Chemistry:Surtout de table

A surtout de table is an ornamental centrepiece displayed on a formal dining table. Evolving from a simple plate or bowl on which to stand candlesticks and condiments, a surtout de table often took the form of a long galleried tray made of precious or gilded metals, on which a series of other objects were placed for display. It was often made in sections allowing its length to be determined by the leaves added to the table. During the later half of the 18th century and throughout the 19th century, no formal table was considered compete without one. Today, they are still seen and used in the most formal dining rooms.
The term can refer either to a large centrepiece object, or the tray type on which objects are placed, or the two in combination.
History

The surtout de table first appeared in the 17th century and was a utilitarian object designed to hold candles, and protect a polished wooden table from the staining caused by spillage from the salt and vinegars in the condiments.[1] As the great central and ceremonial salt cellars fell from favour, to be replaced by smaller individual salt cellars, during the first half of the 18th century, the surtout de table evolved to fill the role of ornamental table centrepiece. It often took the form of a raised galleried tray which would be filled with matching candelabra, figurines, vases and epergnes, the gallery itself sometimes containing candle sconces. They were not always constructed from precious metals; porcelain and glass were often used,[2] as might be sculptures made from sugar. The top of the tray was often a mirror, to show the underside of the objects on it, and increase reflected light.
It was not uncommon, if a surtout de table were commissioned for a specific house, for an indigenous theme to be used in the style. Hence, a hunting lodge may have a surtout de table with figurines of dogs and their quarry while a grander town palace would feature the most fashionable Rococo or Baroque styles of the day.
During the 1850s, the fashion for themed dining table decoration reached its apogee and the surtout de table reflected this. Porcelain factories such as Meissen produced elaborate models and figurines which replaced the classical statuary of the Empire style with coloured porcelain mountains, rustic scenes with cattle and goats and, occasionally, even a jungle theme complete with lifelike porcelain snakes.[3]
Notable examples
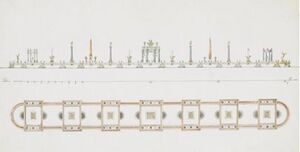
Notable examples of surtouts de table include those made the Italian goldsmith Luigi Valadier, often designed by his son, the architect Giuseppe Valadier. These monumental surtouts de table often represent Roman cities in miniature, complete with temples, colonnades and triumphal arches of coloured marbles and alabaster mounted on gold and mosaic pediments.[4]
Waddesdon Manor in England is now home to a vast 6.7 metre long gilt tray surtout de table made by Pierre-Philippe Thomire (1751-1843). Made circa 1818, it was given to Prince Ruffo della Scaletta by Louis XVIII.[5]
France distributing wreaths of glory is the name and theme of a large silver plate on bronze surtout de table commissioned from the Parisian jeweller Charles Christofle by Napoleon III in 1852. Intended for use at state banquets at the Tuileries Palace, the gilded tray contains a garniture of fifteen sculptures. The central figure is a winged Victory bearing laurel leaves which she awards to two horse-drawn chariots representing war and peace. At Victory's feet sit figurines representing Justice, Concord, Force and Religion.[6]
The surtout de table was still in situ when the palace caught fire in 1871. It was pulled from the smoking debris damaged but intact. It has never been restored and is today displayed with its smoke-blackened gilt and dents at the Musée des Arts Décoratifs in Paris.[7]
-
Chatsworth House
Notes
- ↑ The Louvre Retrieved 27 January 2016.
- ↑ Musee Chateau de Fontainebleau retrieved 21 January 2016
- ↑ See the Surtout de table by Charles-Jean Avisseau (1795-1861). Exhibited at the 1867 Exposition Universelle. 1903 Infantry: 10573 Musée des Arts Décoratifs, Paris.
- ↑ Musee Chateau de Fontainebleau retrieved 21 January 2016
- ↑ Yannick Chastang Conservation retrieved 27 January 2016
- ↑ Napoleon.org retrieved 28 January 2016
- ↑ Napoleon.org retrieved 28 January 2016






