Engineering:Bach Air Yacht
| 3-CT Air Yacht | |
|---|---|

| |
| 3-CT-4 Air Yacht | |
| Role | Airliner |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Bach Aircraft |
| Designer | Morton Bach |
| First flight | 1927 |
| Primary users | West Coast Air Transport
|
| Number built | ca. 21 |
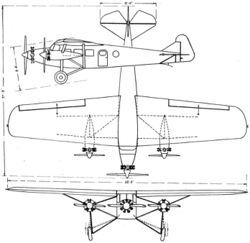
The Bach Air Yacht was a trimotor airliner produced in the United States in the 1920s. Typical of its day, it was a high-wing braced monoplane, with fixed tailwheel undercarriage. Unusual for airliners of the late 1920s (due to legislation that forbade carrying passengers in wooden aircraft), the Air Yachts were constructed almost entirely of wood with steel fittings, undercarriage, and struts. Different models were powered by varying combinations of Wright, Ryan-Siemens, Kinner, Comet, and Pratt & Whitney engines, a large engine in the nose of the aircraft, and two smaller "helpers" under the wings in nacelles supported by struts. As with so many aircraft companies of the late 1920s, the Bach Aircraft Company succumbed to the Great Depression, thus further development of the Air Yacht was abandoned after the 3-CT-9.
On 26 July 1929, a 3-CT-9 model piloted by Waldo Waterman set a new altitude record, lifting a 1,000 kg payload to 20,820 ft (6,347 m).
Variants
- 3-CT-2
- Variant with one Wright J-5 and two Ryan-Siemens 9 engines.
- 3-CT-3
- Variant with one Pratt & Whitney Wasp and two Ryan-Siemens 9 engines, one built.
- 3-CT-4
- Variant with one Pratt & Whitney Wasp and two Ryan-Siemens 9 engines, two built.
- 3-CT-5
- Variant with one Pratt & Whitney Wasp and two Comet 100hp engines, one built.
- 3-CT-6
- Variant with one Pratt & Whitney Hornet and two Comet 100hp engines, five built.
- 3-CT-8
- Variant with one Pratt & Whitney Hornet and two Wright J-6 engines, four or five built.
- 3-CT-9
- Variant with one Pratt & Whitney Wasp and two Wright J-6 engines, three built.
- 3-CT-9K
- Variant of the 3-CT-9 with one Pratt & Whitney Wasp and two Kinner C-5 engines, ten built.
- 3-CT-9S
- Deluxe variant of the 3-CT-9 with engine cowls, wheel spats, and custom interior, one built.
- 3-CTS
- Variant with one 3-CT-8 modified with a Pratt & Whitney Wasp and two Wright J-5 engines, one built.
- T-11P
- Three aircraft, being single-engined conversions (formerly NC219H, NC53M, and 34998 built from spare parts)
- Note
- As it was common practice to upgrade airframes as improvements became available, some 'N' numbers and/or serial numbered airframes were redesignated as different or new models. Total number of Bach Air Yachts built verified by Air Commerce Bureau and FAA records is 21.
Specifications (3-CT-6)
Data from [2]
General characteristics
- Crew: two (pilot, copilot)
- Capacity: ten passengers
- Length: 36 ft 10 in (11.23 m)
- Wingspan: 58 ft 5 in (17.81 m)
- Height: 9 ft 9 in (2.97 m)
- Wing area: 512 sq ft (47.6 m2)
- Empty weight: 4,739 lb (2,150 kg)
- Gross weight: 8,000 lb (3,629 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney Hornet 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 525 hp (391 kW)
- Powerplant: 2 × Comet 7-RA 7-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 130 hp (97 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 154 mph (248 km/h, 134 kn)
- Cruise speed: 126 mph (203 km/h, 109 kn)
- Stall speed: 60 mph (97 km/h, 52 kn)
- Range: 600 mi (970 km, 520 nmi)
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Fokker F.VII/3m
- Ford Trimotor
- Kreutzer K-5 Air Coach
References
- ↑ AAHS Journal: 73. Spring 1990.
- ↑ Eckland, K.O.. "Aircraft of North America 1903-2003:AIRCRAFT Ba to Bl". http://aerofiles.com/_ba.html.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. pp. 112.
- Juptner, Joseph P.. (1964). U.S. Civil Aircraft Vol.2. Los Angeles: Aero Publishers. pp. 40 to 42 & 206 to 208.
- Juptner, Joseph P.. (1964). U.S. Civil Aircraft Vol.3. Los Angeles: Aero Publishers.
- FAA Archives. 1927–1935.
External links
 |