Engineering:7AK7
From HandWiki
Short description: Pentode vacuum tube
| 7AK7 | |
|---|---|
| Classification | Pentode |
| Service | Digital computers |
| Height | 3 5⁄32 in (80 mm) |
| Diameter | 1 3⁄16 in (30 mm) |
| Cathode | |
| Cathode type | Coated Unipotential |
| Heater voltage | 7.0 V (6.3 V nominal) |
| Heater current | 800 mA |
| Anode | |
| Max dissipation Watts | 8.5 W |
| Max voltage | 200 V |
| Socket connections | |
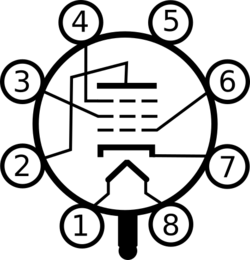 Pin 1 – Heater | |
| References | |
| https://web.archive.org/web/20221114011216/http://www.nj7p.org/Tubes/PDFs/Frank/137-Sylvania/7AK7.pdf | |
The 7AK7 is a pentode vacuum tube (thermionic valve). According to its manufacturer, Sylvania, it was "designed for service in electronic computers".[1]

The tube was developed in 1948,[2] designed at the request of L. D. Wilson for use in the Whirlwind computer.[3] Significant attention was directed towards its manufacturing process in order to ensure the part's reliability.[4] Dubbed the "computer tube",[5] it became a popular tube for computers for a while.[2] IBM, however, switched to more compact miniature tubes, starting with the IBM 604 in 1948.
See also
- 25L6, another type of tube found in early computers
References
- ↑ Sylvania. Engineering Data Service. 7AK7. July 1953.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Green, Tom (2010). Bright Boys: The Making of Information Technology. CRC Press. p. 141. ISBN 978-1568814766. https://archive.org/details/Bright_Boys_The_Making_of_Information_Technology_by_Tom_Green_2010.
- ↑ Wilson, L. D. (1954). "Tube Reliability in the Univac". 10. National Engineering Conference, Incorporated. pp. 699–703.
- ↑ David R. Brown, T. F. Clough, and P. Youtz. Investigation of 7AK7 Processing, Emporium, Pa., March 2, 1948. URI: http://hdl.handle.net/1721.3/38986
- ↑ Haigh, Thomas; Priestley, Mark; Ropefir, Crispin (2016). ENIAC in Action: Making and Remaking the Modern Computer. MIT Press. p. 211. ISBN 9780262334419.
 |
