Engineering:9×19mm Parabellum
| 9×19mm Parabellum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Left to right; 9×19mm Parabellum, .40 S&W, 10mm Auto, .45 ACP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Pistol | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Place of origin | German Empire | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Used by | Many military and civilian agencies around the world | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wars | World War I – present | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Production history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Designer | Georg Luger | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Designed | 1901 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Produced | 1902–present | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | 9×19mm Parabellum +P | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parent case | 7.65×21mm Parabellum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case type | Rimless, tapered | |||||||||||||||||||||||
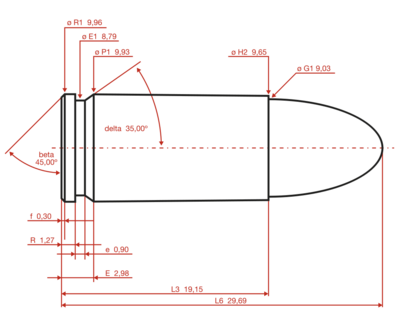
| Bullet diameter | 9.01 mm (0.355 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neck diameter | 9.65 mm (0.380 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Base diameter | 9.93 mm (0.391 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rim diameter | 9.96 mm (0.392 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rim thickness | 1.27 mm (0.050 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case length | 19.15 mm (0.754 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall length | 29.69 mm (1.169 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case capacity | 0.862 cm3 (13.30 gr H2O) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifling twist | 250 mm (1-9.84in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primer type | Berdan or Boxer small pistol | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum pressure ([[Engineering:Small arms ammunition pressure testing|]]) | 235.00 MPa (34,084 psi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum pressure ([[Engineering:Small arms ammunition pressure testing|]]) | 241.3165 MPa (35,000.00 psi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ballistic performance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test barrel length: 118mm (4.65") Source(s): Sellier & Bellot,[1] CIP,[2] Norma Ammunition,[3] Underwood Ammunition,[4] RBCD Performance Plus Ammunition[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 9×19mm Parabellum (also known as 9mm Parabellum or 9mm Luger or simply 9mm) is a rimless, tapered firearms cartridge.
Originally designed by Austrian firearm designer Georg Luger in 1901,[6] it is widely considered the most popular handgun and submachine gun cartridge due to its low cost and extensive availability.[7][8][9]
Since the cartridge was designed for the Luger semi-automatic pistol, it has been given the designation of 9mm Luger by the Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers' Institute (SAAMI)[10] and the Commission internationale permanente pour l'épreuve des armes à feu portatives (CIP).[2]
A 2007 US survey concluded that "about 60 percent of the firearms in use by police are 9mm [Parabellum]" and credited 9×19mm Parabellum pistol sales with making semiautomatic pistols more popular than revolvers.[11]
Origins
The cartridge was developed by Austrian firearm designer Georg Luger in 1901. The cartridge was derived from an earlier round designed by Luger (7.65×21mm Parabellum), which itself was derived from a cartridge used in the Borchardt C-93 pistol (7.65×25mm Borchardt). Shortening the length of the cartridge case used in the Borchardt pistol allowed Luger to improve the design of the toggle lock and to incorporate a smaller, angled grip.
Luger's work on the Borchardt design evolved into the Luger pistol, which was first patented in 1898 and chambered in 7.65×21mm Parabellum. Demand from Germany for a larger caliber in their military sidearm led Luger to develop the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge for the eventual P08 pistol. This was achieved by removing the bottleneck shape of the 7.65×21mm Parabellum case, resulting in a tapered rimless cartridge encasing a bullet that was 9 millimeters in diameter.
