Biology:Unicorn (spider)
| Unicorn | |
|---|---|
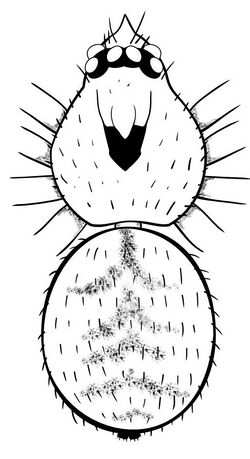
| |
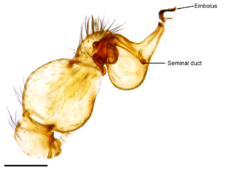
| Male Unicorn sikus, viewed from above (legs omitted). | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Oonopidae |
| Genus: | Unicorn Platnick & Brescovit, 1995 |
| Type species | |
| Unicorn catleyi Platnick & Brescovit, 1995
| |
| Species | |
|
7, see text | |
Unicorn ("one horn", in Latin) is a genus of goblin spiders (family Oonopidae) from South America, containing seven species that occur predominantly in high elevation, semi-desert regions of Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Individuals are relatively large for goblin spiders, measuring up to 3.0 mm (0.12 in) in body length. The genus name refers to a characteristic pointed projection between the eyes and jaws of males. In at least one species, broken-off tips of the male pedipalps have been found within the genitalia of females, postulated as a means of sperm competition. Unicorn possesses several traits that suggest it is a relatively "primitive" member of the Oonopidae, and is classified with other similar, soft-bodied goblin spiders in the subfamily Sulsulinae.
Description
Species of Unicorn range from 2.2 to 3.0 mm in body length (from tip of the cephalothorax to end of abdomen, excluding legs). The cephalothorax, yellow in color, ranges from 1 to 1.2 mm long (around 40–49% of body length depending on species) and often possesses a central grey patch with four lines radiating towards the eyes. The abdomen is white with dark chevron patterns on the dorsal surface, and in some species a pair of dark lines on the underside. The body is covered with a dense covering of long stiff hairs (setae). The legs are long, slender, and yellow. There are six eyes, roughly equal in size, arranged in roughly triangular groups of three, with two eyes meeting in the middle, forming a wide "H" or bow-tie pattern. Species of Unicorn are considered "soft-bodied", as the abdomen lacks the hardened plates that occur in many other goblin spiders. The abdomen possesses six spinnerets.[1][2]
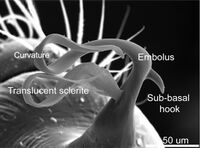
Males and females show some differences in morphology: male jaws (chelicerae) are longer and more slender than those of females; the male palpal tibiae—the penultimate segment of the pedipalps—are enlarged compared to females; and males alone possess a "clypeal horn", a forward-pointing projection of the clypeus surrounded by long stiff hairs, from which the genus name Unicorn ("one horn" in Latin) derives.[1][lower-alpha 1]
The copulatory bulb of males (the sperm-transferring organ at the tip of the pedipalps), terminates in a narrow, curving tip called an embolus, which in Unicorn bears a hook at its base and is accompanied by a similar curved extension called a translucent sclerite.[1]
Reproduction
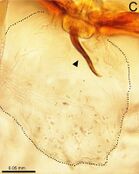
Right: Dissected female genitalia with broken embolus tip (arrow).
