Engineering:Argonaut Pirate
| Pirate | |
|---|---|

| |
| H.24 Pirate | |
| Role | Three place amphibian |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Argonaut Aircraft |
| Designer | Howard J. Heindell |
| First flight | 1935 |
| Number built | 2 |
The Argonaut Pirate was a 1930s, U.S., three place, single-engined pusher configuration amphibious aircraft. Only two were built.
Design and development
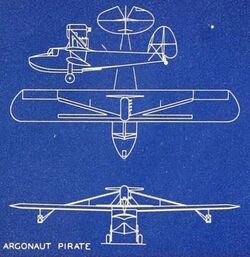
The H.20 Pirate was Argonaut aircraft's first product, flying in 1935. Its wire-braced high wing was rectangular in plan out to blunted tips. It had solid spruce spars and wooden ribs and was fabric-covered apart from plywood-covered leading edges. Its ailerons were relatively short but broad.[1]
The hull was also wooden, a semi-monocoque structure with ply planking, ply frames and spruce stringers. It had a single step planing bottom. Pilot and co-pilot sat side by side in an enclosed cabin forward of the wing leading edge.[1] The third seat was just behind them on the centreline and was more like a jump-seat than a true passenger seat.[2] The H.20 Pirate's inverted, air-cooled, 125 hp (93 kW) Menasco C-4[1] was mounted close to the top of the fuselage[2] above the wing, its four-bladed propeller just clearing the central wing trailing edge. The steel tube engine mounting ran down through the fuselage to the main landing gear mountings. The vertical tail was rather straight-edged in profile, with its tailplane mounted about halfway up carrying lobate plan elevators.[1]
The Pirate was stabilized on water with a pair of rather bulky, flat-bottomed, strut-mounted floats at about two-thirds span. Its retractable landing gear was narrow track, with wheels on short, rubber ring-damped legs that were manually retracted into a horizontal position with a wheel in the cabin. The mainwheels had brakes and the tailwheel swivelled for ground manoeuvrability.[1]

The Pirate prototype H.20 first flew in 1934. Its development programme was successfully concluded in late 1935; by then it was described more realistically as a two place aircraft.[3] This programme led to a second aircraft, the H.24, intended as the production prototype. Its span was increased to 42 ft (13 m) and the Menasco was strut-mounted well above the fuselage, in clearer air, allowing a 7 ft (2.1 m) diameter, two-bladed propeller to be fitted. Long, V-form struts from the top of the engine mounting to the spars replaced the earlier wire bracing. More refined, V-bottom, floats were used. Its tail was revised with more rounded fixed surfaces and a deeper and more rounded rudder and the elevators had more area with only a small cut-out for rudder movement. These and other production aircraft related changes increased the empty weight of the H.24 by 45%. By 1937 it was once again described as a three-seater, though little is known about the cabin and there was no glazing aft of the cockpit.[4] It was on display at the National Aviation Show held in New York from 28 January 1937[5] but no production followed.
Development continued after Argonaut's acquisition by the (Donald G) White Aircraft Co. in 1938, as the White A-R 3-seat amphibian and the White Gull 4-seat amphibian. Only a single White A-R was registered as NX77Y and further work was halted due to lack of market.[6]
Specifications (H.24 Pirate)
Data from Aero Digest, March 1937.[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: one or two
- Capacity: two or one passengers
- Length: 27 ft 1 in (8.26 m)
- Wingspan: 42 ft (13 m)
- Height: 10 ft 3 in (3.12 m)
- Wing area: 224.75 sq ft (20.880 m2)
- Airfoil: Clark Y
- Empty weight: 1,600 lb (726 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,250 lb (1,021 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 40 US gal (33 imp gal; 150 l)
- Powerplant: 1 × Menasco C-4 Pirate four cylinder, air-cooled inverted inline, 125 hp (93 kW) at 2,175 rpm
- Propellers: 2-bladed Hartzell Propeller or Sensenich
Performance
- Maximum speed: 100 mph (160 km/h, 87 kn)
- Cruise speed: 90 mph (140 km/h, 78 kn)
- Landing speed: 55 mph (89 km/h; 48 kn)
- Range: 375 mi (604 km, 326 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 10,500 ft (3,200 m)
- Rate of climb: 550 ft/min (2.8 m/s)
See also
Related lists
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Argonaut Pirate". Aero Digest 26 (4): 52. April 1935. https://archive.org/details/aerodigest2619unse/page/n319/mode/1up.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Mystery Plane". Vintage Aircraft 23 (10): 7-8,27. October 1995. https://issuu.com/vintageeaa/docs/va-vol-23-no-10-oct-1995.
- ↑ "New Aircraft Types Developing". Aero Digest 27 (6): 58. December 1935. https://archive.org/details/aerodigest2719unse/page/58/mode/1up.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Argonaut Pirate". Aero Digest 30 (3): 5. March 1937. https://archive.org/details/aerodigest3019unse/page/n267/mode/1up.
- ↑ "National Aviation Show". Aero Digest 30 (2): 26-7. February 1937. https://archive.org/details/aerodigest3019unse/page/n135/mode/1up.
- ↑ Eckland, K.O.. "AIRCRAFT Wh to Wy#White". http://aerofiles.com/_wh.html. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
 |
