Chemistry:Deflectin
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
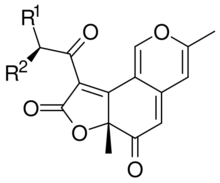
A deflectin is one of a family of antibiotic chemicals produced by Aspergillus deflectus which contain a 6H-furo[2,3-h]-2-benzopyran-6,8(6aH)-dione core.
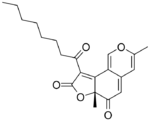
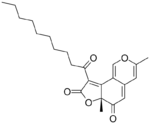
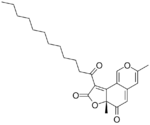
Deflectins are yellow coloured crystalline substances when pure. They react with ammonia, by replacing an oxygen atom in the six-membered ring with an NH group. They are weak acids. On adding a strong base to an alcoholic solution of deflectin, it show a red colour for a short time.[1] Deflectin 1a contains a 1-oxooctyl side chain. It has a melting point of 161 °C. Deflectin 1b contains a ten carbon side chain and melts at 152 °C. Deflectin 1c has a 12-atom side chain and melts at 141 °C.[1]
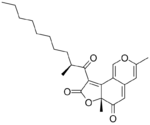
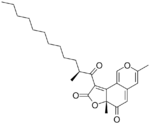
Deflectin 2a melts at 122 °C. It has a 10 carbon atom side chain with a 2-methyl branch. Deflectin 2b is similar but the side chain is 2 atoms longer. It melts at 111 °C.[2]
Chemical structures
|
|
|
|
|
| Deflectin 1a | Deflectin 1b | Deflectin 1c | Deflectin 2a | Deflectin 2b |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Anke, H.; Kremmer, T.; Ho..fle, G. (August 1981). "Deflectins, New Antimicrobial Azaphilones From Aspergillus deflectus". The Journal of Antibiotics 34 (8): 923–928. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.34.923. PMID 7319924. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/antibiotics1968/34/8/34_8_923/_pdf.
- ↑ Bycroft, Barrie W. (1987) (in en). Dictionary of Antibiotics & Related Substances. CRC Press. p. 258. ISBN 9780412254505. https://books.google.com/books?id=7ZBIdy-KpSYC&pg=PA258.
 |