Like most spiders, the pedipalps of mature males end in a bulb terminating in a thin, curved projection called an embolus, through which sperm is released during mating. Female U. catleyi have been observed with broken-off embolus tips lodged in their genitalia. This has been hypothesized as a type of "sperm-plug" or copulatory plug, where, by breaking off a piece of his anatomy (a process known as genital mutilation or genital breakage), a male physically precludes other males from successfully mating with the female, one of many types of sperm competition in animals.[3] An alternative to the sperm competition function is that genital mutilation might allow males to more rapidly escape and avoid being cannibalized after mating, although this function is thought to be unlikely in Unicorn since there are no significant size differences between sexes, and cannibalism is more common when females are much larger than males.[3] Sperm plugs of various types, including gelatinous or waxy substances, have been observed in at least 41 spider families, and are generally thought to ensure paternity.[4] U. catlyei is one of only few goblin spiders known or suspected to utilize sperm plugs.[3]
Habitat
Species of Unicorn have mostly been found at elevations between 1,000 to 4,000 m (3,300 to 13,100 ft) above sea level, many from semi-desert regions. U. socos has been collected at 360 m (1,180 ft) in central Chile.[1] The spiders are hard to detect in the field, and most species have been collected by pitfall trapping. They are uncommon in museum collections, and almost nothing is known about their natural history.[2][3]
Species and distribution
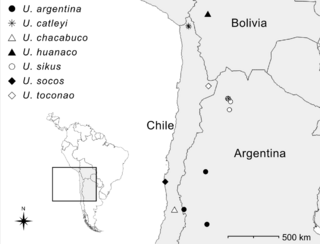
The genus Unicorn was established in 1995 by Norman Platnick and Antônio Brescovit, to encompass five newly described species and one species, U. argentina, that had previously been described as a species of Orchestina.[lower-alpha 2] A seventh species was described in 2010. The type species of Unicorn is U. catleyi. Unicorn species occur in central and northern Chile, western Argentina, and Bolivia.[1][2]
- Unicorn argentina (Mello-Leitão, 1940) — Western Argentina
- Unicorn catleyi Platnick & Brescovit, 1995 — Northern Chile and northwestern Argentina
- Unicorn chacabuco Platnick & Brescovit, 1995 — Chacabuco Province, central Chile
- Unicorn huanaco Platnick & Brescovit, 1995 — La Paz Department, Bolivia
- Unicorn sikus González, Corronca & Cava, 2010 — Salta Province, northwestern Argentina
- Unicorn socos Platnick & Brescovit, 1995 — Limarí Province, central Chile
- Unicorn toconao Platnick & Brescovit, 1995 — Antofagasta Province, northern Chile
Classification
Unicorn is a member of the family Oonopidae (oonopids, or goblin spiders), which contains over 1,500 species worldwide. Within oonopids, Unicorn is classified in the subfamily Sulsulinae, which contains other soft-bodied genera such as Xiombarg and Dalmasula.[5] Due to certain features of the eyes and jaws that resemble those found in other families, and which are differently modified in many other oonopids, Platnick and Brescovit suggested Unicorn was among the most primitive or basal members of the Oonopidae,[1] which was corroborated by a 2014 study that examined DNA similarities among the Oonopidae, finding that Unicorn and other sulsulines diverged before almost all other oonopids.[6]
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Platnick, N. I.; Brescovit, A. D. (1995). "On Unicorn, a new genus of the spider family Oonopidae (Araneae, Dysderoidea)". American Museum Novitates (3152): 1–12. http://digitallibrary.amnh.org/dspace/bitstream/handle/2246/3670//v2/dspace/ingest/pdfSource/nov/N3152.pdf?sequence=1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Gonzales Reyes, A. X.; Corronca, J. A.; Cava, M. B. (2010). "New species of Unicorn Platnick & Brescovit (Araneae, Oonopidae) from north-west Argentina". Munis Entomology & Zoology 5 (2): 374–379. http://www.munisentzool.org/yayin/vol5/issue2/374-379.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Izquierdo, Matías A.; Rubio, Gonzalo D. (2011). "Male genital mutilation in the high-mountain goblin spider, Unicorn catleyi". Journal of Insect Science 11 (118): 1. doi:10.1673/031.011.11801. PMID 22225476.
- ↑ "Securing paternity in spiders? A review on occurrence and effects of mating plugs and male genital mutilation". Genetica 13 (1): 75–104. 2010. doi:10.1007/s10709-009-9388-5. PMID 19705286.
- ↑ Platnick, Norman I. (2012). "Tarsal organ morphology and the phylogeny of goblin spiders (Araneae, Oonopidae), with notes on basal genera.". American Museum Novitates (3736): 1–52. http://digitallibrary.amnh.org/dspace/bitstream/handle/2246/6160/N3736.pdf.
- ↑ Busschere, C.; Fannes, W.; Henrard, A.; Gaublomme, E.; Jocqué, R.; Baert, L. (2014). "Unravelling the goblin spiders puzzle: rDNA phylogeny of the family Oonopidae (Araneae)". Arthropod Systematics & Phylogeny 72 (2): 177–192. http://www.senckenberg.de/files/content/forschung/publikationen/arthropodsystematics/asp_72_2/06_asp_72_2-debusschere_et_al_177-192.pdf. Retrieved 2015-04-11.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q3549947 entry
 |