Earth:Southern England Chalk Formation


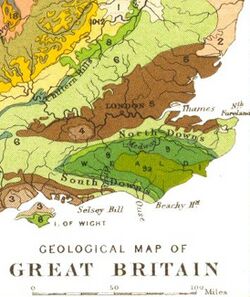
The Chalk Formation of Southern England is a system of chalk downland in the south of England . The formation is perhaps best known for Salisbury Plain, the location of Stonehenge, the Isle of Wight, and the twin ridgeways of the North Downs and South Downs.
Geography

The North Downs are confined chiefly to the counties of Kent and Surrey, and the South to Sussex. Each forms a well-defined long range springing from the chalk area of Dorset and Hampshire, to which, though broken up into a great number of short ranges and groups of hills, the general name of the Western Downs is given. The Downs enclose the rich district of the Weald, where the chalk has eroded to form a much flatter landscape.
In Wiltshire is Salisbury Plain, the Wiltshire Downs, and Cranborne Chase, all three famous for their archaeology, and it was on these downs that Augustus Pitt Rivers developed the methods of modern archaeological field work in the 19th century. The Berkshire Downs and White Horse Hills adjoin the northernmost part of this formation. The formation called Cranborne Chase (grid reference ST970180) is a chalk plateau in central southern England , straddling the counties Dorset, Hampshire and Wiltshire.
To the north of these downs, mostly in Buckinghamshire, are the Chiltern Hills, running north east.
At the far south west of the formation are the Dorset Downs, notable for their rich Roman and pre-Roman archaeology, including a number of Iron Age hill forts. The Purbeck Hills fork from the Dorset Downs to run on, or near the Jurassic Coast in south east Dorset, where they form part of Lulworth Cove, White Nothe and Old Harry Rocks, some of the many famous landforms on one of England's two natural World Heritage Sites.
Smooth convex curves are characteristic of the Downs; their graceful and striking outline gives them an importance in the landscape in excess of their actual height; their flanks are well wooded, their summits covered with close springy turf.
Where the chalk hills meet the sea there are white cliffs such as the White Cliffs of Dover, Seven Sisters and The Needles on the Isle of Wight The chalk would once have extended across the English Channel and similar cliff features can be found on the French coast.
Geology
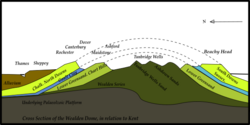
The Chalk Formation was laid down under the sea during the Upper Cretaceous period, and was later uplifted at around the same time as the Alps were formed. In south-east England, the chalk deposits were formed into an elongated dome, with the long axis in a roughly east–west direction. Erosion along the line of this axis removed the central part of the chalk and revealed the underlying Wealden deposits. The remaining chalk forms the characteristic escarpments of the North and South Downs.
Stronger uplift and folding occurred in Dorset and the Isle of Wight, where the chalk strata are almost vertical in some places, such as The Needles.
See also
- Chalk stream
- Uffington White Horse
References
- ↑ "Ivinghoe Hills citation". Natural England. http://www.sssi.naturalengland.org.uk/citation/citation_photo/1001419.pdf. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ↑ "Map of Ivinghow Hills". Natural England. http://magic.defra.gov.uk/MagicMap.aspx?startTopic=Designations&activelayer=sssiIndex&query=HYPERLINK%3D%271001419%27. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
