Engineering:American Eagle A-129
The American Eagle A-129 was an American biplane first flown in 1929.
Design and development
The preceding American Eagle A-101 of 1926 had achieved some success, but its fierce spin characteristics had resulted in several crashes during training flights. Giuseppe Bellanca redesigned the biplane with a longer fuselage and narrower cowling to accommodate the five-cylinder Kinner K-5 100 h.p. radial engine, which had its cylinder heads exposed. To mark the year of its first appearance, the designation A-129 was applied.[1]
Operational history
Initially designed to replace the Porterfield Flying Schools A-101s, the new biplane proved to have good flying characteristics and more than 400 were built. The aircraft were also flown by "barnstormers" and sports pilots.
Several A-129s remain airworthy and examples are preserved at the Rhinebeck Aerodrome Museum at Old Rhinebeck in New York state and in the Kansas Aviation Museum Wichita, Kansas.[2]
Variants
A range of engines was fitted to the A-129 without changing the type designation. They included the 90 hp (67 kW) Curtiss OX-5 straight engine and others up to the 200 h.p. Wright J-4.
The American Eagle A-229 was a two seat trainer version with a Curtiss OX-5 engine.[3]
Specifications (100 h.p. Kinner K-5)
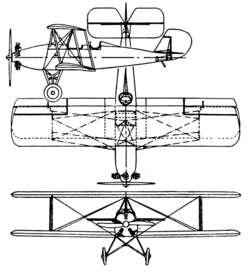
Data from Aero Digest June 1929[3]
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Capacity: two passengers
- Length: 25 ft 1 in (7.65 m)
- Wingspan: 30 ft 0 in (9.14 m)
- Height: 8 ft 4 in (2.54 m)
- Wing area: 160 sq ft (15 m2) upper, lower 140 sq ft (13 m2) lower
- Empty weight: 1,220 lb (553 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,041 lb (926 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 42 US gal (35 imp gal; 160 l)
- Powerplant: 1 × Kinner K-5 five cylinder radial, 100 hp (75 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed wooden, fixed pitch
Performance
- Maximum speed: 105 mph (169 km/h, 91 kn)
- Cruise speed: 95 mph (153 km/h, 83 kn) /bk>
- Take-off run: 100–150 ft (30–46 m)
- Landing speed: 30 mph (48 km/h; 26 kn)
- Stall speed: 35 mph (56 km/h, 30 kn)
- Range: 500 mi (800 km, 430 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 14,000 ft (4,300 m)
- Rate of climb: 900 ft/min (4.6 m/s) initial
References
- Notes
- ↑ Simpson, 2001, p. 40
- ↑ Ogden, 2007, p. 572
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "American Eagle". Aero Digest (New York City: Aeronautical Digest Publishing Corp) 14 (6): 116. June 1929. https://archive.org/details/aerodigest1415unse/page/n395/mode/1up.
- Bibliography
- Ogden, Bob (2007). Aviation Museums and Collections of North America. Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd. ISBN 978-0-85130-385-7.
- Simpson, Rod (2001). Airlife's World Aircraft. Airlife Publishing Ltd. ISBN 1-84037-115-3.
External links
 |