In 1902, Luger presented the new round to the British Small Arms Committee, as well as three prototype versions to the U.S. Army for testing at Springfield Arsenal in mid-1903. The Imperial German Navy adopted the cartridge in 1904, and in 1908, the German Army adopted it as well.[7]
To conserve lead during World War II in Germany, the lead core was replaced by an iron core encased with lead. This bullet, identified by a black bullet jacket, was designated as the 08 mE (mit Eisenkern—"with an iron core"). By 1944, the black jacket of the 08 mE bullet was dropped, and these bullets were produced with normal copper-colored jackets. Another wartime variation was designated the 08 sE bullet and identified by its dark gray jacket, and was created by compressing iron powder at high temperature into a solid material (Sintereisen—"sintered iron").[12]
The name Parabellum is derived from the Latin motto of Deutsche Waffen- und Munitionsfabriken (DWM), Si vis pacem, para bellum ("If you want peace, prepare for war").[13][14]
Popularity
After the end of World War I, the acceptance of the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge increased in popularity, with the vast amount of pistols and submachine guns being adopted by the majority of militaries and law enforcement personnel from around the world.[15] The 9×19mm Parabellum has become the most common caliber used by U.S. law enforcement agencies, primarily due to the availability of controllable compact pistols with large magazine capacities that use the cartridge.[16]
From the 1980s to the 1990s, a sharp increase occurred in the popularity of semi-automatic pistols in the U.S., a trend foreshadowed by the adoption of the Smith & Wesson Model 39 by the Illinois State Police in 1968. In addition, the Beretta M9 (a military version of the Beretta Model 92) was adopted by the U.S. Army in 1985. Previously, most American police departments issued .38 Special caliber revolvers with a six-shot capacity. The .38 Special was preferred to other weapons, such as variants of the M1911, because it offered low recoil, was small and light enough to accommodate different shooters, and was inexpensive.[17] The 9×19mm cartridge is ballistically superior to the .38 Special revolver cartridge,[18] is shorter overall, and being an autoloader cartridge, it is stored in flat magazines, as opposed to cylindrical speedloaders. This, coupled with the advent of the so-called "wonder nines", led to many U.S. police departments exchanging their revolvers for some form of 9mm semiautomatic pistols by the late 20th century.[17]
According to Ammunition Depot, from a retail standpoint, the top three 9×19mm Parabellum variants include Full Metal Jacket, Jacketed Hollow Point, and Standard Range Ammo.
Full Metal Jacket (FMJ): By far the most common, 9mm FMJ ammo features a lead 9mm bullet encased in copper (or another hard metal) and is used for target or range shooting.
Jacketed Hollow Point (JHP): Used by military members, law enforcement, and for self-defense, 9mm JHP ammunition features a lead bullet with a hollow point inside. The round is still encased in copper but will expand on impact, increasing stopping power.
Standard Range Ammunition: Known as practice or target ammunition, 9mm range ammo is specifically designed for recreational shooting and typically uses full metal jacket (FMJ) bullets. The primary purpose of 9mm range ammo is to provide shooters with a cost-effective option for honing their shooting skills and improving accuracy.[19]
In 2013, a chart of popular calibers that was released by the website Luckygunner.com showed 9×19mm Parabellum as having 21.4% of the entire cartridge market, followed by the .223 Remington at 10.2% (with 5.56 mm included this is 15.7%). The next most popular caliber was .45 ACP.[20]
Cartridge dimensions

The 9×19mm Parabellum has 0.86 ml (13.3 grains H2O) of cartridge case capacity.
9×19mm Parabellum maximum CIP cartridge dimensions:[2] All sizes are given in millimeters (mm).
The cartridge headspaces on the mouth of the case:[21] The common rifling twist rate for this cartridge is 250 mm (1 in 9.84 in), six grooves, ø lands = 8.82 mm, ø grooves = 9.02 mm, land width = 2.49 mm and the primer type is small pistol.
