Earth:Foiba

A foiba (from Italian: pronounced [ˈfɔiba]; plural: foibe ['fɔibe] or foibas) — jama (pronounced [ˈja̟mə]) in South Slavic languages scientific and colloquial vocabulary (borrowed since early research in the Western Balkan Dinaric Alpine karst) — is a type of deep natural sinkhole, doline, or sink, and is a collapsed portion of bedrock above a void. Sinks may be a sheer vertical opening into a cave or a shallow depression of many hectares. They are common in the Karst (Carso) region shared by Italy and Slovenia, as well as in a karst of Dinaric Alps in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro and, Croatia. The foibe massacres, a war crime that took place during and after World War II, take their name from the foibe.
Etymology
The Italian name "foiba" derives from Friulan "foibe", which in turn derives from the Latin fŏvea (meaning "pit" or "chasm").[1][2] The oldest document on which it is reported is an official report in 1770, written by the Italian naturalist Alberto Fortis,[3] who wrote a series of books on the Dalmatian karst.
Description

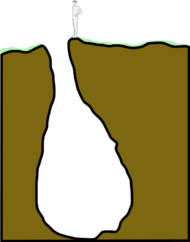
They are chasms excavated by water erosion, have the shape of an inverted funnel, and can be up to 200 metres (660 ft) deep. Such formations number in the hundreds in Istria. In karst areas, a sinkhole, sink, or doline is a closed depression draining underground. It can be cylindrical, conical, bowl-shaped or dish-shaped. The diameter ranges from a few to many hundreds of metres. The name "doline" comes from dolina, the Slovenian word for this very common feature. The term "foiba" may also refer to a deep wide chasm of a river at the place where it goes underground.[4]
Foibe massacres
During and right after the end of World War II, OZNA and Yugoslav Partisans killed a number between 11,000[5][6] and 20,000[7] of the local ethnic Italian population (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians), as well against anti-communists in general (even Croats and Slovenes), usually associated with Fascism, Nazism and collaboration with Axis,[7][5] as well as against real, potential or presumed opponents of Tito communism[8] by throwing their still living bodies into the foibe. This event is known as foibe massacres. The type of attack was state terrorism,[7][9] reprisal killings,[7][10] and ethnic cleansing against Italians.[7]Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag[11]
In literature
Foiba is also the name of the well-known sinkhole that opens near the castle of Montecuccoli, in Pisino, and of the stream that flows into it. The place plays a central role in Jules Verne's novel Mathias Sandorf.[12]
See also
- Foibe massacres
- Karst Plateau
References
- ↑ Ottavio Lurati, Toponymie et géologie, in Quaderni di semantica, year XXIX, number 2, December 2008, 443.
- ↑ "Foiba" (in it). http://www.treccani.it/vocabolario/foiba/.
- ↑ Hofmann, Peter (2014) (in de). Unterirdisches Istrien: Ein Exkursionsführer zu den ungewöhnlichsten Höhlen und Karsterscheinungen. BoD – Books on Demand. p. 33. ISBN 978-3732298501. https://books.google.com/books?id=qcT6AgAAQBAJ&q=foiba. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ↑ "Glossary of speleology: letter F". http://www.speleogenesis.info/glossary/glossary_by_letter.php?Authors=f.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Guido Rumici (2002) (in it). Infoibati (1943-1945). Ugo Mursia Editore. ISBN 9788842529996. https://books.google.com/books?id=x0ZnAAAAMAAJ&q=massacri+foibe+sloveni+croati+anticomunisti.
- ↑ Micol Sarfatti (11 February 2013). "Perché quasi nessuno ricorda le foibe?" (in Italian). http://www.huffingtonpost.it/micol-sarfatti/perche-quasi-nessuno-ricorda-le-foibe_b_2658946.html.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Collective Identities and Post-War Violence in Europe, 1944–48. Springer International Publishing. 2021. p. 20. ISBN 9783030783860. https://books.google.com/books?id=xXRREAAAQBAJ&dq=foibe+massacres+istrian+dalmatian+italians&pg=PA20.
- ↑ "Relazione della Commissione storico-culturale italo-slovena - V Periodo 1941-1945". http://www.kozina.com/premik/porita4.htm.
- ↑ Il tempo e la storia: Le Foibe, Rai tv, Raoul Pupo
- ↑ Lowe, Keith (2012). Savage continent. London. ISBN 9780241962220. https://books.google.com/books?id=5sKNeVcOH3wC&q=Belgium.
- ↑ "Le foibe e il confine orientale" (in it). https://www.convittocicogniniprato.edu.it/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/dossier_foibe_e_confine_orientale.pdf.
- ↑ "La Foiba di Pisino che ispirò Jules Verne" (in it). 22 August 2009. https://www.anvgd.it/la-foiba-di-pisino-che-ispiro-jules-verne-viaroma100net-21-ago/.
External links
 |
