclimenes guarapari De Grave, 2008
- Periclimenes harringtoni Lebour, 1949
- Periclimenes hertwigi Balss, 1913
- Periclimenes hongkongensis Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes hydrothermophilus Hayashi & Ohtomi, 2001
- Periclimenes imperator Bruce, 1967
- Periclimenes incertus Borradaile, 1915
- Periclimenes infraspinis (Rathbun, 1902)
- Periclimenes ingressicolumbi Berggren & Svane, 1989
- Periclimenes inornatus Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes investigatoris Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes involens Bruce, 1996
- Periclimenes iridescens Lebour, 1949
- Periclimenes ischiospinosus Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes josephi X. Li, 2008
- Periclimenes jugalis Holthuis, 1952
- Periclimenes kallisto Bruce, 2008
- Periclimenes kempi Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes kornii (Lo Bianco, 1903)
- Periclimenes laccadivensis (Alcock & Anderson, 1894)
- Periclimenes laevimanus Duriš, 2010
- Periclimenes lanipes Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes latipollex Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes lepidus Bruce, 1978
- Periclimenes leptodactylus Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes leptopus Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes leptunguis X. Li, Mitsuhashi & Chan, 2008
- Periclimenes longimanus (Dana, 1852)
- Periclimenes longipes (Stimpson, 1860)
- Periclimenes loyautensis X. Li & Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes macrophthalmus Fujino & Miyake, 1970
- Periclimenes madreporae Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes magnus Holthuis, 1951
- Periclimenes mahei Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes maldivensis Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes manihine Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes mclaughlinae Fransen, 2006
- Periclimenes mclellandi Heard & Spotte, 1997
- Periclimenes meyeri Chace, 1969
- Periclimenes milleri Bruce, 1986
- Periclimenes murcielagensis Vargas, 2000
- Periclimenes nevillei Bruce, 2010
- Periclimenes ngi X. Li, Mitsuhashi & Chan, 2008
- Periclimenes nomadophila Berggren, 1994
- Periclimenes novaffinis Bruce & Coombes, 1997
- Periclimenes obscurus Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes ordinarius Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes ornatellus Bruce, 1979
- Periclimenes ornatus Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes paivai Chace, 1969
- Periclimenes pandionis Holthuis, 1951
- Periclimenes panglaonis X. Li, Mitsuhashi & Chan, 2008
- Periclimenes paralcocki X. Li & Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes paraleator X. Li & Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes paraparvus Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes parvispinatus Bruce, 1990
- Periclimenes parvus Borradaile, 1898
- Periclimenes patae Heard & Spotte, 1991
- Periclimenes pauper Holthuis, 1951
- Periclimenes pectiniferus Holthuis, 1952
- Periclimenes pectinipes Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes perlucidus Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes perryae Chace, 1942
- Periclimenes perturbans Bruce, 1978
- Periclimenes pholeter Holthuis, 1973
- Periclimenes platalea Holthuis, 1951
- Periclimenes platydactylus X. Li, 2008
- Periclimenes platyrhynchus Bruce, 1991
- Periclimenes polynesiensis X. Li, 2008
- Periclimenes poriphilus Bruce, 2010
- Periclimenes poupini Bruce, 1989
- Periclimenes pseudalcocki X. Li & Bruce, 2006
- Periclimenes rathbunae Schmitt, 1924
- Periclimenes rectirostris Bruce, 1981
- Periclimenes rex Kemp, 1922
- Periclimenes richeri Bruce, 1990
- Periclimenes robustus (Borradaile, 1915)
- Periclimenes ruber Bruce, 1982
- Periclimenes sagittifer (Norman, 1861)
- Periclimenes sandybrucei Mitsuhashi & Chan, 2009
- Periclimenes sandyi De Grave, 2009
- Periclimenes sarkanae Bruce, 2007
- Periclimenes scriptus (Risso, 1822)
- Periclimenes sibogae Holthuis, 1952
- Periclimenes sinensis Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes soror Nobili, 1904
- Periclimenes tangeroa Bruce, 2005
- Periclimenes tenellus (Smith, 1882)
- Periclimenes terangeri Bruce, 1998
- Periclimenes thermohydrophilus Hayashi & Ohtomi, 2001
- Periclimenes toloensis Bruce, 1969
- Periclimenes tonga Bruce, 1988
- Periclimenes uniunguiculatus Bruce, 1990
- Periclimenes vaubani Bruce, 1990
- Periclimenes veleronis Holthuis, 1951
- Periclimenes vicinus X. Li, 2008
- Periclimenes watamuae Bruce, 1976
- Periclimenes wirtzi d'Udekem d'Acoz, 1996
- Periclimenes yaldwyni Holthuis, 1959
- Periclimenes yucatanicus (Ives, 1891)
- Periclimenes zanzibaricus Bruce, 1967
- Periclimenes zevinae Duriš, 1990
Habitat
Periclimenes is widely distributed throughout tropical and temperate reef ecosystems of the Atlantic, Caribbean, Mediterranean, as well as Indo-Pacific Oceans.[8][9]
Behavior
Symbiosis, commensalism, and parasitism
Many species of Periclimenes are commensal and often symbiotic organisms within their reef ecosystems. The most common organisms forming symbiotic relationships with this genus are species of fish, cnidarians, echinoderms, and sponges. Some species such as Periclimenes caraibicus have been observed to interact parasitically with species of sponges, living within the sponge and directly eating the sponge tissue. Another species, Periclimenes soror, is commonly found on a species of sea star known as cushion stars with no effect on the star making it a commensalistic relationship. Anecdotal evidence suggests that P. soror may choose a host star that matches its own coloration for camouflage.[10] Other research demonstrated that the Periclimenes species, P. yucatanicus, has a symbiotic cleaning relationship with different species of reef fish studied in the pacific. P. yucatanicus performed a waving motion with its antennae to signal to reef fish that it is available to clean. The cleaner shrimps then ate parasitic organisms present on the reef fish species.[11]
Characteristics
Species present in this genus typically have a transparent to semi transparent body with antennae protruding from the head region. Additionally, large variation of color and patterns exist on the organisms throughout, making them highly sought out ornamental species in the marine aquarium industry.[12]
-
Periclimenes colemani on an Asthenosoma varium.
