Biology:Themisto libellula
| Themisto libellula | |
|---|---|
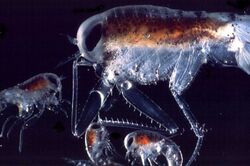
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Superorder: | Peracarida |
| Order: | Amphipoda |
| Suborder: | Hyperiidea |
| Family: | Hyperiidae |
| Genus: | Themisto |
| Species: | T. libellula
|
| Binomial name | |
| Themisto libellula (Lichtenstein in Mandt, 1822)
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Euthemisto libellula | |
Themisto libellula is a marine amphipod of the family Hyperiidae. The species lives for 2 to 3 years, and grows up to 60 millimetres (2.4 in) over its lifetime.[2][3] They are found in large quantities in Arctic water.[4]
In the summer, they eat more lipids to store as fuel for the winter.[3] During the mid-winter, they eat copepods, such as Calanus finmarchicus.[5] T. libellula is eaten by cod, polar cod, and mammals at the ice edge.[4] In the early 2000s, the population of the species began to decrease; these effects rippled through the food chain.[4] The levels later rose in cool years, and T. libellula have moved south of the Arctic Circle.[3] They have been observed in "mass mortalities", where millions of T. libellula wash up dead on the coast.[6][7]
References
- ↑ Cuvelier, Daphne; Gasca, Rebeca (2013). "Themisto libellula (Lichtenstein in Mandt, 1822)". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=156452.
- ↑ Koszteyn, J.; Timofeev, S.; Węsławski, J. M.; Malinga, B. (1995). "Size structure of Themisto abyssorum Boeck and Themisto libellula (Mandt) populations in European Arctic seas". Polar Biology 15 (2): 85–92. doi:10.1007/BF00241046.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Pinchuk, Alexei I.; Coyle, Kenneth O.; Farley, Edward V.; Renner, Heather M. (May 19, 2013). "Emergence of the Arctic Themisto libellula (Amphipoda: Hyperiidae) on the southeastern Bering Sea shelf as a result of the recent cooling, and its potential impact on the pelagic food web". ICES Journal of Marine Science 70 (6): 1244–1254. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fst031.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Johannesen, E.; Ingvaldsen, R. B.; Bogstad, B.; Dalpadado, P.; Eriksen, E.; Gjosaeter, H.; Knutsen, T.; Skern-Mauritzen, M. et al. (2012). "Changes in Barents Sea ecosystem state, 1970–2009: climate fluctuations, human impact, and trophic interactions". ICES Journal of Marine Science 69 (5): 880–889. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fss046.
- ↑ Kraft, Angelina; Berge, Jørgen; Varpe, Øystein; Falk-Petersen, Stig (January 2013). "Feeding in Arctic darkness: mid-winter diet of the pelagic amphipods Themisto abyssorum and T. libellula". Marine Biology 160 (1): 241–248. doi:10.1007/s00227-012-2065-8.
- ↑ Mosher, Alyssa (August 1, 2016). "'Dead Sea': Millions of themisto plankton rotting ashore in Paulatuk, N.W.T.". CBC/Radio-Canada. http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/north/themisto-libellula-dead-paulatuk-july-2016-1.3701320. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
- ↑ Eiane, Ketil; Daase, Malin (May 2002). "Observations of mass mortality of Themisto libellula (Amphipoda, Hyperidae)". Polar Biology 25 (5): 396–398. doi:10.1007/s00300-002-0361-3.
Wikidata ☰ Q4483655 entry
 |

