Earth:Loxodromic navigation
From HandWiki
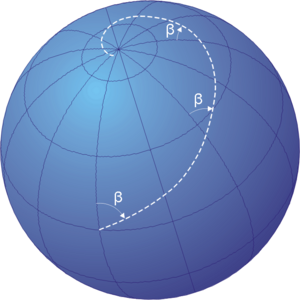
Loxodromic navigation (from Greek λοξóς, oblique, and δρóμος, path) is a method of navigation by following a rhumb line, a curve on the surface of the Earth that follows the same angle at the intersection with each meridian. This serves to maintain a steady course in sailing.[1]
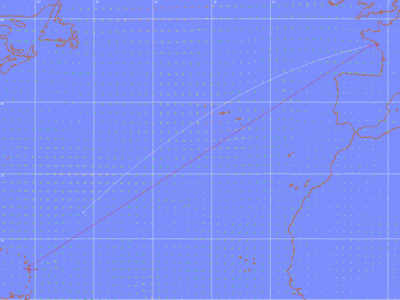
Navigating on a spherical surface with a fixed course ( in the figure) results in a spiral path that approaches the North Pole for courses ranging from 270º to 090º and the South Pole for courses from 090º to 270º. On a nautical chart plotted according to the Mercator projection, a loxodromic course appears as a straight line.
Comparison Chart
See also
- Great circle navigation
- Windrose network
- Map
- Portolan map
- Marine sandglass
- Compass rose
- Isoazimuthal
References
- ↑ Adam Weintrit; Tomasz Neumann (7 June 2011). Methods and Algorithms in Navigation: Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation. CRC Press. pp. 139–. ISBN 978-0-415-69114-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=buMsPGyE7boC&q=loxodromic+navigation&pg=PA139.
External links
 |