-
Periclimenes soror on a pillow starfish Culcita schmideliana.
-
Periclimenes pedersoni
-
Periclimenes magnificus
-
Periclimenes holthuisi.
-
Periclimenes tenuipes.
-
Periclimenes tosaensis
References
- ↑ "Periclimenes Costa, 1844". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=96414. Retrieved February 11, 2011.
- ↑ I. N. Marin & Tin-Yam Chan (2006). "Two new genera and a new species of crinoid-associated pontoniine shrimps (Decapoda: Caridea: Palaemonidae)". Journal of Crustacean Biology 26 (4): 524–539. doi:10.1651/S-2705.1. http://decapoda.nhm.org/pdfs/26153/26153.pdf.
- ↑ Rauch, Hoeksema, Hermanto, Fransen, Cessa, Bert W, Bambang, Charles H.J.M. (2019). "Shrimps of the genus Periclimenes (Crustacea, Decapoda, Palaemonidae) associated with mushroom corals (Scleractinia, Fungiidae): linking DNA barcodes to morphology". Contributions to Zoology 88 (2): 201–235. doi:10.1163/18759866-20191357.
- ↑ Tan, Ng, Leo, Peter (1988). "Glass Shrimp". http://mangrove.nus.edu.sg/pub/seashore/text/180.htm.
- ↑ Debelius, Helmut (2001). Crustacea Guide of the World: Shrimps, Crabs, Lobsters, Mantis Shrimps, Amphipods : Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean. Frankfurt: IKAN-Unterwasserachiv. pp. 321. ISBN 3925919554.
- ↑ Ďuriš, Horká, Zdeněk, Ivona (2017). "Towards a revision of the genus Periclimenes: resurrection of Ancylocaris Schenkel, 1902, and designation of three new genera (Crustacea, Decapoda, Palaemonidae)". ZooKeys (646): 25–44. doi:10.3897/zookeys.646.11397. PMID 28228674.
- ↑ Bruce, Alexander (2004). "A partial revision of the genus Periclimenes Costa, 1884 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Palaemonidae)". Zootaxa 582: 1–26. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.582.1.1.
- ↑ Wicksten, Mary (1995). "Within-species variation in Periclimenes yucatanicus (Ives), with taxonomic remarks on P, pedersoni Chace (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea: Palaemonidae)". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 108 (3): 458–464.
- ↑ dos Santos, Calado, Bartilotti, Narciso, Antonina, Ricardo, Catia, Luis (2004). "The larval development of the partner shrimp Periclimenes sagittifer (Norman, 1861) (Decapoda: Caridea: Palaemonidae: Pontoniinae) described from laboratory-reared material, with a note on chemical settlement cues". Helgoland Marine Research 58 (2): 129–139. doi:10.1007/s10152-004-0178-2.
- ↑ Ollif, Eric (2013). "Symbiosis of the Sea Star Shrimp, Periclimenes Soror Nobili, 1904 (Decapoda, Palaemonidae), and Cushion Star, Culcita Novaeguineae Müller & Troschel, 1842 (Echinodermata, Asteroidea, Oreasteridae): Host Finding and Benefits". Crustaceana 86 (5): 564–577. doi:10.1163/15685403-00003192.
- ↑ Titus, Vondriska, Daly, Benjamin, Clayton, Marymegan (2017). "Comparative behavioural observations demonstrate the 'cleaner' shrimp Periclimenes yucatanicus engages in true symbiotic cleaning interactions". Royal Society Open Science 4 (4): 170078. doi:10.1098/rsos.170078. PMID 28484634. Bibcode: 2017RSOS....470078T.
- ↑ Calado, Narciso, Morais, Rhyne, Jin, R., L., S., A., J (2003). "A rearing system for the culture of ornamental decapod crustacean larvae". Aquaculture 218 (1–4): 329–339. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00583-5.
Wikidata ☰ Q3019910 entry