According to CIP rulings, the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge case can handle up to 235.00 MPa (34,084 psi) Pmax piezo pressure. In CIP-regulated countries, every pistol cartridge combination has to be proofed at 130% of this maximum CIP pressure to certify for sale to consumers. This means that 9×19mm Parabellum chambered arms in CIP-regulated countries are currently (2014) proof tested at 305.50 MPa (44,309 psi) PE piezo pressure.[2]
The SAAMI pressure limit for the 9×19mm Parabellum is set at 241.32 MPa (35,001 psi) piezo pressure.[22]
Performance
The round was originally designed to be lethal to 50 metres (160 ft), but is still lethal at longer ranges.[23] The 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge combines a flat trajectory with moderate recoil. According to the 1986 book Handloading, "the modern science of wound ballistics has established beyond reasonable doubt that the 9mm cartridge is highly effective."[24]
In 2014, the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) released a report detailing the potential combat effectiveness of the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge when compared to other calibers such as the .40 S&W and the .45 ACP cartridges that were specifically developed for use by the FBI.[25] The report indicated that the new powders and more advanced bullet designs used in current 9×19mm Parabellum defensive loads allowed for the caliber to deliver adequate performance compared to other calibers, like the .40 S&W and .45 ACP. In addition to this, the lower recoil, less wear, cheaper ammunition, and higher capacity were all reasons that the report cited for the recent surge in orders of the ammunition from various police agencies. With a wider selection of officers able to shoot handguns chambered in 9×19mm Parabellum, many departments chose this caliber to standardize a single firearm and loading, making logistics and supply easier. Due to all these factors, law enforcement orders of 9×19mm Parabellum ammunition from all major ammunition manufacturers have risen significantly.[26][27]
Improvements and variations
NATO standard
The 9mm is called NATO because it has become a standard pistol caliber for NATO and other military forces worldwide.[28] The cartridge has been manufactured by, or for, more than 70 countries and has become a standard pistol caliber for NATO and other military forces around the world. Its official nomenclature among NATO members is "9mm NATO".[9]
9mm NATO can be considered an overpressure variant of 9×19mm Parabellum that is defined by NATO standards.[29]
While the NATO standards do not specify the type of bullet to be used, Declaration III of the Hague Convention of 1899 prohibits the use of expanding ammunition in warfare by signatories, so official NATO 9mm ammunition is FMJ "ball" bullets.[30] Declaration III does not apply in conflicts involving non-signatories to the Hague Convention, including paramilitary and other nongovernmental fighting forces.[31]
Swedish m/39
9mm Parabellum entered Swedish service as m/39 with the import of the Kulsprutepistol m/39 from Austria, with a bullet weight of 7.5 grams (116 gr).[32] During the Congo Crisis, the Swedish UN-contingent issued complaints about the performance of the m/39 cartridge (regular 9mm Parabellum) used. This resulted in a commission of the Swedish Army establishing in 1962 that a new round was needed for the Carl Gustav m/45. The resulting m/39B had a tombac-plated steel jacket surrounding the lead core. While the lands of the barrel can cut into the tombac, the steel jacket resists deformation, thus causes the gas pressure to rise higher than the previous soft-jacketed m/39, giving the 7.0 grams (108 gr) bullet a Vo of 420 m/s (1,378 ft/s)[33] and an impact energy of 600 joules.[citation needed] The mantle also acts like a penetrator when striking a target, going through up to 50 layers of kevlar, 7 cm of bricks, or 25 cm of wood, allowing the bullet to defeat body armor up to Type IIIA.
+P variant
Attempts to improve the cartridge's ballistics came in the early 1990s with the widespread availability of high-pressure loadings of the 9mm cartridge. Such overpressure cartridges are labeled "+P" (38,500 psi) or in the case of very high pressure loadings, "+P+" (42,000 psi).[34] Velocity of these rounds is improved over standard loadings. In addition, improvements in jacketed hollow-point bullet technology have produced bullet designs that are more likely to expand and less likely to fragment than earlier iterations, giving a 9mm bullet better terminal effectiveness.[35]
SESAMS
SESAMS weapons or components are normally painted blue or marked to denote their inert status and avoid a potentially catastrophic mixup with live-fire weapons.[36] This allows the armed forces to train with nearly identical equipment as used in real-life situations.[37]
Russian military overpressure variants
The Russian military has developed specialized 9×19mm cartridges that use relatively light bullets at high muzzle velocities for both pistols and submachine guns to defeat body armor.[38]
Besides enhanced penetration capabilities, these overpressure variants offer a flatter trajectory and lessened recoil. The increase in service pressure causes a rise in bolt thrust, so this overpressure ammunition induces more stress on critical weapon parts during firing. After initial research conducted in the late 1980s under the codename "Grach", the Russian armed forces adopted two specialized 9×19mm variants.[39][40]
| 7Н21 (7N21) | 7Н31 (7N31) / PBP | |
| Cartridge weight | 9.5 g (147 gr) | 8.1 g (125 gr) |
| Bullet weight | 5.2 g (80.2 gr) | 4.1 g (63.3 gr) |
| Muzzle velocity | 460 m/s (1,509 ft/s) | 600 m/s (1,969 ft/s) |
| Muzzle energy | 561 J (414 ft⋅lbf) | 756 J (558 ft⋅lbf) |
| Accuracy of fire at 25 m (27 yd) (R50) |
25 mm (1.0 in) | |
| Maximum pressure | 280 MPa (41,000 psi) |
- R50 at 25 m (27 yd) means the closest 50 percent of the shot group will all be within a circle of 25 mm (1.0 in) radius at 25 m (27 yd).
