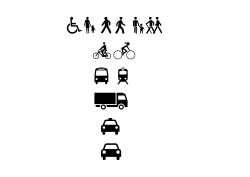
Earth:Green transport hierarchy
The green transport hierarchy (Canada), street user hierarchy (US), sustainable transport hierarchy (Wales),[1] urban transport hierarchy or road user hierarchy (Australia, UK)[2] is a hierarchy of modes of passenger transport prioritising green transport.[3] It is a concept used in transport reform groups worldwide[4][5] and in policy design.[6] In 2020, the UK government consulted about adding to the Highway Code a road user hierarchy prioritising pedestrians.[7] It is a key characteristic of Australian transport planning.[8]
| Green transport hierarchy |
|---|
| Pedestrians |
| Bicycles |
| Public transit |
| Trucks and commercial vehicles |
| Taxis |
| High occupancy vehicles |
| Cars and single occupancy vehicles |
History
The Green Transportation Hierarchy: A Guide for Personal & Public Decision-Making by Chris Bradshaw was first published September 1994[9] and revised June 2004.[citation needed] As part of a pedestrian advocacy group in the United States, he proposed the hierarchy ranking passenger transport based on environmental emissions. The reviewed ranking listed, in order: walking, cycling, public transport, car sharing, and finally private car.[3]
It was first prepared for Ottawalk and the Transportation Working Committee of the Ottawa-Carleton Round-table on the Environment in January 1992, only stating 'Walk, Cycle, Bus, Truck, Car'.[10]
Factors
- Mode
- Energy source
- Trip length
- Trip speed
- Vehicle size
- Passenger load factor
- Trip segment
- Trip purpose
- Traveller
Adoption
The author directed the hierarchy at both individual lifestyle choices and public authorities who should officially direct their resources – funds, moral suasion, and formal sanctions – based on the factors.
Bradshaw described the hierarchy to be logical, but the effect of applying it to seem radical.[11]
The model rejects the concept of the balanced transportation system, where users are assumed to be free to choose from amongst many different yet ‘equally valid’ modes. This is because choices incorporating factors that are ranked low are seen as generally having a high impact on other choices.
See also
- Alternatives to car use
- Bicycle-friendly
- Bill Boaks campaigned for pedestrian priority everywhere
- Car-free movement
- Complete streets
- Cycling advocacy
- Cyclability
- Induced demand
- Jaywalking
- Peak car
- Planetizen
- Priority (right of way)
- Reclaim the Streets
- Road hierarchy
- Road traffic safety
- Traffic § Rules of the road
- Settlement hierarchy
- Street hierarchy
- Street reclamation
- Sustainable transport
- Traffic bottleneck
- Traffic code
- Traffic conflict
- Traffic flow
- Transportation demand management
- Walkability
- Walking audit
References
- ↑ Reid, Carlton. "Car Dependency Must End, Transport Minister Lee Waters Tells Welsh Parliament" (in en). Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/carltonreid/2020/11/18/car-dependency-must-end-transport-minister-lee-waters-tells-welsh-parliament/.
- ↑ Walking, Riding and Access to Public Transport: Draft report for discussion. Australian Government Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications. October 2012. ISBN 978-1-921769-90-0. https://infrastructure.gov.au/infrastructure/pab/active_transport/files/active_travel_discussion.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Practices and policies of green urban transport in China". Journeys (Berghahn Books) 1 (4): 26–35. 2010. https://www.academia.edu/download/30908369/JOURNEYS_May2010_(full).pdf#page=26.
- ↑ "Pedestrian and bicyclist safety and mobility in Europe /". https://www.loc.gov/item/2010443270/.
- ↑ Fischer, Edward L; International Scanning Study Team (U.S.), FHWA International Technology Scanning Program; United States; Federal Highway Administration; Office of International Programs; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials; American Trade Initiatives, Inc (2010) (in English). Pedestrian and bicyclist safety and mobility in Europe. Washington, DC: Office of International Programs, U.S. Federal Highway Administration. OCLC 537680874. http://purl.fdlp.gov/GPO/gpo3988. Retrieved 2021-11-06.
- ↑ Zhenqi, Chen; Weichi, Lu (2016-11-09), "Toward a Green Transport System: A Review of Non-technical Methodologies for Developing Cities", Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing (Cham: Springer International Publishing): pp. 509–520, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-38789-5_59, ISBN 978-3-319-38787-1, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-38789-5_59, retrieved 2023-12-05
- ↑ "What do Highway Code proposals mean for pedestrians and cyclists?" (in en). the Guardian. 28 July 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/environment/bike-blog/2020/jul/28/what-do-the-highway-code-proposals-mean-for-pedestrians-and-cyclists.
- ↑ "2. Key characteristics of active travel" (in en). https://www.atap.gov.au/mode-specific-guidance/active-travel/2-key-characteristics-of-active-travel.
- ↑ Yang, Jiawen; Alterman, Rachelle; Li, Bin (2020). "References". Value Capture Beyond Public Land Leasing (Lincoln Institute of Land Policy): 45–49. https://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep25487.10. Retrieved 2021-05-12.
- ↑ "The Valuing of Trips - Transportation - Sierra Club". https://vault.sierraclub.org/sprawl/articles/trips.asp.
- ↑ see a separate paper by the author, ‘Using Our Feet to Reduce Our Footprint: The Importance of Scale in Life’ (1997) for the ‘NRFUT’ system of comparing the ‘footprint’ of different trips.
External links
 |