Chemistry:Michaelis–Becker reaction
From HandWiki
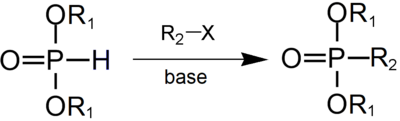
The Michaelis–Becker reaction is the reaction of a hydrogen phosphonate with a base, followed by a nucleophilic substitution of phosphorus on a haloalkane, to give an alkyl phosphonate. Yields of this reaction are often lower than the corresponding Michaelis–Arbuzov reaction.[1][2]
Further reading
- Savignac, Philippe; Iorga, Bogdan (2003). Modern phosphonate chemistry. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-1099-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=iH5PBtf3_MQC&pg=PA411.
References
- ↑ Fletcher, M.D. Organophosphorus Reagents; Murphy, P.J. Ed.; University Press: Oxford, 2002; pp. 185.
- ↑ Murphy, Dr. Patrick J (2004). Organophosphorus reagents: a practical approach in chemistry. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-850262-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=mBfS8kNZA5gC&pg=PA185.
 |