The 7N21 (Cyrillic: 7Н21) 9×19mm overpressure variant features an armor-piercing bullet and generates a peak pressure of 280 MPa (41,000 psi).[39] The 7N21 bullet features a hardened (sub-caliber) steel penetrator core, enclosed by a bimetal jacket. The space between the core and jacket is filled with polyethylene, and the tip of the penetrator is exposed at the front of the bullet to achieve better penetration. The penetration range for body armor is specified at up to 40 m (130 ft). The MP-443 Grach and GSh-18 pistols and PP-19 Vityaz, PP-90M1 and PP-2000 submachine guns were designed for use with this overpressure cartridge. Jane's Infantry Weapons stated in 2003 that the 7N21 cartridge combined the 9×19mm Parabellum dimensions with a 9×21mm Gyurza bullet design and was developed specifically for the penetration of body armor and for the MP-443 Grach pistol, the latest Russian service pistol.[41]
The 7N31 (Cyrillic: 7Н31) / PBP 9×19mm overpressure variant uses the same concept with a similar but lighter bullet that achieves higher muzzle velocity. The penetration of an 8 mm (0.31 in)-thick St3 steel plate is specified at up to 10 m (33 ft).[42] The 7N31 cartridge was developed in the late 1990s for the GSh-18 pistol. The 7N31 was adopted for the PP-90M1 and PP-2000 submachine guns. Its maximum service pressure remains unclear.
The construction of the two rounds allows them to be effective against both unarmored and armored targets. If the bullet strikes an unarmored target, it holds together to produce a wide wound channel. If the bullet strikes an armored target, the sleeve is stripped away, and the core penetrates alone. The disadvantage of the rounds is that high impact velocities are needed to work effectively, so the bullets are relatively light to maximize their muzzle velocity. This means they lose velocity relatively quickly, limiting their effective range.[43]
Other variants
VBR-B produces specialized bullets for this cartridge, a two-part controlled fragmenting projectile and an armor-piercing bullet that features a brass sabot and a hardened steel penetrator. These are designed to increase the content of the permanent wound cavity and double the chance of hitting a vital organ.[44]
U.S. data
The energy delivered by most 9mm loads allows for significant expansion and penetration with premium hollow-point bullets. Illinois State Police, Border Patrol, Federal Air Marshals, and United States Secret Service favored and used 115 gr (7.5 g) +P+ 9mm loads at 1,300 ft/s (400 m/s) for years with excellent results.[35] Massad Ayoob has stated that the "Tried, Tested, and True" 115 gr (7.5 g) +P or +P+ is the best self-defense load in this caliber.[35] Proponents of the hydrostatic shock theory contend that the energy of the 9mm cartridge is capable of imparting remote wounding effects in human-sized living targets.[45][46][47]
