Biology:Tridacna
| Tridacna Temporal range: Miocene – recent[1]
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Giant clam (T. gigas), Michaelmas Cay, QVD | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Animalia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Mollusca |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Bivalvia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Cardiida |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Cardioidea |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Cardiidae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Tridacninae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Tridacna Bruguière, 1797 |
| Synonyms | |
| |
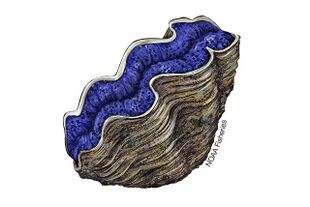
Tridacna is a genus of large saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the subfamily Tridacninae, the giant clams. Many Tridacna species are threatened. They have heavy shells, fluted with 4 to 6 folds. The mantle is brightly coloured. They inhabit shallow waters of coral reefs in warm seas of the Indo-Pacific region.[2] These clams are popular in marine aquaria, and in some areas, such as the Philippines , members of the genus are farmed for the marine aquarium trade. They live in symbiosis with photosynthetic algae (zooxanthellae). Some species are eaten by humans.
All species in the genus Tridacna are protected under CITES Appendix II.[3]
Etymology
The name Tridacna arises from Greek words tri, meaning three, and dacno, meaning bite. In the Ancient Roman text Natural History, Pliny the Elder explained the nomenclature comes from the fact that "they are so large as to require three bites in eating them.”[4]
List of Species, Systematics, and Phylogeny
The genus contains the following species:[5][6]
- Tridacna crocea Lamarck, 1819 -- Western Pacific
- Tridacna derasa (Röding, 1798) -- Western Pacific
- Tridacna elongatissima Bianconi, 1856
- Tridacna gigas (Linnaeus, 1758) -- Tropical Indo-Pacific
- Tridacna maxima Röding, 1798 ( =Tridacna elongata) -- Tropical Indo-Pacific
- Tridacna mbalavuana Ladd, 1934 -- Fiji, Tonga
- Tridacna noae (Röding, 1798) -- China sea
- Tridacna rosewateri Sirenho & Scarlato, 1991 -- Mascarene region
- Tridacna squamosa Lamarck, 1819 -- Tropical Indo-Pacific
- Tridacna squamosina Sturany, 1899 (= Tridacna costata Roa-Quiaoit, Kochzius, Jantzen, Al-Zibdah & Richter 2008) -- Indo-Pacific
- Synonyms
- Tridacna acuticostata G. B. Sowerby III, 1912: synonym of Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798)
- Tridacna compressa Reeve, 1862: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) maxima (Röding, 1798) represented as Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna costata Roa-Quiaoit, Kochzius, Jantzen, Zibdah & Richter, 2008: synonym of Tridacna squamosina Sturany, 1899
- Tridacna cumingii Reeve, 1862: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) crocea Lamarck, 1819 represented as Tridacna crocea Lamarck, 1819 (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna detruncata Bianconi, 1869: synonym of Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna elongata Lamarck, 1819: synonym of Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna ferruginea Reeve, 1862: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) crocea Lamarck, 1819 represented as Tridacna crocea Lamarck, 1819 (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna fossor Hedley, 1921: synonym of Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798)
- Tridacna glabra Link, 1807: synonym of Tridacna derasa (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym, synonym)
- Tridacna imbricata (Röding, 1798): synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) maxima (Röding, 1798) represented as Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798)
- Tridacna lamarcki Hidalgo, 1903: synonym of Tridacna squamosa Lamarck, 1819 (synonym - pars)
- Tridacna lanceolata G. B. Sowerby II, 1884: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) maxima (Röding, 1798) represented as Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna lorenzi Monsecour, 2016 -- Mascarene region: synonym of Tridacna lorenzi K. Monsecour, 2016: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) rosewateri Sirenko & Scarlato, 1991 represented as Tridacna rosewateri Sirenko & Scarlato, 1991
- Tridacna mutica Lamarck, 1819: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) maxima (Röding, 1798) represented as Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (synonym - pars)
- Tridacna ningaloo Penny & Willan, 2014: synonym of Tridacna noae (Röding, 1798)
- Tridacna obesa G. B. Sowerby III, 1899: synonym of Tridachnes derasa Röding, 1798: synonym of Tridacna derasa (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna reevei Hidalgo, 1903: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) maxima (Röding, 1798) represented as Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym, synonym)
- Tridacna rudis Reeve, 1862: synonym of Tridacna (Chametrachea) maxima (Röding, 1798) represented as Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym)
- Tridacna serrifera Lamarck, 1819: synonym of Tridacna derasa (Röding, 1798)
- Tridacna tevoroa Lucas, Ledua & Braley, 1990: synonym of Tridacna mbalavuana Ladd, 1934
- Tridacna troughtoni Iredale, 1927: synonym of Tridacna maxima (Röding, 1798) (junior subjective synonym)
An alternative older classification recognises a third subgenus Persikima containing T. derasa and T. mbalavuana.[7] Recent biochemical studies have suggested that there may exist morphologically indistinct cryptic species.[2][8]
