Blockchain-based Service Network
The Blockchain-based Service Network (BSN) is a non-cryptocurrency blockchain infrastructure that enables a distributed cloud environment within existing private or public clouds for mainstream businesses or institutions to build and manage distributed applications.[1] The BSN was founded in 2018 under the lead of the State Information Center of China, a government think tank under the National Development and Reform Commission, and was officially launched in 2019. Other founding members include China Mobile, China UnionPay, and Red Date Technology Limited.[2] The BSN’s primary function is to provide a set of DLT-based cloud environment software[3], supporting traditional cloud service providers, data centers, and businesses in setting up private or public[4] distributed networks and thus simplifying the adoption of blockchain technology for their users.[5][2]
On April 25, 2020[6], The Blockchain-based Service Network (BSN) was announced for commercial use, categorized into Chinese and International operations.[7] On June 29, 2022, the BSN-DDC Network surpassed Ethereum’s transaction volume (938,166 transactions) within a 24-hour period (974,517 transactions).[8] In September 2022, the BSN Spartan Network, the equivalent of BSN-DDC outside Mainland China, was officially launched in Hong Kong with initial adopters including HSBC, Prenetics, and FUJIFILM Business Innovation Hong Kong.[9]
Technology Stacks
The Blockchain-based Service Network functions as an infrastructure network rather than a standalone blockchain protocol, integrating dozens of independent blockchain frameworks.[10][11] The BSN establishes a foundational cloud environment supporting the deployment of distributed Multi-Party Systems, or Public IT Systems[12], which allows developers on these platforms to use shared computing resources rather than installing a full set of cloud services or computing infrastructure. [13][14]
The technology stack of the Blockchain-based Service Network includes both Enterprise BSN and Public BSN. The latter operates under two distinct governance frameworks for Mainland China and international users.
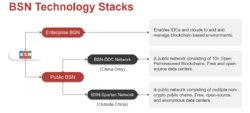
Enterprise BSN
Enterprise BSN is an enterprise-level software platform integrated into public cloud, private cloud, or intranet for enterprises and institutions to embed a blockchain-based environment into their existing systems.[15] While traditional cloud environments handle centralized private IT systems, Enterprise BSN, working in parallel, manages distributed Multi-Party Systems or Public IT Systems to establish a private network where developers can design, deploy, and manage the lifecycle of blockchain applications.[16]
Enterprise BSN's environment can manage cross-cloud, cross-framework, and cross-application virtual machines and resources directly on top of OpenStack.[17] The platform integrates permissioned frameworks like Hyperledger Fabric and FISCO BCOS and public blockchains such as Ethereum and EOS as operating systems.[18]
Public BSN
BSN-DDC Network
The BSN-DDC comprises over ten Open Permissioned Blockchains (OPBs), adapted from public chain blueprints such as Ethereum to align with Chinese regulatory frameworks.[19] The network operates exclusively in Mainland China and adopts Distributed Digital Certificate technology, a “Chinese version of NFT,” as the certification and distributed database technology that can be applied in business or government scenarios where digital proof is required.[20] The data center software of the BSN-DDC Network mandates permissions and KYC procedures.[21] Examples include Xi'an Qujiang Cultural Tourism and Chongqing News's Shangyou News, both of which have established DDC platforms on the BSN-DDC Network to promote local culture and tourism industries.[22]
BSN-Spartan Network
The BSN Spartan Network is a public infrastructure network built on the BSN Spartan data centers, which functions as the gateway to the network and is open-source, free, and KYC-free[23][24], operating exclusively outside Mainland China[25]. The BSN Spartan Network integrates several Non-Cryptocurrency Public Chains (NC Chains), which are non-crypto hard forks derived from their original public chains.[2] The network is developed to support the adoption of blockchain for mainstream enterprises without exposure to the volatility and regulatory uncertainty of the cryptocurrency market.[26]
Bifurcated Operation
According to the United States–China Economic and Security Review Commission’s investigation, the BSN architecture is bifurcated between Chinese and international users.[1] BSN China operates under the guidance of the BSN Development Association (BSNDA), which is backed by Chinese government-linked entities and major state-owned enterprises [27]and uses cloud infrastructure from China Mobile, China Telecom, and Baidu AI Cloud[28]. The BSN Spartan Network functions independently under the BSN Foundation based in Singapore, and uses Amazon Web Services[18] and other commercial cloud service providers in Hong Kong, USA, and Europe[28]. In November 2023, five founding members of the BSN Foundation were announced in Singapore: Blockdaemon, GFT Technologies, TOKO, Zeeve, and Red Date Technology, with membership from the USA, Europe, and Asia.[29]
