Engineering:Biosatellite
From HandWiki
Short description: Artificial satellite designed to carry plants or animals in outer space
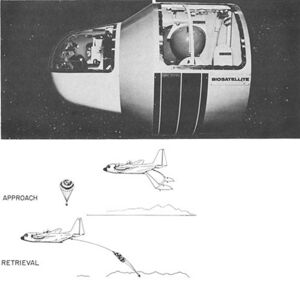 Drawing of Biosatellite and Retrieval | |
| Applications | To carry plants or animals in outer space |
|---|---|
| Specifications | |
| Spacecraft type | Artificial satellite |
A bio satellite is an artificial satellite designed to carry plants or animals in outer space. They are used to research the effects of space (cosmic radiation, weightlessness, etc.) on biological matter while in orbit around a celestial body. The first satellite carrying an animal (a dog, "Laika") was Soviet Sputnik 2 on November 3, 1957. On August 20, 1960 Soviet Sputnik 5 launched and recovered dogs from Earth orbit.
NASA launched 3 satellites between 1966 and 1969 for the Biosatellite program.[1][2]
The most famous biosatellites include:
- Biosatellite program launched by NASA between 1966 and 1969.
- Bion space program by Soviet Union
- The Mars Gravity Biosatellite
- Orbiting Frog Otolith (OFO-A)
See also
- Animals in space
- Biosatellite (NASA)
References
- ↑ Biosatellite, David Darling's Internet Encyclopedia of Science
- ↑ Biosatellite, Encyclopedia Astronautica
 |