| Manufacturer | Load | Bullet mass | Velocity | Energy | Expansion[48] | Penetration[48] | PC[48] | TSC[48] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cor-Bon | JHP+P | 7.5 g (115 gr) | 410 m/s (1,350 ft/s) | 630 J (465 ft⋅lb) | 14 mm (0.55 in) | 360 mm (14.2 in) | 56 mL (3.4 cu in) | 631 mL (38.5 cu in) |
| ATOMIC Ammo | JHP+P | 8.0 g (124 gr) | 400 m/s (1,300 ft/s) | 630 J (465 ft⋅lb) | 15 mm (0.60 in) | 330 mm (13 in) | "N/A" | "N/A" |
| Speer | Gold Dot JHP | 8.0 g (124 gr) | 350 m/s (1,150 ft/s) | 494 J (364 ft⋅lb) | 18 mm (0.70 in) | 337 mm (13.25 in) | 84 mL (5.1 cu in) | 616 mL (37.6 cu in) (est)[49] |
| Federal | HydraShok JHP +P+ | 8.0 g (124 gr) | 360 m/s (1,170 ft/s) | 511 J (377 ft⋅lb) | 17 mm (0.67 in) | 340 mm (13.4 in) | 77 mL (4.7 cu in) | 734 mL (44.8 cu in)[49] |
| Remington | Golden Saber JHP | 9.5 g (147 gr) | 300 m/s (990 ft/s) | 430 J (320 ft⋅lb) | 16 mm (0.62 in) | 370 mm (14.5 in) | 72 mL (4.4 cu in) | 544 mL (33.2 cu in) |
| Winchester | Silvertip | 7.5 g (115 gr) | 373 m/s (1,225 ft/s) | 519 J (383 ft⋅lb) | 18 mm (0.72 in) | 200 mm (8.0 in) | 54 mL (3.3 cu in) | 274 mL (16.7 cu in) |
| Winchester | WWB JHP | 9.5 g (147 gr) | 300 m/s (990 ft/s) | 430 J (320 ft⋅lb) | 15 mm (0.58 in) | 400 mm (15.9 in) | 69 mL (4.2 cu in) | 321 mL (19.6 cu in) |
| Winchester | FMJ | 7.5 g (115 gr) | 352 m/s (1,155 ft/s) | 462 J (341 ft⋅lb) | 9.1 mm (0.36 in) | 620 mm (24.5 in) | 41 mL (2.5 cu in) | 174 mL (10.6 cu in) |
Key:
Expansion: expanded bullet diameter (ballistic gelatin)
Penetration: penetration depth (ballistic gelatin)
PC: permanent cavity volume (ballistic gelatin, FBI method)
TSC: temporary stretch cavity volume (ballistic gelatin)
See also
- 9 mm caliber
- List of firearms
- List of handgun cartridges
- List of rifle cartridges
- Table of handgun and rifle cartridges
References
- ↑ "Sellier & Bellot". http://www.sellier-bellot.cz/pistol-and-revolver-ammunition.php?product=9/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "CIP TDCC sheet 9 mm Luger". http://www.cip-bobp.org/homologation/uploads/tdcc/tab-iv/tabivcal-en-page28.pdf.
- ↑ "Norma 9 mm Luger ENVY 124gr". https://www.norma-ammunition.com/en-us/products/dedicated-precision/pistol-and-revolver/norma-envy/norma-9-mm-luger-envy-124-gr---299440050.
- ↑ "Underwood 9mm Luger +P+ 115gr. Sporting Jacketed Hollow Point Hunting & Self Defense Ammo". https://www.underwoodammo.com/9mm-luger-plus-p-plus-115-grain-jacket-hollow-point.html.
- ↑ "9mm RBCD Performance Plus 60gr Total Fragmenting Soft Point Ammo". https://www.ammunitiontogo.com/product_info.php/pName/20rds-9mm-rbcd-performance-plus-60gr-total-fragmenting-soft-point-ammo.
- ↑ Hogg, Ian V.; Weeks, John S. Military Small Arms of the 20th Century (7th Edition), p.40. Krause Publications, 2000
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Barnes, Frank (2006). Skinner, Stan. ed. Cartridges of the World. 11th Edition.. Cartridges of the World. Gun Digest Books. p. 295. ISBN 978-0-89689-297-2.
