Biology:Stenomesson leucanthum
| Stenomesson leucanthum | |
|---|---|
| |
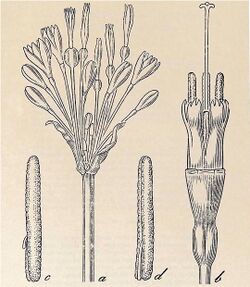
| Botanical illustration of Pucara leucantha (basionym of Stenomesson leucanthum) flower and floral parts.[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Amaryllidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Amaryllidoideae |
| Genus: | Stenomesson |
| Species: | S. leucanthum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Stenomesson leucanthum Meerow & van der Werff
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Stenomesson leucanthum is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to Peru.[3] Pierfelice Ravenna the Chilean botanists who first formally described the species, using the basionym Pucara leucantha, named it after its white (Latinized form of Greek λευκός, leukós) flowers (Latinized form of Greek ἄνθος, ánthos).
Description
It is a perennial herb with a round bulb that is 3.7-4.8 centimeters in diameter. Its leaves are often solitary and are 10-12 by 2-3 centimeters with pointed tips. Its inflorescences are on a stem-like stalk that is 15-50 centimeters long. The flowering stalk is 5 millimeters at its apex. The flowering stalk is circular in cross section. Its flowers occur in clusters at the top of the stalk. The cluster of flowers is subtended by narrow, papery bracts that are 2.5-3.1 centimeters long and come to a point at their tips. Each flower is on a 3-6 millimeter long pedicel. The white, bell-shaped flowers are 1.2-1.4 centimeters in diameter. Atop the floral tube are 6 tepals arranged in two rows. The elliptical outer tepals are 12-14 by 4 millimeters and come to a point at their tip. The elliptical inner tepals are 14 by 5 millimeters. Its anthers are 3.6-5.8 millimeters long. Its flowers have a single thread-like style that is 1.9-2 centimeters long and topped by a 3-lobed stigma. Its flowers have an ellipsoid ovary that is 3.8-4 by 1.5-2 millimeters with 3 chambers. Its fruit are round.[4][1]
Distribution and habitat
It grows in northern Peru on rocky slopes and sandy places at elevations of 990-1,650 meters above sea level.
Reproductive biology
The yellow pollen of S. leucanthum is shed as permanent tetrads.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ravenna, Pierfelice (1972). "Pucara, Genero Nuevo de Amaryllidaceae del Norte de Peru" (in Spanish, Latin). Anales del Museo de Historia Natural de Valparaiso 5: 85–90. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/257366.
- ↑ "Stenomesson leucanthum (Ravenna) Meerow & van der Werff". theplantlist.org. http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-309571. Retrieved December 21, 2018.
- ↑ "Stenomesson leucanthum (Ravenna) Meerow & van der Werff". The Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. n.d.. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77062950-1.
- ↑ Meerow, Alan W.; van der Werff, Henk (2004). "Pucara (Amaryllidaceae) Reduced to Synonymy with Stenomesson on the Basis of Nuclear and Plastid DNA Spacer Sequences, and a New Related Species of Stenomesson". Systematic Botany 29 (3): 511–517. doi:10.1600/0363644041744400. ISSN 0363-6445.
- ↑ Meerow, AW; van der Werff, H (2004). "Pucara (Amaryllidaceae) Reduced to Synonymy with Stenomesson on the Basis of Nuclear and Plastid DNA Spacer Sequences, and a New Related Species of Stenomesson". Systematic Botany 29 (3): 511–517. doi:10.1600/0363644041744400.
Wikidata ☰ Q15504946 entry

