Biology:U5 spliceosomal RNA
| U5 spliceosomal RNA | |
|---|---|
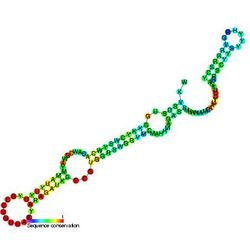 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of U5 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | U5 |
| Rfam | RF00020 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; splicing |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | 0000351 0000353 0005682 0046540 |
| SO | 0000395 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
U5 snRNA is a small nuclear RNA (snRNA) that participates in RNA splicing as a component of the spliceosome. It forms the U5 snRNP (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein) by associating with several proteins including Prp8 - the largest and most conserved protein in the spliceosome, Brr2 - a helicase required for spliceosome activation, Snu114, and the 7 Sm proteins.[1] U5 snRNA forms a coaxially-stacked series of helices that project into the active site of the spliceosome.[2][3] Loop 1, which caps this series of helices, forms 4-5 base pairs with the 5'-exon during the two chemical reactions of splicing.[4][5] This interaction appears to be especially important during step two of splicing, exon ligation.[6]
Medical relevance
Specific heterozygous variants in RNU5B-1, a gene that encodes one of the functional homologs of U5 spliceosomal RNA in humans, cause an autosomal dominant Neurodevelopmental disorder with seizures and joint laxity (OMIM 621090) also called RNU5B-1 syndrome[7].
References
- ↑ "Biochemical and genetic analyses of the U5, U6, and U4/U6 x U5 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae". RNA 7 (11): 1543–53. November 2001. PMID 11720284.
- ↑ "The architecture of the spliceosomal U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP". Nature 523 (7558): 47–52. July 2015. doi:10.1038/nature14548. PMID 26106855. Bibcode: 2015Natur.523...47N.
- ↑ "Structure of a yeast spliceosome at 3.6-angstrom resolution". Science 349 (6253): 1182–91. September 2015. doi:10.1126/science.aac7629. PMID 26292707. Bibcode: 2015Sci...349.1182Y.
- ↑ "U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites". Cell 68 (4): 743–54. February 1992. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. PMID 1739979.
- ↑ "The U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs as active site components of the spliceosome". Science 262 (5142): 1989–96. December 1993. doi:10.1126/science.8266094. PMID 8266094. Bibcode: 1993Sci...262.1989S.
- ↑ "The invariant U5 snRNA loop 1 sequence is dispensable for the first catalytic step of pre-mRNA splicing in yeast". Cell 86 (4): 679–89. August 1996. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80140-3. PMID 8752221.
- ↑ Jackson, Adam; Thaker, Nishi; Blakes, Alexander; Rice, Gillian; Griffiths-Jones, Sam; Balasubramanian, Meena; Campbell, Jennifer; Shannon, Nora et al. (2025-06-24). "Analysis of R-loop forming regions identifies RNU2-2 and RNU5B-1 as neurodevelopmental disorder genes" (in en). Nature Genetics 57 (6): 1362–1366. doi:10.1038/s41588-025-02209-y. ISSN 1061-4036. PMID 40442284. PMC 12165836. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02209-y.
Further reading
- "The uRNA database". Nucleic Acids Research 25 (1): 102–3. January 1997. doi:10.1093/nar/25.1.102. PMID 9016512.
- "The spliceosomal snRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans". Nucleic Acids Research 18 (9): 2633–42. May 1990. doi:10.1093/nar/18.9.2633. PMID 2339054.
External links
 |