- ↑ Barnes, Frank C (2014). Cartridges of the World (14th ed.). Iola, WI, USA: Krause Publications. pp. 446–447. ISBN 9781440242656.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 STANAG No. 4090 (Edition 2) (2 ed.). North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 15 April 1982. p. C-1. http://gigconceptsinc.com/files/STANAG4090-cartridge_9x19.pdf. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ↑ "Cartridge and Chamber Drawing". http://saami.org/specifications_and_information/publications/download/Z299-3_ANSI-SAAMI_CFPandR.pdf.
- ↑ Adler, Jerry, et al. "Story of a Gun." Newsweek 149.18 (30 April 2007): 36–39. MasterFILE Premier. EBSCO. Dallas Public Library, Dallas, TX. Retrieved 10 June 2009. Newsweek online edition
- ↑ Dunlap, Roy (1948). Ordnance went up front: some observations and experiences of a sergeant of Ordnance, who served throughout World War II with the United States Army in Egypt, the Philippines, and Japan, including way stations. Small-Arms Technical Pub. Co.. pp. 43–45.
- ↑ James, Frank (2004). Effective Handgun Defense: A Comprehensive Guide to Concealed Carry. Iola, Wisconsin: Krause Publications. p. 117. ISBN 978-0-87349-899-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=yCzZwDMBOtkC. "The word "Parabellum" is derived from the Latin phrase Si Vis Pacem Para Bellum or "If you want Peace, Prepare for War". It naturally followed this new cartridge would be commonly referred to as the 9mm Parabellum"
- ↑ Sweeney, Patrick (2009). Gun Digest Big Fat Book of the .45 ACP. Gun Digest Books. p. 33. ISBN 978-1-4402-0219-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=55Td91jZOa0C&pg=PA33. "Georg Luger looked at his design, took the .30 Luger case and expanded it to hold a 9mm bullet. ... From the Latin phrase Si vic pacem, para bellum came parabellum. Translated it means "If you desire peace, prepare for war."
- ↑ Shideler, Dan (2010). "The Luger Pistol". The Greatest Guns of Gun Digest. Krause Publications. p. 24. ISBN 978-1-4402-1414-1.
- ↑ CCI/Speer Inc. (2007). Reloading Manual #14. ISBN:978-0-9791860-0-4.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Clede, Bill (1985). Police Handgun Manual: How to Get Street-Smart Survival Habits. Stackpole Books. pp. 116–118. ISBN 978-0-8117-1275-0.
- ↑ "Ballistics by the inch". http://www.ballisticsbytheinch.com/.
- ↑ "About 9mm Ammo - Ammunition Depot". https://www.ammunitiondepot.com/288-9mm/.
- ↑ "Ammo in 2013: A Look Behind the Scenes at Lucky Gunner". January 2014. http://www.luckygunner.com/labs/2013-ammo-stats/.
- ↑ Wilson, R. K. Textbook of Automatic Pistols, p.239. Plantersville, SC: Small Arms Technical Publishing Company, 1943.
- ↑ "SAAMI Pressures". http://www.leverguns.com/articles/saami_pressures.htm.
- ↑ "How Far Will a 9mm Kill?". YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_wXFf34bB34.
- ↑ Davis, William C. (1986). Handloading, Second Printing: National Rifle Association. ISBN:0-935998-34-9 p242-243
- ↑ "FBI 9MM Justification, FBI Training Division". 25 September 2014. http://soldiersystems.net/2014/09/25/fbi-9mm-justification-fbi-training-division/.
- ↑ "How the FBI reignited the pistol caliber war". http://www.policeone.com/Officer-Safety/articles/7453193-Why-the-FBI-reignited-the-pistol-caliber-war/.
- ↑ "FBI 9MM Justification, FBI Training Division". soldiersystems.net. http://soldiersystems.net/2014/09/25/fbi-9mm-justification-fbi-training-division/.
- ↑ "9mm Nato vs. 9mm Luger: What Is The Difference". https://www.bulkcheapammo.com/blog/9mm-nato-vs-9mm-luger-what-is-the-difference.
