Earth:Sebago Granite
| Sebago Granite Stratigraphic range: Carboniferous | |
|---|---|
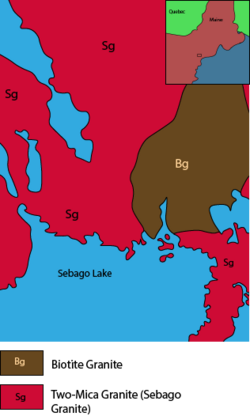 A map of the Sebago Granite unit and the surrounding biotite granite, modified from the Naples Quadrangle USGS geologic map.[1] | |
| Type | Geological Formation |
| Overlies | Central Maine Belt |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Granite |
| Location | |
| Region | Southern Maine, United States |
| Country | United States |
The Sebago Granite is a Carboniferous aged granite that appears in southern Maine.[2][3] The formation covers around 400 square kilometers in area, and intruded into the surrounding rock approximately 325 million years ago.[2][3][4]
Location
The Sebago Granite is a geological formation that makes up the Sebago Pluton (or the Sebago Granite Pluton) that appears mainly throughout southern Maine, near the Sebago Lake region.[2] It is also considered to be part of the New Hampshire Plutonic Suites, and partly extends into New Hampshire.[5][6]
Composition
This Sebago Granite is a 2-mica granite, and is mainly composed of potassium feldspar, quartz, biotite, and muscovite. Its composition is homogeneous in nature with fine to medium grain sizes.[2][5] The proportions of biotite and muscovite vary throughout the unit, and garnet is common in some locations.[3] The uranium concentration in this unit is noteworthy, but varies greatly throughout the formation.[3][7]
There are two phases of the Sebago Granite: a white phase and a pink phase. The pink phase is younger, and regularly cross-cuts the white phase throughout the formation. Some debate still exists as to whether or not these are truly two separate phases, or if the pink granite is simply the result of an alteration to the white granite.[8] There are significant amounts of zircon present, which have been used to determine the age of the formation.[8]
| Oxide | White Phase | Pink Phase |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 71.8 | 71.6 |
| TiO2 | 0.22 | 0.24 |
| Al2O3 | 14.9 | 14.8 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.41 | 1.69 |
| MgO | 0.33 | 0.38 |
| CaO | 1.07 | 1.12 |
| Na2O | 3.06 | 3.33 |
| K2O | 5.92 | 5.62 |
| P2O5 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| MnO | <0.02 | <0.02 |
| LOI | 0.74 | 0.61 |
| Total | 99.63 | 99.54 |
Structure
The unit is nearly horizontal (although it dips slightly to the northeast), and gravity studies indicate that it is an average of 1 kilometer thick.[8] The thickness of the granite varies greatly around the formation, however, and it can range from about 0.5 kilometers to 2 kilometers.[5]
Related Lithologies
The Sebago Granite makes up the Sebago Pluton, which is itself a part of the Sebago Migmatite Domaine.[9] The larger Sebago Batholith is composed of both the Sebago Granite and the Sebago Pegmatite System.[2] The pegmatites from the Sebago Pegmatite Group surround the granite within the batholith. These two units differ in grain size, as well as composition; while the Sebago Granite is homogeneous, the Sebago Pegmatite Group is heterogeneous.[9][2] The formation appears near the Songo Pluton and overlies the Central Maine Belt.[2][9] The Sebago Granite has been intruded by several mafic dikes, and at least 3 of these dikes have been identified in the field.[4]
Age and History
The Sebago Granite initially intruded into the surrounding metasedimentary rock 325 million years ago. However, some studies indicate that the granitic intrusion could have occurred in multiple phases rather than occurring in a singular event. It then cooled slowly for 50 million years following this. However, the pink and white phases appear to have finished cooling at different times (272 million years ago and 282 million years ago, respectively).[3][8][10] The remainder of the pluton then cooled at a much faster rate for another 50 million years in another phase related to tectonic uplift.[8][5] Although the Sebago Granite is igneous in origin, the muscovite present throughout the unit indicates some partial melting of surrounding sedimentary or metasedimentary rocks at some point in its history.[8]
References
- ↑ "NGMDB Product Description Page". https://ngmdb.usgs.gov/Prodesc/proddesc_64288.htm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Wise, Michael A.; Brown, Cathleen D. (2010-04-15). "Mineral chemistry, petrology and geochemistry of the Sebago granite-pegmatite system, southern Maine, USA". Journal of Geosciences 55 (1): 3–26. doi:10.3190/jgeosci.061. ISSN 1802-6222. http://www.jgeosci.org/content/jgeosci.061.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Tomascak, P. B.; Krogstad, Eirik J.; Walker, Richard J. (1996-09-01). "Nature of the crust in Maine, USA: evidence from the Sebago batholith" (in en). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology 125 (1): 45–59. doi:10.1007/s004100050205. ISSN 1432-0967. Bibcode: 1996CoMP..125...45T. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050205.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Gibson, David; Osthoff, Donald; Rerrick, Chase (2017-10-01). "C2: Field Relations, Petrography and Provenance of Mafic Dikes, Western Maine". New England Intercollegiate Geological Conference 2017: 273–286. doi:10.26780/2017.001.0015. https://scarab.bates.edu/neigc2017/day3/tripc/2.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Behn, Mark D.; J Dykstra Eusden, Jr; III, John A. Notte (2011-02-09). "A three-dimensional gravity model of the southern contact of the Sebago pluton, Maine" (in en). Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 35 (6): 649–656. doi:10.1139/e98-010. https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/abs/10.1139/e98-010.
- ↑ "NGMDB Product Description Page". https://ngmdb.usgs.gov/Prodesc/proddesc_64288.htm.
- ↑ Wathen, John B. (2020-10-28), "The Effect of Uranium Siting in Two-Mica Granites on Uranium Concentrations and Radon Activity in Ground Water", Radon, Radium, and Other Radioactivity in Ground Water (CRC Press): pp. 31–46, doi:10.1201/9781003069836-4, ISBN 978-1-003-06983-6, http://dx.doi.org/10.1201/9781003069836-4, retrieved 2021-03-27
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 Aleinikoff, John N.; Moench, Robert H.; Lyons, John B. (1985-08-01). "Carboniferous U-Pb age of the Sebago batholith, southwestern Maine: Metamorphic and tectonic implications" (in en). GSA Bulletin 96 (8): 990–996. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1985)96<990:CUAOTS>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606. Bibcode: 1985GSAB...96..990A. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article/96/8/990/203089/Carboniferous-U-Pb-age-of-the-Sebago-batholith.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Webber, Karen L.; Simmons, William B.; Falster, Alexander U.; Hanson, Sarah L. (2019-09-30). "Anatectic pegmatites of the Oxford County pegmatite field, Maine, USAAnatectic Pegmatites of the Oxford County Pegmatite Field, Maine" (in en). The Canadian Mineralogist 57 (5): 811–815. doi:10.3749/canmin.AB00028. ISSN 0008-4476. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/canmin/article/57/5/811/573910/Anatectic-pegmatites-of-the-Oxford-County.
- ↑ Tomascak, Paul B.; Krogstad, Eirik J.; Walker, Richard J. (1996). "U-Pb Monazite Geochronology of Granitic Rocks from Maine: Implications for Late Paleozoic Tectonics in the Northern Appalachians". The Journal of Geology 104 (2): 185–195. doi:10.1086/629813. ISSN 0022-1376. Bibcode: 1996JG....104..185T. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30064163.
