Biology:Phellibaumin
From HandWiki
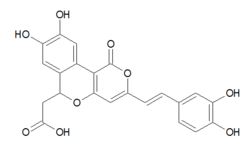
Phellibaumins are hispidin derivatives made by the fungus Phellinus.[1][2] Five such derivatives have been identified, known as Phellibaumin A through E.[3] Phellibaumins A and B are classified as pyranones, while Phellibaumins C, D, and E are classified as styrylpyranones.[4]
Phellibaumin A was also identified as being produced by the fungus Inonotus hispidus,[5] and Phellibaumins B and C were identified in Sanghuangporus vaninii.[6] Phellibaumin E is of interest to medical researchers due to potential anti-dementia effects.[7]
References
- ↑ Wu, Chang-Sheng; Lin, Zhao-Min; Wang, Li-Ning; Guo, Dong-Xiao; Wang, Shu-Qi; Liu, Yong-Qing; Yuan, Hui-Qing; Lou, Hong-Xiang (2011-06-01). "Phenolic compounds with NF-κB inhibitory effects from the fungus Phellinus baumii". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 21 (11): 3261–3267. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.04.025. ISSN 1464-3405. PMID 21531558. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21531558/.
- ↑ "Chemical constituents from Phellinus igniarius and their anti-tumor activity in vitro". China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2016-08-15. doi:10.4268/cjcmm20161617. http://www.cjcmm.com.cn/cjcmmen/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20161617&flag=1.
- ↑ Cao, Yinglong; Liu, Yi; Wang, Ge; Wang, Wenqiong; Li, Yougui; Xuan, Lijiang (2021-08-01). "Styryl pyranones with apoptosis activities from the sporocarps of Phellinus igniarius" (in en). Phytochemistry Letters 44: 154–159. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2021.06.018. ISSN 1874-3900. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1874390021001282.
- ↑ He, Pingya; Zhang, Yi; Li, Ning (2021). "The phytochemistry and pharmacology of medicinal fungi of the genus Phellinus : a review" (in en). Food & Function 12 (5): 1856–1881. doi:10.1039/D0FO02342F. ISSN 2042-6496. http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0FO02342F.
- ↑ Li, Qingjie; Bao, Haiying; Bau, Tolgor; Li, Yu (2018). "Influence of Inonotus hispidus in hemorheology in rat model with blood stasis due to cold syndrome and analysis on spectral efficiency" (in zh). Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition): 30–35. http://dx.doi.org/10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180106.
- ↑ Zhang, Yangyang; Lv, Guoying; Song, Tingting; Chen, Chun; Zhang, Zuofa; Cai, Weiming (2022-09-06). "Recovery of the phenolic compounds from artificial cultivated Sanghuangporus vaninii using a green method and biological properties of phenolic extract in vitro" (in en). International Journal of Food Science & Technology: ijfs.15993. doi:10.1111/ijfs.15993. ISSN 0950-5423. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ijfs.15993.
- ↑ Liu, Ruoyao; Zhang, Yuchi; Li, Sainan; Liu, Chunming; Zhuang, Siyuan; Zhou, Xu; Li, Yanjie; Liang, Jiaqi (2022-10-15). "Receptor-ligand affinity-based screening and isolation of water-soluble 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors from Phellinus igniarius" (in en). Journal of Chromatography B 1209: 123415. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2022.123415. ISSN 1570-0232. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1570023222003191.
 |