Despite the separation of the Chinese vs international businesses, BSN's Chinese origins have elicited apprehension from some in the global community.[30] These concerns are reminiscent of challenges faced by companies such as TikTok vs DouYin.[31] On Nov 8, 2023, a U.S. bill[32], titled the Creating Legal Accountability for Rogue Innovators and Technology (CLARITY) Act, proposed to outlaw federal agencies from using the Blockchain-based Service Network (BSN) and its IT infrastructure service Spartan Network, along with the tech provider Red Date Technology over national security and privacy concerns.[33]
BSN Foundation member Red Date Technology responded to media requests for comment in a statement clarifying that BSN is a politically neutral, application-agnostic technology initiative. The Spartan Network is fully open source for code auditing and is under decentralized governance by the Singapore-based BSN Foundation. The Hong Kong-based Red Date Technology, a voting member of the Foundation, holds no special status.[26]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "THE CHINESE COMMUNIST PARTY'S ECONOMIC AND TECHNOLOGICAL AMBITIONS: SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY, NEW MOBILITY, CLOUD COMPUTING, AND DIGITAL CURRENCY". p. 200. https://www.uscc.gov/sites/default/files/2021-11/Chapter_2_Section_2--CCPs_Economic_and_Technological_Ambitions.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kharpal, Arjun (2022-05-23). "China's state-backed blockchain company is set to launch its first major international project" (in en). https://www.cnbc.com/2022/05/22/chinas-state-backed-blockchain-firm-to-launch-major-overseas-project.html.
- ↑ Areddy, James T. (2021-05-11). "Beijing Tries to Put Its Imprint on Blockchain" (in en-US). Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. https://www.wsj.com/articles/beijing-tries-to-put-its-imprint-on-blockchain-11620735603.
- ↑ "China's BSN predicted as long-term global project, still ahead of others" (in en). 2020-11-14. https://cointelegraph.com/news/china-s-bsn-predicted-as-long-term-global-project-still-ahead-of-others.
- ↑ Bhimani, Alnoor; Hausken, Kjell; Arif, Sameen (2022-08-01). "Do national development factors affect cryptocurrency adoption?". Technological Forecasting and Social Change 181: 121739. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121739. ISSN 0040-1625. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162522002657.
- ↑ "Commercial use of China's blockchain-based service network kicks off - Xinhua | English.news.cn". http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2020-04/26/c_139009492.htm.
- ↑ Yuming, Lian (2022-09-05) (in en). Sovereignty Blockchain 2.0: New Forces Changing the World of Future. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-981-19-3862-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=2HGHEAAAQBAJ&dq=blockchain-based+service+network&pg=PA40.
- ↑ "Back to Fundamentals: Five Predictions for Crypto in 2023". Newman Capital. 4 January 2023. https://www.newmancapital.com/post/5-predictions-for-crypto-2023.
- ↑ "HSBC, Hong Kong firms sign up for China's state-backed blockchain" (in en). 2022-09-06. https://www.scmp.com/tech/tech-trends/article/3191553/chinas-state-backed-architect-non-crypto-blockchain-makes-first.
- ↑ "China's New Belt and Road Has Less Concrete, More Blockchain" (in en). Bloomberg.com. 2021-03-24. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-03-24/china-s-new-belt-and-road-has-less-concrete-more-blockchain.
- ↑ Ma, Winston (2021-01-19) (in en). The Digital War: How China's Tech Power Shapes the Future of AI, Blockchain and Cyberspace. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-74891-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=lAYTEAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ DiBiasio, Jame (2022-05-24). "BSN is building blockchain future without the crypto" (in en-US). https://www.digfingroup.com/bsn-spartan/.
- ↑ "China Launches National Blockchain Network in 100 Cities - IEEE Spectrum" (in en). https://spectrum.ieee.org/china-launches-national-blockchain-network-100-cities.
- ↑ Dhuddu, Rajesh; Mahankali, Srinivas (2021-03-13) (in en). Blockchain in e-Governance: Driving the next Frontier in G2C Services (English ed.). BPB Publications. ISBN 978-93-90684-46-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=sxcjEAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ Gordon, David; Nouwens, Meia (2022-11-29) (in en). The Digital Silk Road: China's Technological Rise and the Geopolitics of Cyberspace. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-000-88520-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=gXqfEAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ "亚马逊云科技案例研究:红枣科技" (in zh-CN). https://aws.amazon.com/cn/solutions/case-studies/reddate-case-study/.