Anatomy
Compared to other clams, the soft mantle that secretes the shell is greatly expanded. The clams even have small lens-like structures called ocelli through which light penetrates.[9]
Ecology and behaviour

Tridacna clams are common inhabitants of Indo-Pacific coral reef benthic communities in shallower waters.[10] They live in symbiosis with photosynthetic dinoflagellate algae (Symbiodinium) that grow in the mantle tissues.[11] Light penetrates the mantle through small lens-like structures called ocelli.[9] They are sessile in adulthood. By day, the clams spread out their mantle so that the algae receive the sunlight they need to photosynthesize, whereas the colour pigments protect the clam against excessive light and UV radiation. Adult clams can get most (70–100%) of their nutrients from the algae and the rest from filter feeding.[12] When disturbed, the clam closes its shell. The popular opinion that they pose danger to divers who get trapped or injured between the closing sharp-edged shell is not very real, as the closing reaction is quite slow. Their large size and easy accessibility has caused overfishing and collapse of the natural stocks in many places and extirpation in some of the species.[13] They are being sustainably farmed in some areas,[14] both for the seafood market in some Asian countries and for the aquarium trade.[15]
Tridacna clams can produce large white pearls with an undulating, porcelain-like surface,[16] which may be described as "non-nacreous pearls".[citation needed] The "Pearl of Lao Tzu", also known as the "Pearl of Allah", is the world's largest pearl weighing 6.4 kilogrammes; it was said to have been found inside a Tridacna gigas by a Filipino diver in 1934.[17][18]
Artistic use
Over a hundred examples of carved Tridacna shells have been found in archaeological expeditions from Italy to the Near East. Similar in artistic style, they were probably produced in the mid-seventh century, made or distributed from the southern coast of Phoenicia. The backs and interior perimeters of the shells show animal, human, and floral motifs, while the interiors typically show recumbent sphinxes. The umbo of the shell is in the shape of a human female or bird's head. They were probably used to store eye cosmetics.[19]
Images
-
Tridacna gigas
-
Tridacna maxima
Notes
- ↑ "The Paleobiology Database". Paleodb.org. http://paleodb.org.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Huelsken, T., Keyse, J., Liggins, L., Penny, S., Treml, E.A., Riginos, C. (2013) A Novel Widespread Cryptic Species and Phylogeographic Patterns within Several Giant Clam Species (Cardiidae: Tridacna) from the Indo-Pacific Ocean. PLoS ONE, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080858.
- ↑ "Checklist of CITES species". http://checklist.cites.org/#/en.
- ↑ Barnett, Cynthia (2021-07-06). "The History, Myth, and Future of the Giant Clam" (in en). http://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/giant-clams-sound-of-the-sea-excerpt.
- ↑ WoRMS. (2009). Tridacna. Accessed through the World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=205753 on 2009-01-08.
- ↑ Schneider, J.A.,and O´Foighil, D. Phylogeny of Giant Clams (Cardiidae: Tridacninae) Based on Partial Mitochondrial 16S rDNA Gene Sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution Vol. 13, No. 1, October, pp. 59–66, 1999
- ↑ Benzie,J.A.H. and Williams,S.T. Phylogenetic relationships among giant clam species (Mollusca: Tridacnidae) determined by protein electrophoresis. Marine Biology (1998) 132: 123±133
- ↑ Mohamed, N.M. et al., Molecular Genetic Analyses of Giant Clam (Tridacna sp.) Populations in the Northern Red Sea. Asian Journal of Biochemistry, 1 (4): 338-342 (2006)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Murphy 2002, p. 25
- ↑ Rosewater, J., The Family Tridacnidae in the Indo-Pacific. Indo-Pacific Mollusca, 1:347-408. 1965
- ↑ Jantzen, Carin; Wild, Christian; El-Zibdah, Mohammed; Roa-Quiaoit, Hilly Ann; Haacke, Christoph; Richter, Claudio (2008). "Photosynthetic performance of giant clams, Tridacna maxima and T. squamosa, Red Sea". Marine Biology 155 (2): 211–221. doi:10.1007/s00227-008-1019-7.
- ↑ Klumpp, D. W.; Lucas, J. S. (1994). "Nutritional ecology of the giant clams Tridacna tevoroa and T. derasa from Tonga: influence of light on filter-feeding and photosynthesis". Marine Ecology Progress Series 107: 147–156. doi:10.3354/MEPS107147. https://www.int-res.com/articles/meps/107/m107p147.pdf.
- ↑ J.W. Copland and J.S. Lucas, (Eds.), Giant Clams in Asia and the Pacific Vol. 9, Australian Center for International Agricultural Research, Canberra(1988).
- ↑ Murphy 2002, p. 28
- ↑ "Aquarium Invertebrates: A Trip to an Indonesian Coral and Clam Farm". advancedaquarist.com. http://www.advancedaquarist.com/2011/9/inverts.
- ↑ CIBJO (2007) THE PEARL BOOK:: Natural, Cultured & Imitation Pearls: Terminology & Classification – 5.216. Tridacna gigas (p. 28)
- ↑ Natural History – PICKS FROM THE PAST: NOVEMBER 1939 – The Pearl of Allah
- ↑ Prager, Ellen (2011), Sex, Drugs, and Sea Slime: The Oceans' Oddest Creatures and Why They Matter, The University of Chicago Press, ISBN 978-0-226-67872-6 (pp. 64–64)
- ↑ Markoe, Glenn. Phoenicians. British Museum Press (2000).
References
- Murphy, Richard C. (2002). Coral Reefs: Cities Under The Sea. Princeton, New Jersey: The Darwin Press. ISBN 978-0-87850-138-0.
- How to Care for Tridacnid Clams FishChannel.com
Wikidata ☰ Q2387255 entry
 |






