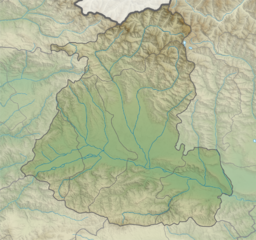
Earth:Keli Highland
| Keli Highland | |
|---|---|
 Keli Lake and Keli Highland | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 3,736 m (12,257 ft) [1] |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] 42°27′N 44°15′E / 42.45°N 44.25°E [1] |
| Geography | |
| Parent range | Greater Caucasus |
The Keli (Qeli) Highland (Georgian: ყელის ზეგანი, qelis zegani) is a volcanic field in Georgia on the western side of the Jvari Pass south to the Greater Caucasus range. More than thirty volcanic edifices on an area of 20x30km2 make up this volcanic field, which consists mostly of monogenetic volcanic structures.[2] The lavas are rhyolites, trachyandesites and andesites.[3]
The rivers Tetri Aragvi, Patara Liakhvi, Ksani and Didi Liakhvi originate from the Keli volcanic area, and some peaks drain into the Terek river. Several mountain ranges separate the area into distinct high plains. Quaternary Dacite lava flows overlie thich Mesozoic sedimentary sequences.[2][4]
Western Khorisar (elevation 3736 m) and Didi-Nepiskalo (3694 m) are the highest summits close to the crest of the Greater Caucasus.[4] In the northeastern part of the system are the Nepiskalo volcanoes and several smaller structures. The Patara-Nepiskalo volcano is strongly degraded by glacial action and may have had a caldera. Other volcanoes are Sharkhokh, Northern Shadilkhokh, and Southern Shadilkhokh in the western Kaidon range and the lava flows created by the latter two volcanoes between the Arkhi Range, Keli Lake and the Aragvistavi river, the Ermani–Akhubata lava plateau, Eastern Sharkhokh volcano and several lava domes (Ermani, Fidarkokh and others).[2][4]
Nikoloz Skhirtladze first studied the volcanoes and divided the volcanism into glacial and postglacial stages.[2] Later research indicated three phases of volcanism: A first phase 245–170ka involved lava dome formation including Kordieritovyi dome, Patara-Nepiskalo volcano and Kabardzhin–Sakokhe centre and its associated a laval flow in the Aragvi valley. A second phase 137–70ka with large scale effusive activity included the "Pyramidal Peak" Volcano which dammed local rivers with lava flows. From 90ka on activity formed Didi-Nepiskalo and the Ekisom and Khorisar domes. The third phase less than 30ka with evidence that it continued into the Holocene formed Eastern Khorisa and Ploskaya Vershina. Activity of East Khorisar Volcano spans both stages and created lava flows in the Terek river valley, at the end involving the collapse of the northern flank of its crater.[4][3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Keli Highland". Smithsonian Institution. https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=214040.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Lebedev, V. A.; Vashakidze, G. T.; Arutyunyan, E. V.; Yakushev, A. I. (2011). "Geochronology and evolution of quaternary volcanism at the Keli Highland, Greater Caucasus". Geochemistry International 49 (11): 1120–1144. doi:10.1134/S0016702911090035. ISSN 0016-7029.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lebedev, V. A.; Chernyshev, I. V.; Sharkov, E. V. (2012). "Geochronological scale and evolution of late Cenozoic magmatism within the Caucasian segment of the alpine belt". Doklady Earth Sciences 441 (2): 1656–1660. doi:10.1134/S1028334X11120051. ISSN 1028-334X.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Lebedev, V. A.; Chernyshev, I. V.; Chugaev, A. V.; Vashakidze, G. T. (2007). "Geochronology of Quaternary volcanism of the Krestovyi Pass Region, Kazbek Neovolcanic Area, Greater Caucasus". Doklady Earth Sciences 413 (1): 272–276. doi:10.1134/S1028334X07020328. ISSN 1028-334X.
 |