- ↑ Clohessy, Trevor (2023-02-24) (in en). Blockchain in Supply Chain Digital Transformation. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-000-84420-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=IGqwEAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "China May Have Banned Bitcoin, But Its Blockchain Ambitions May Help Other Nations Launch CBDCs". Nasdaq. 14 December 2023. https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/china-may-have-banned-bitcoin-but-its-blockchain-ambitions-may-help-other-nations-launch.
- ↑ Feng, Coco (25 January 2022). "China introduces state-backed NFT platform unlinked to cryptocurrencies". South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/tech/tech-trends/article/3164681/china-introduces-state-backed-nft-platform-unlinked.
- ↑ Ma, Winston; Huang, Ken (2022-08-19) (in en). Blockchain and Web3: Building the Cryptocurrency, Privacy, and Security Foundations of the Metaverse. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-89110-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=v5SDEAAAQBAJ&q=BSN+Open+Permissioned+Blockchains.
- ↑ Harsono, Hugh (2022). "The Utilization of Web3 Native Resources to Create a Centralized Base of Authoritarian Power". Journal of International Affairs 75 (1): 153–168. ISSN 0022-197X. https://www.jstor.org/stable/27203126.
- ↑ "中办国办印发《"十四五"文化发展规划》丨数字艺术每周观察(8.22) - 21财经" (in zh). 26 August 2022. https://m.21jingji.com/article/20220826/herald/8b9a660225daf30be6d79d9bdbb2184c.html.
- ↑ Shen, Xinmei (6 September 2022). "China's state-backed architect of non-crypto blockchain makes first major push outside mainland". South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/tech/tech-trends/article/3191553/chinas-state-backed-architect-non-crypto-blockchain-makes-first.
- ↑ Lam, Sheila (2022-10-10). "Can BSN Spartan Network Reignite Public Blockchain Interest?" (in en). https://www.cdotrends.com/story/17422/can-bsn-spartan-network-reignite-public-blockchain-interest.
- ↑ "China-Backed Crypto Guru Wants to Unify World's Blockchains" (in en). Bloomberg.com. 2020-07-26. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-07-26/china-backed-crypto-guru-wants-to-unify-the-world-s-blockchains.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "US lawmakers target Chinese blockchains in Web3 decoupling push" (in en). 2023-11-09. https://www.scmp.com/tech/policy/article/3240921/us-lawmakers-target-chinese-blockchains-bsn-conflux-bill-brings-tech-decoupling-web3.
- ↑ V.S, Anoop; S, Asharaf; Goldston, Justin; Williams, Samson (2022-12-23) (in en). Blockchain for Industry 4.0: Blockchain for Industry 4.0: Emergence, Challenges, and Opportunities. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-000-81244-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=h3qfEAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Knowledge Base: Blockchain-based Service Network (BSN, 区块链服务网络)" (in en). 2 July 2021. https://digichina.stanford.edu/work/knowledge-base-blockchain-based-service-network-bsn-%E5%8C%BA%E5%9D%97%E9%93%BE%E6%9C%8D%E5%8A%A1%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C/.
- ↑ "Blockchain Infrastructure Organization BSN Foundation Officially Established in Singapore" (in en). https://www.binance.com/en/feed/post/2023-11-16-blockchain-infrastructure-organization-bsn-foundation-officially-established-in-singapore-1789024.
- ↑ Ekman, Alice. "CHINA'S BLOCKCHAIN AND CRYPTOCURRENCY AMBITIONS". https://www.iss.europa.eu/sites/default/files/EUISSFiles/Brief_15_2021.pdf.
- ↑ "China's BSN builds blockchain systems on its own terms — with no crypto and Xi's guiding hand" (in en). https://www.dlnews.com/articles/markets/china-bsn-builds-crypto-systems-without-cryptocurrencies/.
- ↑ Nunn, Zach. "A Bill". https://nunn.house.gov/sites/evo-subsites/nunn.house.gov/files/evo-media-document/clarity-act.vf_.pdf.
- ↑ "Nunn Introduces Bipartisan Legislation To Combat Critical Chinese National Security Threat | Representative Nunn" (in en). 2023-11-08. http://nunn.house.gov/media/press-releases/nunn-introduces-bipartisan-legislation-combat-critical-chinese-national.
 |