- ↑ "Proof of Ordnance, Munitions, Armour and Explosives, Ministry of Defence Defence Standard 05–101 Part 1". http://www.dstan.mod.uk/data/05/101/01000100.pdf.
- ↑ "Sniper Use of Open-Tip Ammunition". http://www.thegunzone.com/opentip-ammo.html.
- ↑ "Declaration on the Use of Bullets Which Expand or Flatten Easily in the Human Body; July 29, 1899". http://avalon.law.yale.edu/19th_century/dec99-03.asp.
- ↑ "Hemvärnet 1940–1990, 1990. Red. Bo Kjellander s. 259–260.
- ↑ Arméstabens taktiska avdelning februari 1962 : "Erfarenheterna från striderna i Kongo under september och december 1961"
- ↑ "What is +P and +P+ ammunition?". http://www.frfrogspad.com/miscellk.htm#+P.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 Ayoob, Massad (2002). The Gun Digest Book of Combat Handgunnery (5 ed.). Iola, Wisconsin: Krause Publications. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-87349-485-4.
- ↑ Bianco, Lance Cpl. Michael A. "Marines conduct urban warfare training". http://www.31stmeu.marines.mil/News/News-Article-View/Article/532754/marines-conduct-urban-warfare-training/.
- ↑ "Commando Warrior adds realistic combat training with simunitions". http://www.andersen.af.mil/News/tabid/1981/Article/416105/commando-warrior-adds-realistic-combat-training-with-simunitions.aspx.
- ↑ "Rosoboronexport - Land Forces Weapons Catalogue". Rosoboronexport. 2003. p. 108. https://www.scribd.com/doc/30301368/Rosoboronexport-Land-Forces-Weapons-Catalogue.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Popenker, Maxim (2005–2008). "Special purpose small arms ammunition of USSR and Russia". Modern Firearms. World Guns. http://world.guns.ru/ammunition/russian-special-cartridges-e.html.
- ↑ "9x19 Russian pistol cartridges". http://gunsru.ru/rg_patron_9x19_eng.html.
- ↑ "9 × 19 mm 7N21 – Jane's Infantry Weapons". Jane's Information Group. 14 August 2003. http://www.janes.com/articles/Janes-Infantry-Weapons/9-x-19-mm-7N21.html.
- ↑ "7N31". Rosoboronexport. http://roe.ru/eng/catalog/special-weapons-and-ammunitions/submachine-guns/7n31/.
- ↑ Williams, Anthony G.. "Where Next For PDWs?". http://www.quarryhs.co.uk/PDWs.htm.
- ↑ "VBR-B Multi-Caliber (9mm NATO/7.92x24mm) Compact PDW Pistol". http://www.defensereview.com/new-multi-caliber-vbr-belgium-pdw-pistol-most-intelligently-developed-personal-defense-weapon-yet/.
- ↑ Courtney, Michael; Courtney, Amy (2008). "Scientific Evidence for Hydrostatic Shock". arXiv:0803.3051 [physics.med-ph].
- ↑ Sturtevant B, Shock Wave Effects in Biomechanics, Sadhana, 23: 579–596, 1998.
- ↑ Courtney, A.; Courtney, M. (2007). "Links between traumatic brain injury and ballistic pressure waves originating in the thoracic cavity and extremities". Brain Injury 21 (7): 657–662. doi:10.1080/02699050701481571. PMID 17653939.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 48.3 Marshall and Sanow, Street Stoppers, Appendix A, Paladin 2006
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 "Law Enforcement - Federal Premium LE, Speer LE, BLACKHAWK!, Eagle - Handgun Details". https://le.vistaoutdoor.com/ammunition/speer/handgun/details.aspx?id=53618.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Article on 9×19 mm Parabellum cartridge collecting including history with photos and descriptions of variations including headstamps
- Ballistics By The Inch 9×19 mm Parabellum Results.
- Data on the Russian ammo (in Russian)
- DIRECT FIRE AMMUNITION Handbook 2021, Project Manager Maneuver Ammunition Systems
 |