Earth:Mount Douglas (Alaska)
| Mount Douglas | |
|---|---|
 Crater lake at the summit, June 1990 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 7,021 ft (2,140 m) |
| Prominence | 6,300 ft (1,900 m) |
| Listing |
|
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 58°51′36″N 153°31′59″W / 58.86°N 153.53306°W |
| Geography | |
| Location | Katmai National Park and Preserve, Alaska, U.S. |
| Parent range | Aleutian Range |
| Topo map | USGS Afognak D-5 |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Aleutian Arc |
| Last eruption | Holocene |
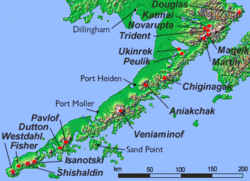
Mount Douglas is a stratovolcano located south of Kamishak Bay, near the northeasternmost part of the Alaska Peninsula. It lies in the Katmai National Park and Preserve in Kenai Peninsula Borough. The mountain was officially named in 1906 after nearby Cape Douglas based on a 1904 report by USGS geologist G. C. Martin. The Alaska Volcano Observatory currently rates Douglas as Level of Concern Color Code Not Assigned.
The volcano has a warm and highly acidic crater lake approximately 160 m (525 ft) wide. In 1982, the lake had a temperature of 21 °C and a pH of 1, and temperatures of 114-118°C were measured in 1991. At the north flank of the volcano unglaciated and relatively uneroded lava flows are found. The last eruption is not known, but probably occurred during the Holocene.[1]
See also
- List of mountain peaks of North America
- List of mountain peaks of the United States
- List of Ultras of the United States
- List of volcanoes in the United States
References
Other Sources
- Volcanoes of the Alaska Peninsula and Aleutian Islands-Selected Photographs
- Mt. Douglas - Alaska Volcano Observatory
 |